

Configure job policies
The Configuration → Job policy page in the ADB Control web interface allows you to configure schedules for different system jobs. This page includes two tabs, each of which is described in detail below.
Data cleanup
On the Configuration → Job policy → Data cleanup tab, you can configure a schedule for removing old metrics from ADB Control.
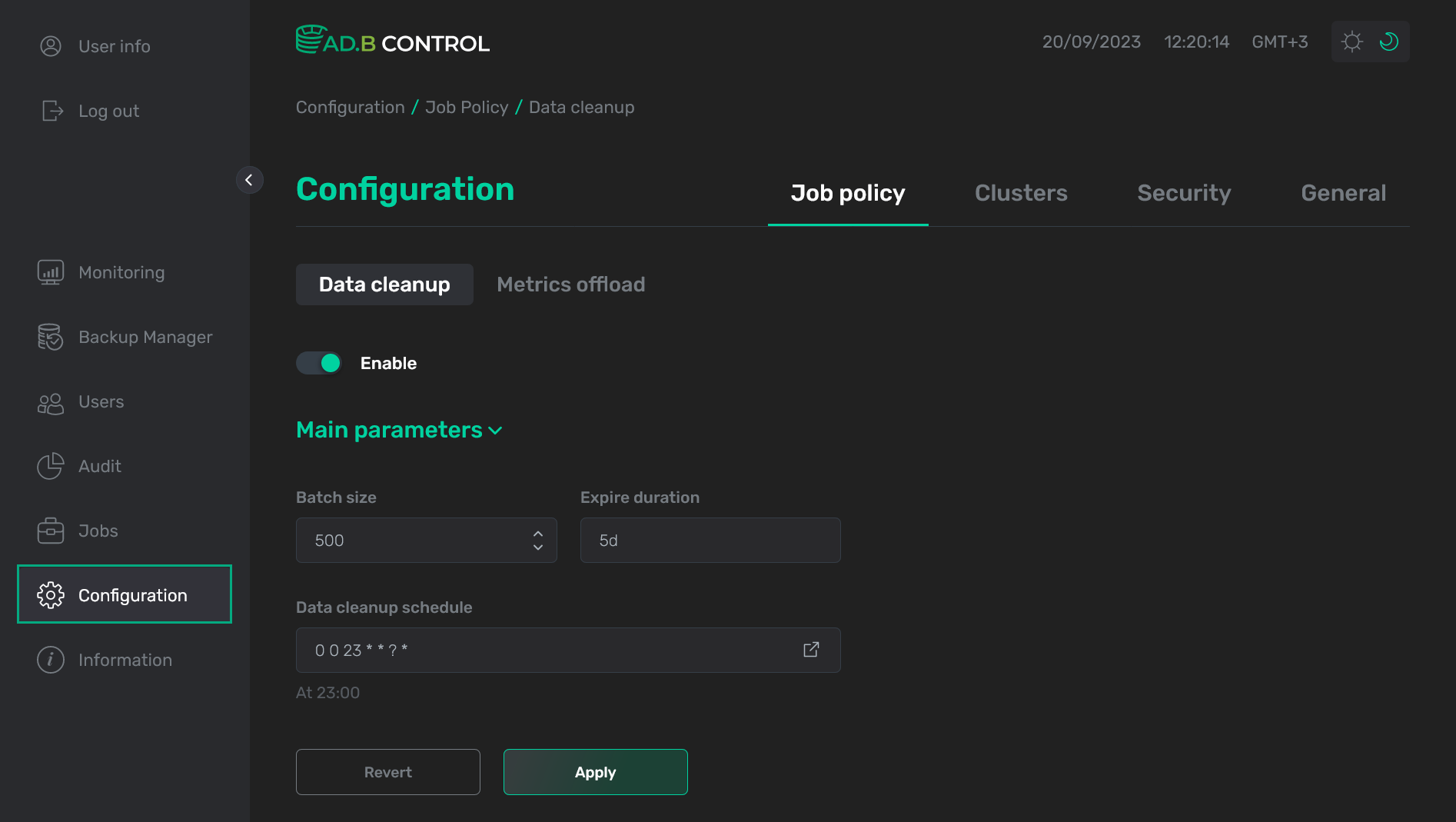
To configure the job, follow the steps:
-
Activate the Data cleanup switcher.
