

Work with arenadata_toolkit
When you install an ADB cluster, the arenadata_toolkit schema is automatically created in the default database. This schema is used to collect information on cluster operations. The schema includes several tables, which allow users to get results of the VACUUM/ANALYZE commands that are launched on a schedule, view information about data files, etc. Additionally, ADB provides a set of scripts that interact with arenadata_toolkit and automatically perform various cluster management operations (according to the predefined schedule).
|
NOTE
In custom databases that are added after ADB installation, the |
Schema tables
The tables included in the arenadata_toolkit schema are described below.
The arenadata_toolkit.daily_operation monthly-partitioned table contains information about the VACUUM and ANALYZE operations that are automatically applied to database tables on a schedule. The table contents are updated daily when the vacuum, analyze, vacuum_analyze_pg_catalog scripts are run.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
schema_name |
A schema name |
table_name |
A table name |
action |
An operation name. Possible values:
|
status |
An operation status. Possible values:
|
time |
An operation duration (in seconds) |
processed_dttm |
Operation date and time |
The arenadata_toolkit.db_files_current table contains information about data files on all cluster segments with links to tables, indexes, and other database objects (if possible). The table contents reflect the state at the time of the last collect_table_stats script launch. The table is overwritten every time the script is run.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
oid |
A table object identifier (OID) |
table_name |
A table name |
table_schema |
A schema name |
type |
A table type. See pg_class.relkind |
relamname |
A table access method. See pg_am.amname |
table_parent_table |
A parent table name ( |
table_parent_schema |
A parent table schema ( |
table_database |
A database name |
table_tablespace |
A tablespace name |
content |
A content identifier of the segment instance where the data file is located. See gp_segment_configuration.content |
segment_preferred_role |
The role that a segment was originally assigned at initialization time. See gp_segment_configuration.preferred_role |
hostname |
A name of the host where the data file is located |
address |
The hostname used to access a particular segment instance on a segment host. This value may be the same as |
file |
A full path to the data file |
modifiedtime |
The last file modification time that is returned by the system command |
file_size |
A data file size (in bytes) |
tablespace_location |
The file system location of the tablespace |
The arenadata_toolkit.db_files_history monthly-partitioned table contains the history of data file changes on all cluster segments with links to tables, indexes, and other database objects (if possible). The table may be useful for tracking the database size changes. The table structure is identical to arenadata_toolkit.db_files_current, except for the additional column collecttime described below.
The arenadata_toolkit.db_files_history contents are updated daily when the collect_table_stats script is run (by copying actual data from arenadata_toolkit.db_files_current).
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
collecttime |
Data collection time |
The arenadata_toolkit.operation_exclude table contains information on database schemas that should be skipped by the VACUUM and ANALYZE commands when the vacuum and analyze scripts are run.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
schema_name |
A schema name |
backup |
The flag that controls whether the row should be included in backups when using the |
Cluster management scripts
Overview
ADB maintenance scripts are displayed on the Primary configuration tab of the ADB service configuration page. To view all scripts, expand the Crontab → Crontab maintenance scripts node in the tree of configuration settings.
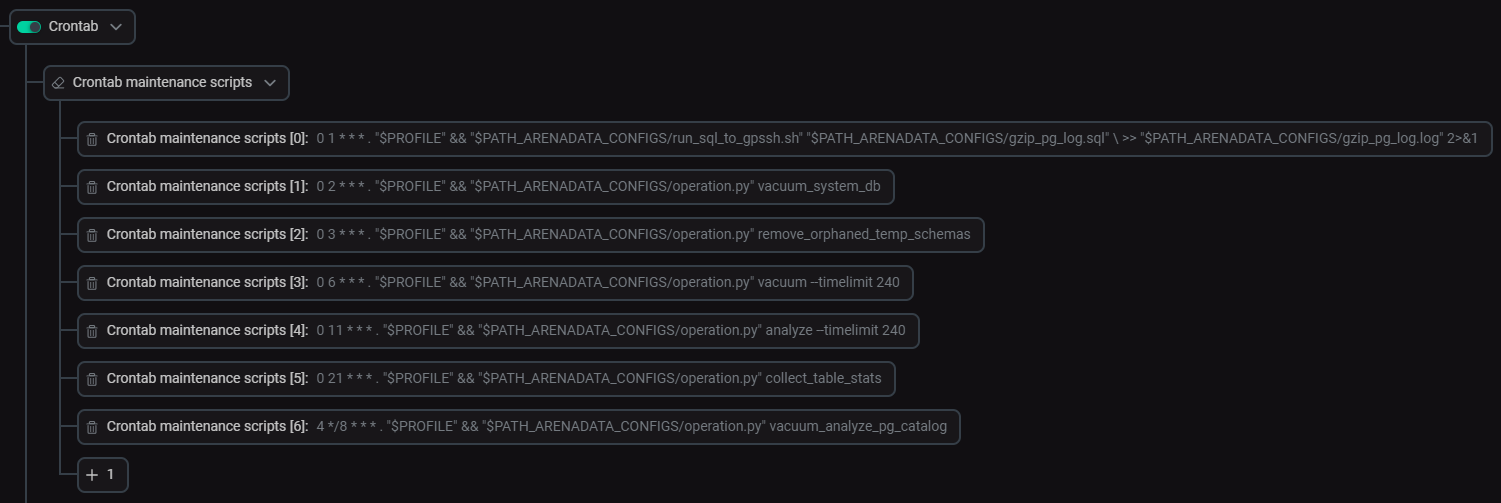
|
CAUTION
If you need to configure custom scripts, use the system |
The cron scheduler is used to run scripts automatically. Scripts are launched on behalf of the system user (by default, gpadmin). In the ADCM interface, each script is described as a separate string including:
-
Start time — a
cronexpression that defines how often a script should be run. -
Path to the script — a full path to the script. Currently, two main scripts are used:
-
run_sql_to_gpssh.sh — sends the result of the selected SQL query as a bash command via
gpssh. Requires a path to the SQL script as an argument. -
operation.py — the Python script that performs various operations at the ADB cluster level. The operation type is defined by the first argument (for example,
vacuumoranalyze).
