

Trino Coordinator high availability
Trino service supports a high availability (HA) mode that allows running multiple Trino Coordinator components. If one Trino Coordinator becomes unavailable, the standby Trino Coordinators kick in without interrupting the entire Trino cluster operation.
Haproxy Trino component
Switching between Trino Coordinators is done with the help of the Haproxy Trino component, which acts as a reverse proxy between Trino clients and Trino Coordinators in ADH. This component is based on the HAProxy project, which is used for ensuring high availability, load balancing, and routing HTTP/TCP traffic among servers.
|
IMPORTANT
|
An ADH cluster may contain one or more Haproxy Trino components. Adding several Haproxy Trino components can be used for implementing a full-fledged high availability mode at the network level.
Haproxy Trino configuration
When you use the Trino service in the HA mode, ADCM automatically configures the Haproxy Trino component to route incoming requests to Trino Coordinators, so the service requires no manual configuration. Additionally, you can tune the Haproxy Trino behavior as described below.
The main settings file for Haproxy Trino is /etc/adh-haproxy/conf/haproxy-trino.cfg. It is a HAProxy configuration file located on the ADH host with the Haproxy Trino component installed.
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Global settings
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
global
log /dev/log local0
log 127.0.0.1:514 local0
chroot /var/lib/adh-haproxy/trino
maxconn 1024
user haproxy
group haproxy
daemon
ssl-server-verify none
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# common defaults that all the 'listen' and 'backend' sections will
# use if not designated in their block
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
defaults
mode http
log global
option httplog
option dontlognull
option http-server-close
option forwardfor except 127.0.0.0/8
option redispatch
retries 3
timeout http-request 10s
timeout queue 1m
timeout connect 10s
timeout client 1m
timeout server 1m
timeout http-keep-alive 10s
timeout check 10s
listen stats
bind *:7001
stats enable
stats uri /
frontend trino_http_in
bind *:18188
default_backend trino_http_servers
backend trino_http_servers
balance first
server trino-coordinator0 ka-adh-1.ru-central1.internal:18188 check inter 1s fall 2 rise 5
server trino-coordinator1 ka-adh-3.ru-central1.internal:18188 check inter 1s fall 2 rise 5 backupThis file should not be edited manually — instead, to change the Haproxy Trino configuration, use the Jinja template available in ADCM (Clusters → <ADHclusterName> → Services → Trino → Components → Haproxy Trino → Configuration). During the Trino service startup, haproxy-trino.cfg is generated from this template.
Below is the default haproxy-trino.cfg template with major settings highlighted.
{% set ssl_sert = '' %}
{%- if trino_ssl_enable -%}
{% set ssl_sert = haproxy_conf_ssl_vars %}
{% endif %}
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Global settings
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
global (1)
log /dev/log local0
log 127.0.0.1:514 local0
chroot /var/lib/adh-haproxy/trino
maxconn 1024
user haproxy
group haproxy
daemon
ssl-server-verify none
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# common defaults that all the 'listen' and 'backend' sections will
# use if not designated in their block
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
defaults (2)
mode http
log global
option httplog
option dontlognull
option http-server-close
option forwardfor except 127.0.0.0/8
option redispatch
retries 3
timeout http-request 10s
timeout queue 1m
timeout connect 10s
timeout client 1m
timeout server 1m
timeout http-keep-alive 10s
timeout check 10s
listen stats (3)
bind *:7001 {{ ssl_sert }}
stats enable
stats uri /
frontend trino_http_in (4)
bind *:{{ roles_trino_vars_component_ports['haproxy']['web'] }} {{ ssl_sert }}
default_backend trino_http_servers
backend trino_http_servers (5)
balance first
{% for host in haproxy_conf_hosts %}
{{ host }}
{% endfor %}| 1 | Global HAProxy parameters, such as logs destination, root directory definition, certificate verification, etc. |
| 2 | Default HAProxy parameters, such as operation mode, logging, and various timeouts. |
| 3 | Enables HAProxy real-time statistics and monitoring. Defines a port and URI for the statistics endpoint (default to http://<Haproxy_Trino_host>:7001/). |
| 4 | Describes a set of listening sockets to accept incoming connections. |
| 5 | Lists Trino Coordinator servers to which Haproxy Trino will forward incoming requests.
In this template, the {% for host in … %} loop produces a list of Trino Coordinator servers available in the ADH cluster.
balance first indicates that the first server is used as an active (main) Trino Coordinator, other servers are used as backup Coordinators if the first one becomes unavailable. |
For more details on HAProxy configuration, see the HAProxy reference.
Logging
By default, the Haproxy Trino component logs its activity and stores logs at /var/log/adh-haproxy/. The logging settings are specified in haproxy-trino.cfg and the default configuration ensures dual logging, namely:
global
log /dev/log local0 (1)
log 127.0.0.1:514 local0 (2)| 1 | Sends logs to the local syslog socket (/dev/log) to be processed by the system’s syslog daemon. |
| 2 | Sends logs to a syslog daemon like rsyslog or syslog-ng listening to the 514 port on localhost.