-
Fill in the following parameters in the Main parameters section.
Field Description Default value Batch size
A maximum number of rows in the data batch
500
Expire duration
A maximum time period that is used to store metrics in ADB Control. If this period expires, the metrics will be removed during the next job launch. Use the following format —
<value><unit>(without spaces), where<unit>can have the following values:-
ms— milliseconds; -
sec— seconds; -
min— minutes; -
hr— hours; -
d— days; -
w— weeks.
Examples:
5min,1hr,1d. The minimal value is100ms; the maximum is1w5d
Data cleanup schedule
A schedule for automatic data cleanup (
cronexpression). Theicon allows you to edit the schedule in the separate form Cron expression generator
0 0 23 * * ? *
-
-
Click Apply. The Revert button is designed to undo the changes that have not been yet saved by clicking Apply.
If all steps are completed successfully, the next launch time of the Data cleanup job is updated on the Jobs → ADB Control → Schedule page.
|
CAUTION
|
Metrics offload
Configuration
|
CAUTION
|
On the Configuration → Job policy → Metrics offload tab, you can configure a schedule for uploading ADB Control metrics and events to an external database (PostgreSQL/ADB). To configure the job, follow the steps:
-
On the target host, ensure you have a database to store the uploaded metrics. Its name will be used when configuring the JDBC connection later.
-
Provide the ADB Control access to the selected external database. PostgreSQL requires the following record in the pg_hba.conf file.
host <database_name> <user_name> <adbc_address> trustwhere:
-
<database_name>— a database name in PostgreSQL. For example,adbc_metrics. -
<user_name>— a user name in PostgreSQL. For example,postgres. -
<adbc_address>— an IP address of the host where ADB Control is deployed (with a subnet number). For example,10.92.43.139/32.
hostssl all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5For more information on how to configure PostgreSQL for using SSL, see SSL encryption.
-
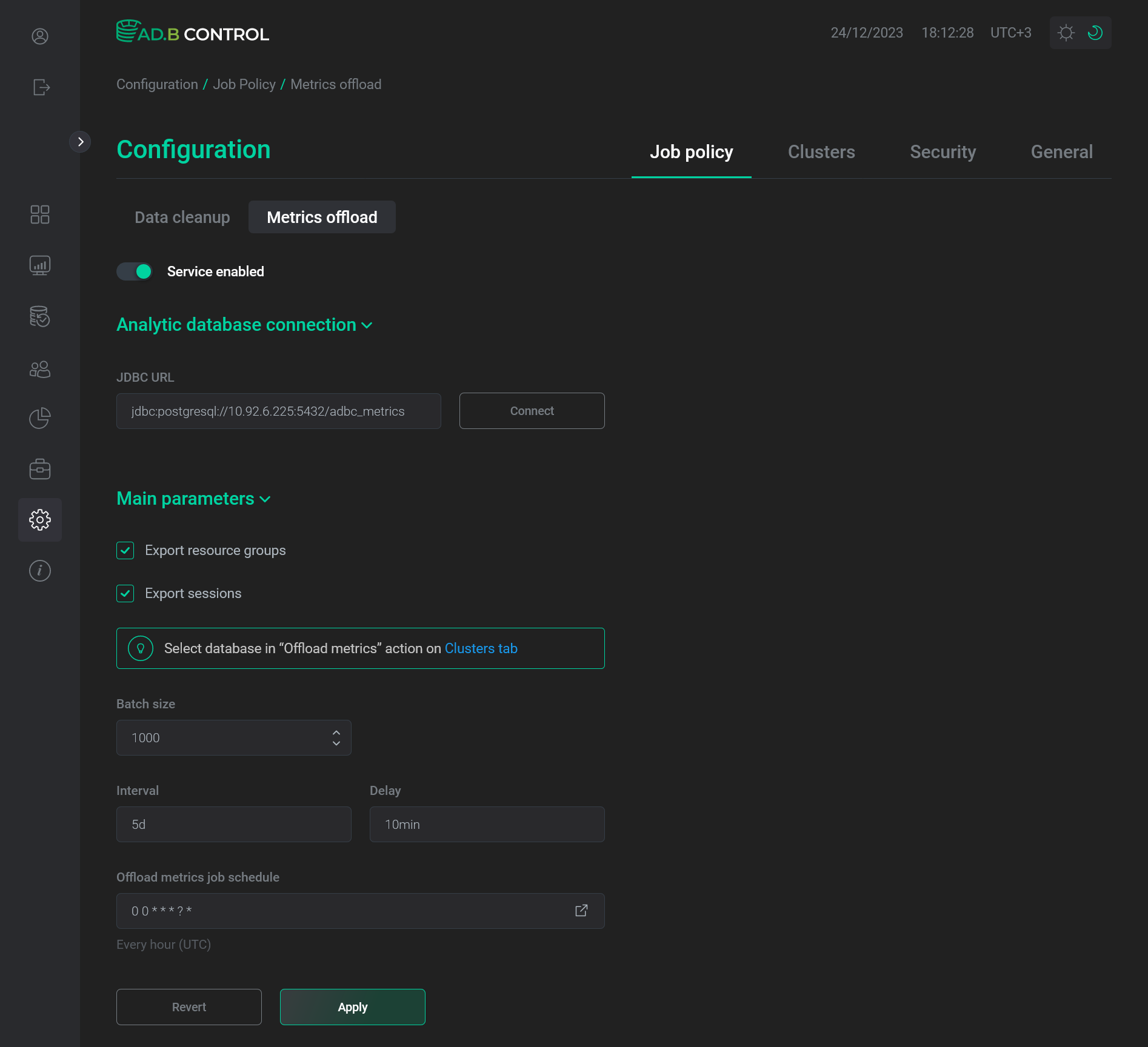
Go to the Configuration → Job policy → Metrics offload tab in the ADB Control interface.