Each of these scripts can in turn refer to other SQL queries, scripts, and functions of the
arenadata_toolkitschema. All bash, Python, and SQL scripts are stored in the /home/gpadmin/<Arenadata_configs_directory_name>/ directory, where<Arenadata_configs_directory_name>is a value of the Advanced → Arenadata configs directory name ADB configuration parameter (by default,arenadata_configs). -
-
Arguments — input parameters that are used to run the script (if available). The arguments available for the operation.py script are listed below.
| Argument | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
The first positional parameter (without alias) |
An operation name:
For information on all operations, see Purpose of ADB cluster management scripts |
— |
--loglevel |
A logging level. Possible values:
For more information on logging levels, see Python documentation |
2 |
--processes |
A number of worker processes. Possible values: |
10 |
--timelimit |
The limit on the script execution time (in minutes). If the limit is reached, the operation will finish processing the current object, and then the script will stop:
When multiple workers are used (via |
— |
--excludedb |
A list of databases that should be excluded from the script process. This list extends databases that are skipped by operation.py by default:
|
— |
--vacuum-order |
The order in which the
|
newest-first |
Script logs are stored in the /home/gpadmin/<Arenadata_configs_directory_name>/operation_log/ directory (for operation.py) and the gzip_pg_log.log file (for gzip_pg_log.sql). You can configure the log retention period via the Crontab → Delete old maintenance script logs configuration parameter of the ADB service. The default parameter value is 30 days.
|
TIP
It is not recommended to change scripts in any way. However, if you need to update the script start time or add/modify script arguments, follow the steps below:
|
Most scripts interact with the arenadata_toolkit schema. The purpose of all scripts is described below.
| # | Script | Description | Start time HH:mm (UTC) |
|---|---|---|---|
0 |
run_sql_to_gpssh.sh → gzip_pg_log.sql |
For each cluster segment, archives CSV logs that are stored in <data_directory>/pg_log and have not changed for more than 3 days (where |
01:00 |
1 |
operation.py → vacuum_system_db |
Applies the VACUUM FREEZE command to the |
02:00 |
2 |
operation.py → remove_orphaned_temp_schemas |
In all custom databases, drops temporary schemas that are no longer in use and whose names start with |
03:00 |
3 |
operation.py → vacuum |
|
06:00 |
4 |
operation.py → analyze |
|
11:00 |
5 |
operation.py → collect_table_stats |
In all custom databases:
|
21:00 |
6 |
operation.py → vacuum_analyze_pg_catalog |
|
00:04 08:04 16:04 |
7 |
gzip_gpadmin_log.sh |
Performs automatic compression of log files that are located in /home/gpadmin/gpAdminLogs/ and are older than 3 days |
01:00 |
Example of a custom function for VACUUM
Below you can find an example of using a custom function that determines the order in which user tables should be processed when performing the VACUUM operation (see --vacuum-order in the operation.py arguments table):
-
Create a function that meets the following conditions:
-
The function should have one input parameter of the
texttype. When the operation.py script is run,VACUUMis always passed as the parameter value. There is no need to use the parameter in the function body. -
The function should return a table with the following columns:
table_schema(schema in DB) andtable_name(table in DB). This is a sorted list of database tables, to which theVACUUMoperation should be applied.