By default, these daemons are configured to write logs to /var/log/adh-haproxy/. |
|
TIP
The Haproxy Trino component has corresponding rsyslog/syslog-ng settings in ADCM (/etc/syslog-ng/conf.d/haproxy-trino.conf, /etc/rsyslog.d/haproxy-trino.conf) where you can configure logs templates, filters, log files location, etc.
|
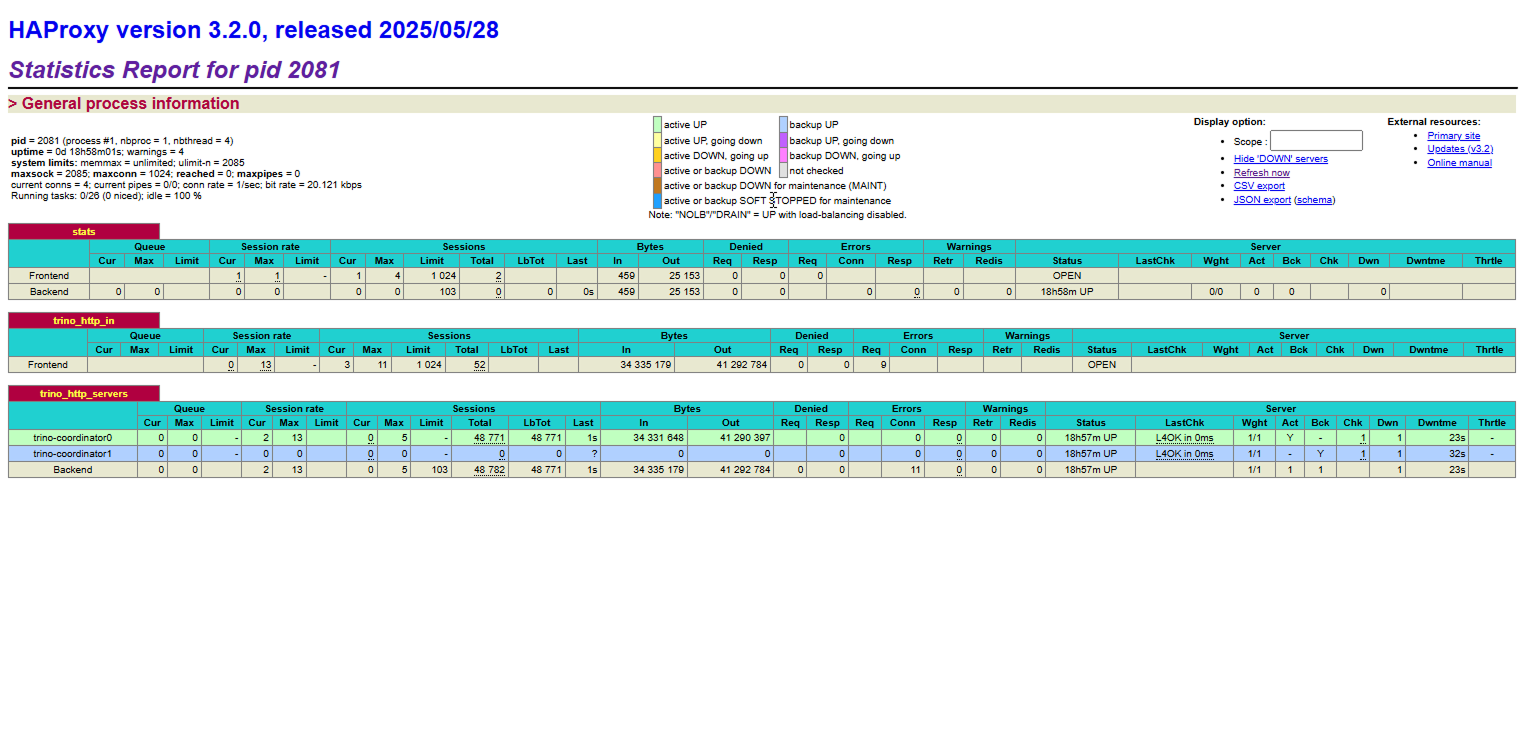
Haproxy Trino statistics
The Haproxy Trino component provides statistics about its operation.
The statistics collection is enabled by default (the listen stats block in haproxy-trino.cfg) and is available at the following endpoint: http://<Haproxy_Trino_host>:7001/.
Kerberos tips and limitations
-
In a kerberized cluster, to connect to a Trino Coordinator directly, you have to specify the Trino Coordinator host in the
krb5-service-principal-patternparameter for the Trino console client, for example:krb5-service-principal-pattern=HTTP@ka-adh-1.ru-central1.internalFor JDBC, use the parameter:
KerberosServicePrincipalPattern=HTTP@ka-adh-1.ru-central1.internal -
Direct connection to Trino Coordinator web UI via a browser (Chrome, Firefox) or cURL is not supported.