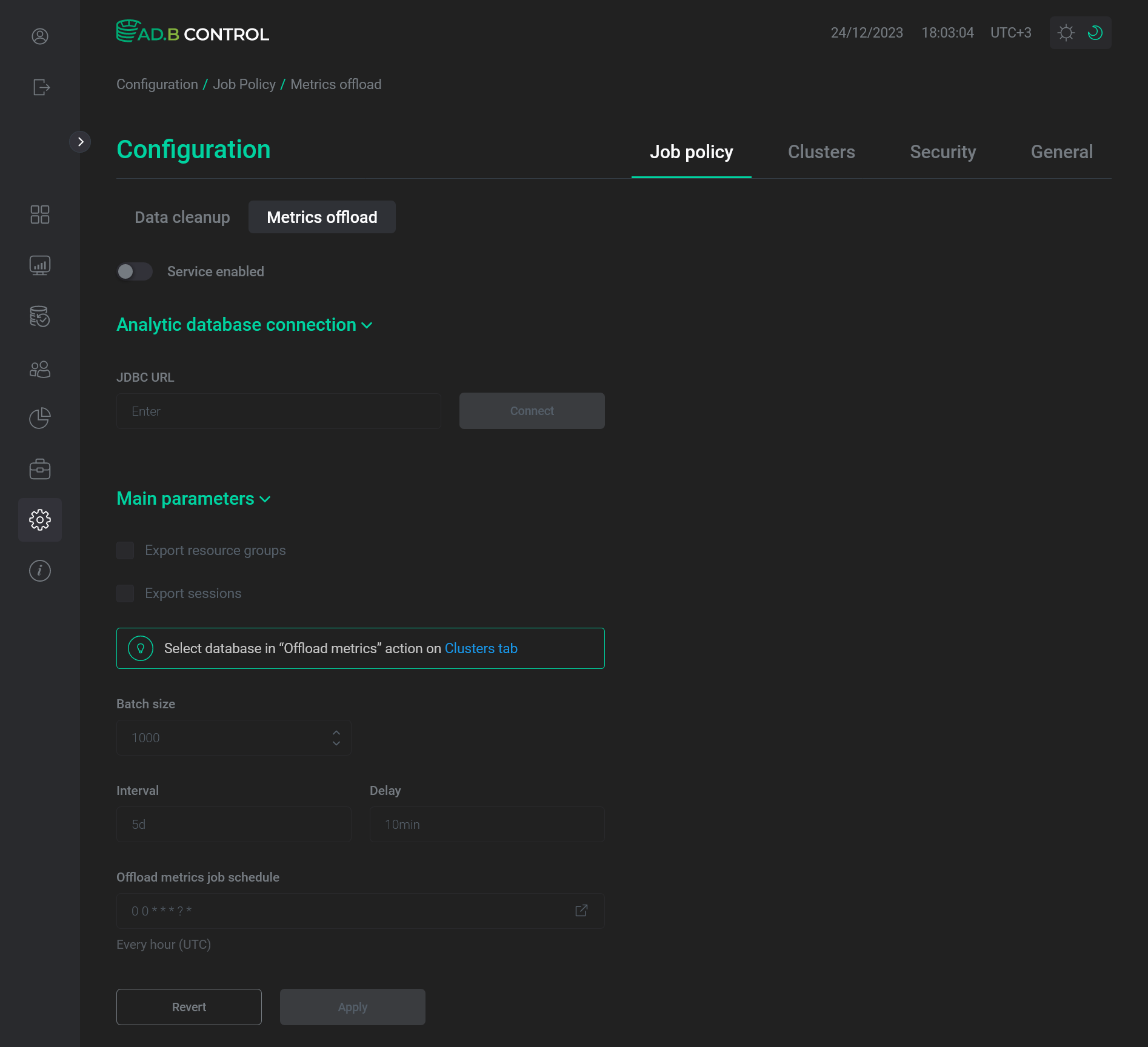 The "Configuration → Job policy → Metrics offload" tab
The "Configuration → Job policy → Metrics offload" tab The "Configuration → Job policy → Metrics offload" tab
The "Configuration → Job policy → Metrics offload" tab -
Activate the Metrics offload switcher.
-
In the JDBC URL field, enter a URL of the JDBC connection to the host where the target database is located. For PostgreSQL, use the following format:
jdbc:postgresql://<external_ip>:5432/<db_name>where:
-
<external_ip>— an IP address of the host where the target database is located. For example,10.92.41.7. -
<db_name>— a target database name. For example,postgres.
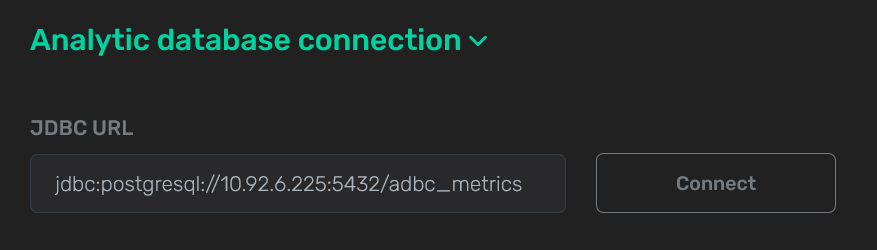 JDBC connection string
JDBC connection string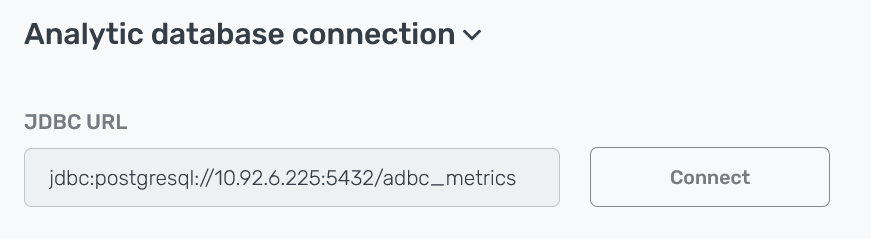 JDBC connection string
JDBC connection string -
-
Click Connect. In the window that opens, fill in the following fields:
-
User — a user name. In the following example, the default user
postgresis used. -
Password — a user password.
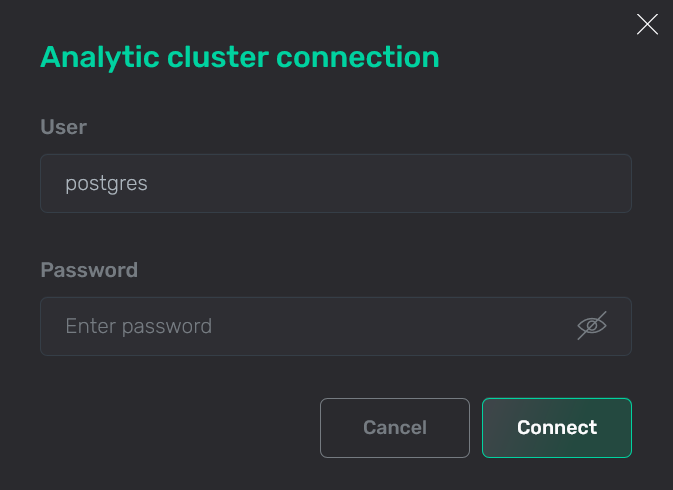 JDBC connection parameters
JDBC connection parameters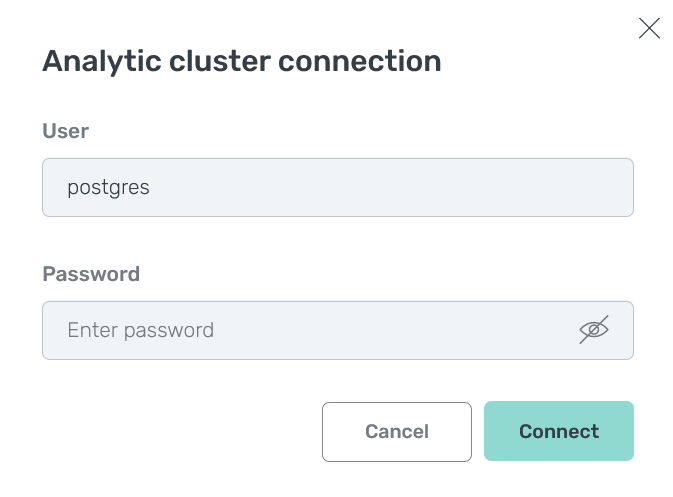 JDBC connection parameters
JDBC connection parameters
-
-
Click Connect.
-
Fill in the following fields in the Main parameters section.
Field Description Default value Export sessions
The flag that indicates whether to export information on sessions (see session)
False
Batch size
A maximum number of rows in the data batch that is sent to an external database
1000
Interval
A maximum date range for metrics offload (in days)
5d
Delay
The time delay that is used to look for new metrics to export (in minutes)
10min
Offload metrics job schedule
A schedule for the automatic data export to an external database (
cronexpression). Theicon allows you to edit the schedule in the separate form Cron expression generator
0 0 * * * ? *
-
Click Apply. The Revert button is designed to undo the changes that have not been yet saved by clicking Apply.
 Data is filled
Data is filled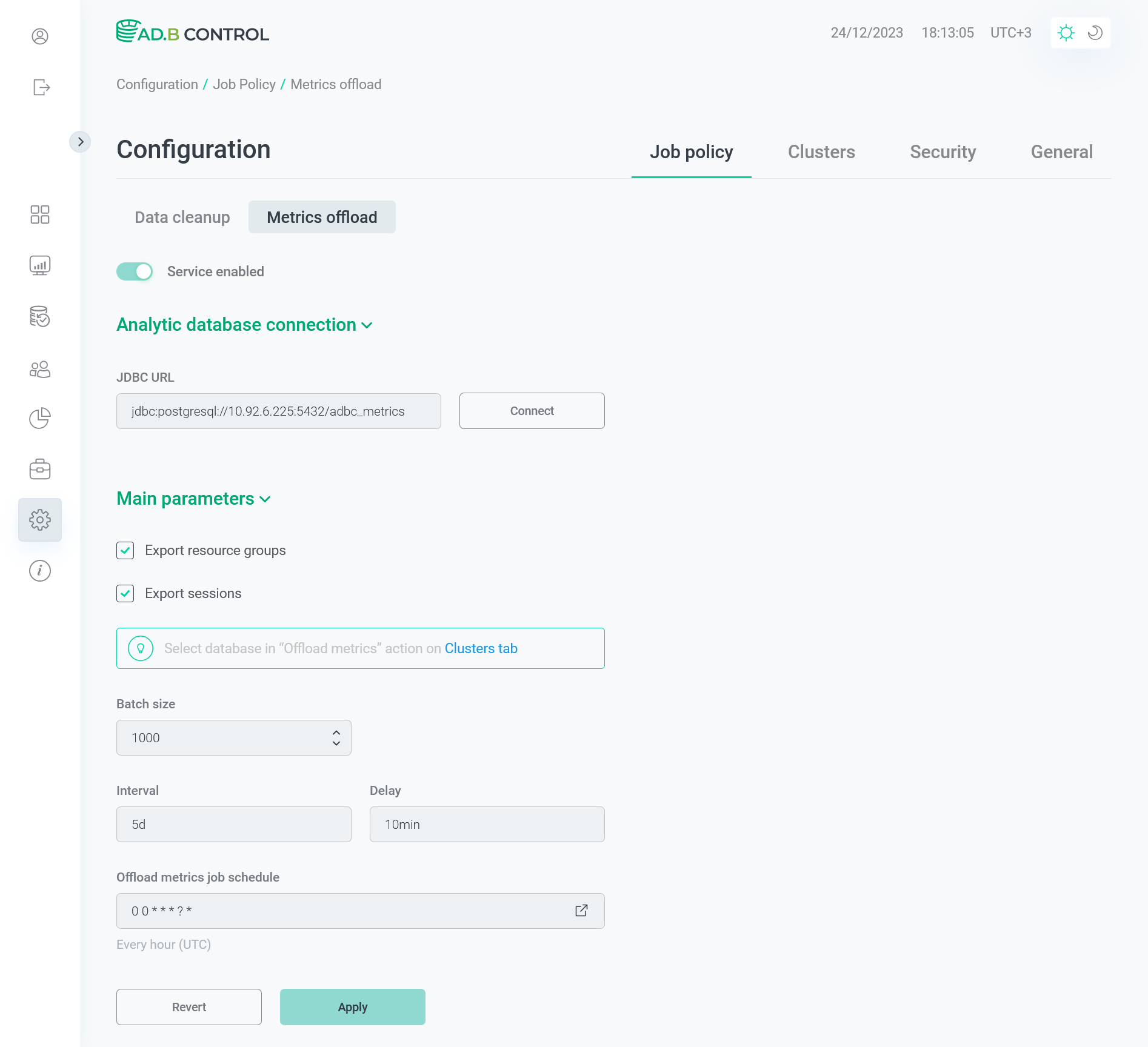 Data is filled
Data is filled -
Get the following message on the successful result.
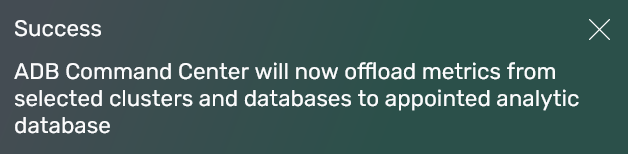 The successful result
The successful result The successful result
The successful result -
As a result, the
adccschema should be created in the external database. The tables in this schema will store metrics and events collected from ADB Control. To check whether all necessary objects are created, you can run the following query in PostgreSQL:SELECT table_name FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema = 'adcc' ORDER BY table_name;Result:
table_name ----------------------------- audit_auth audit_auth_adb audit_operation cluster cluster_query_metric query query_error relation_statistic session transaction (10 rows)
If all steps are completed successfully, the new scheduled job Export job should be added to the Jobs → ADB Control → Schedule page.
|
IMPORTANT
In addition to the job schedule, you should specify the clusters and databases which metrics should be exported to the external database. For more information, see Cluster management. |
Structure of offloaded data
The following tables are used in external databases to store metrics and events offloaded from ADB Control. Note that the conditions for offloading data to the listed tables are different:
-
audit_auth,audit_auth_adb,audit_operation,relation_statistic— it is enough to configureExport jobon the Configuration → Job policy → Metrics offload tab. -
cluster,cluster_query_metric,query,query_error,transaction— besides configuringExport jobon the Configuration → Job policy → Metrics offload tab, it is necessary to specify the databases which metrics should be exported. You should do it on the Configuration → Clusters tab. -
session— besides configuringExport jobon the Configuration → Job policy → Metrics offload tab (with the Export sessions checkbox selected), it is necessary to set the Sessions flag on the Configuration → General → Sessions tab.
This table stores user login attempts to ADB Control, as well as failed ADB authorizations. For more information on the below mentioned parameters, see the Authorizations section of the Audit article.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
id |
A unique identifier of the authorization event |
time |
An event timestamp |
username |
A user name |
session_time |
A start timestamp of the session within which the current event took place |
session |
An identifier of the session within which the current event took place |
host |
IP address of the host from which the event was initiated |
auth_type |
An authorization type:
|
type |
An event type. Possible values:
|
result |
An event result. Possible values:
|
message |
An error message |
This table contains additional information about failed login attempts to ADB.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
auth_id |
An identifier of the authorization event. Refers to |
pid |
An identifier of the process within which the current event took place |
database |
A name of the database to which the connection was made |
port |
The port number that was used for the current connection |
segment |
A content identifier for a segment instance. Corresponds to |
transaction |
A transaction identifier |
cmd_count |
A command identifier |
cluster |
A name of the ADB cluster to which the connection was made |
This table contains information about user operations in ADB Control. For more information on the below mentioned parameters, see the Operations section of the Audit article.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
id |
A unique operation identifier |
object_name |
A name of the object on which the operation was performed |
object_type |
A type of the object on which the operation was performed. Possible values:
|
operation_type |
A type of the operation that was applied to the
|
operation_result |
An operation result. Possible values:
|
operation_time |
An operation end timestamp |
username |
A name of the user who performed the operation |
session |
An identifier of the ADB Control user session |
hostname |
IP address of the host from which the operation was initiated |
diffs |
Information about changed attributes of the
The example: |
This table contains information on ADB clusters selected in ADB Control for export of metrics and events to the external database.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
id |
A cluster unique identifier |
name |
A cluster name |
This table stores statistics of system resource consumption by commands at the cluster level. For more information, see the System metrics collected for commands section of the Monitoring of commands article.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
query_id |
A command identifier. Refers to |
cpu_usage_total |
The total CPU consumption during the command execution (in seconds) |
cpu_usage_percent_sum |
The CPU amount consumed at the end of the command execution (percentage) |
cpu_usage_percent_avg |
The average amount of CPU consumed across cluster segments at the end of the command execution (percentage) |
cpu_usage_percent_skew |
The indicator that displays the CPU consumption skew across cluster segments at the end of the command execution (percentage) |
mem_sum |
The RAM amount consumed at the end of the command execution (in bytes) |
mem_max |
The maximum amount of RAM consumed at the end of the command execution (in bytes) |
mem_avg |
The average amount of RAM consumed across cluster segments at the end of the command execution (in bytes) |
mem_skew |
The indicator that displays the RAM consumption skew across cluster segments at the end of the command execution (percentage) |
vmem_sum |
The virtual memory amount allocated at the end of the command execution (in bytes) |
vmem_max |
The maximum amount of virtual memory allocated at the end of the command execution (in bytes) |
vmem_avg |
The average amount of virtual memory allocated across cluster segments at the end of the command execution (in bytes) |
vmem_skew |
The indicator that displays the virtual memory consumption skew across cluster segments at the end of the command execution (percentage) |
spill |
The amount of spill files on cluster segment hosts (excluding coordinator) at the end of the command execution (in bytes) |
spill_hosts |
The amount of spill files on cluster hosts (including coordinator) at the end of the command execution (in bytes) |
spill_max |
The maximum amount of spill files produced on cluster segments at the end of the command execution (in bytes) |
spill_skew |
The indicator that displays the spill file amount skew at the end of the command execution (percentage) |
read_bytes_total |
The total amount of data read during the command execution (in bytes) |
read_bytes_sum |
The amount of data read at the end of the command execution (in bytes) |
read_bytes_max |
The maximum amount of data read at the end of the command execution (in bytes) |
read_bytes_avg |
The average amount of data read across cluster segments per second at the end of the command execution (in bytes) |
read_bytes_skew |
The indicator that displays the data reading skew across cluster segments at the end of the command execution (percentage) |
write_bytes_total |
The total amount of data written during the command execution (in bytes) |
write_bytes_sum |
The amount of data written at the end of the command execution (in bytes) |
write_bytes_max |
The maximum amount of data written at the end of the command execution (in bytes) |
write_bytes_avg |
The average amount of data written across cluster segments per second at the end of the command execution (in bytes) |
write_bytes_skew |
The indicator that displays the data writing skew across cluster segments at the end of the command execution (percentage) |
This table contains information on completed SQL commands that were registered in ADB Control.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
query_id |
A unique command identifier |
status |
A command status. Possible values:
|
pid |
An identifier of the process, within which the command was started |
submitted |
The timestamp when the user submitted the command |
run_at |
A command start timestamp |
finish_at |
A command end timestamp |
username |
A name of the user who started the command |
database |
A name of the database where the command was started |
resource_group |
A name of the resource group that was used for the command |
planner |
A name of the query optimizer that was used to produce the query execution plan. Possible value:
|
querytext |
A text of the SQL query |
plantext |
A text of the command execution plan |
session_id |
An identifier of the session, within which the command was started |
cluster_id |
An identifier of the ADB cluster where the command was started. Refers to |
queued_time |
The total time that the command was queued (in hours, minutes, seconds) |
run_time |
The total command duration (in hours, minutes, seconds) |
sql_id |
A common identifier for SQL commands with the same structure |
tags |
The query tags |
This table contains information about errors that occurred during execution of SQL commands.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
id |
A unique identifier of the error record |
query_id |
A command identifier. Refers to |
seg_id |
A content identifier for a segment instance. Corresponds to |
slice_id |
An identifier of the slice during which execution the current error occurred |
message |
An error message text |
This table contains information on sessions that were registered in ADB Control.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
cluster_id |
An identifier of the ADB cluster. Refers to |
datetime |
The timestamp when the data was received |
datid |
A database OID |
datname |
A database name |
pid |
A backend process identifier |
sess_id |
A session identifier |
usesysid |
An OID of the user who connected to the backend |
usename |
A name of the user who connected to the backend |
application_name |
A name of the application that is connected to the backend |
client_addr |
A client IP address. The |
client_hostname |
A host name of the connected client, as reported by a reverse DNS lookup of the |
client_port |
The TCP port number that is used by the client to communicate with the backend, or |
backend_start |
The time when the backend process was started |
xact_start |
A transaction start timestamp |
query_start |
A command execution start timestamp |
state_change |
The last time the value of the |
waiting |
|
state |
The current session state. Possible values:
|
query |
A text of the most recent SQL query that was run at the backend. If |
rsgid |
A resource group OID or |
rsgname |
A resource group name or |
rsgqueueduration |
The total time the query has been queued (if applicable) |
This table contains information on completed transactions that were registered in ADB Control.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
txn_id |
A unique transaction identifier in ADB Control |
status |
A transaction status. Possible values:
|
pid |
An identifier of the process, within which the transaction was started |
start_time |
A transaction start timestamp |
end_time |
A transaction end timestamp |
username |
A name of the user who started the transaction |
database |
A name of the database where the transaction was started |
resource_group |
A name of the resource group that was used for the transaction |
session_id |
An identifier of the session, within which the transaction was started |
cluster_id |
An identifier of the ADB cluster where the transaction was started. Refers to |
tags |
The transaction tags |