Suppose that you want certain ETL data in the staging environment to be processed by the
VACUUMoperation only after all other data has been processed. The following function moves tables whose names start withetl_stagingto the end of the list and sorts tables by schema names and then by table names in the alphabetical order.CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.adb_vacuum_strategy_etl_staging(actionname text) RETURNS TABLE (table_schema name, table_name name) LANGUAGE sql STABLE AS $$ SELECT nspname, relname FROM pg_catalog.pg_class c JOIN pg_catalog.pg_namespace n ON relnamespace = n.oid WHERE relkind = 'r' AND nspname NOT IN (SELECT schema_name FROM arenadata_toolkit.operation_exclude) ORDER BY CASE WHEN relname LIKE 'etl_staging%' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END, nspname, relname; $$ EXECUTE ON MASTER;CAUTIONThe function should be added to all custom databases to which the
VACUUMoperation will be applied, i.e. all databases except for system ones (template0,template1,postgres) and those that can be optionally specified in the --excludedb argument of the operation.py script. -
-
Ensure the function works:
SELECT * FROM public.adb_vacuum_strategy_etl_staging('VACUUM');In the resulting output, tables related to ETL staging (
etl_staging_*) are placed at the very bottom:table_schema | table_name -------------------+-------------------------------- arenadata_toolkit | daily_operation_1_prt_other arenadata_toolkit | daily_operation_1_prt_p202510 arenadata_toolkit | daily_operation_1_prt_p202511 arenadata_toolkit | db_files_current arenadata_toolkit | db_files_history_1_prt_other arenadata_toolkit | db_files_history_1_prt_p202510 arenadata_toolkit | db_files_history_1_prt_p202511 arenadata_toolkit | operation_exclude kadb | offsets public | spatial_ref_sys public | etl_staging_main public | etl_staging_orders public | etl_staging_products public | etl_staging_users (14 rows)
-
In ADCM, open the Primary configuration tab on the configuration page of the ADB service.
-
Expand the Crontab → Crontab maintenance scripts node in the tree of configuration settings and click a description of the script that performs
vacuum.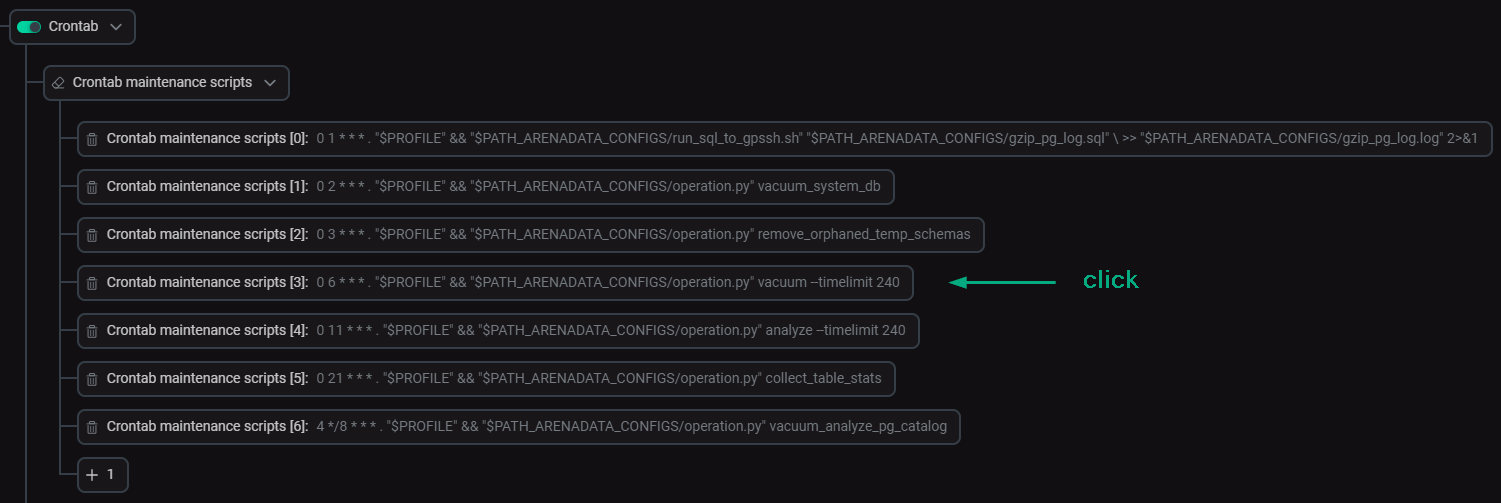 Proceed to editing the script arguments
Proceed to editing the script arguments -
In the window that opens, add the
--vacuum-order <schema_name>.<function_name>argument to the end of the current script description. For example:--vacuum-order public.adb_vacuum_strategy_custom. Click Apply.IMPORTANTThe custom function name should be defined in the following format:
<schema_name>.<function_name>, where<schema_name>— a name of the schema where the function was created;<function_name>— the function name. Note that passing arguments to the function is not supported.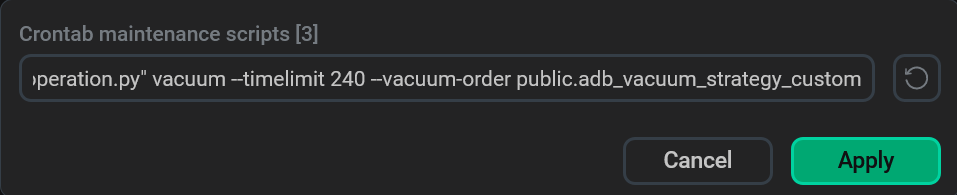 Add the --vacuum-order argument
Add the --vacuum-order argument -
Click Save to save the configuration changes. Then, apply the Reconfigure action to the ADB service.
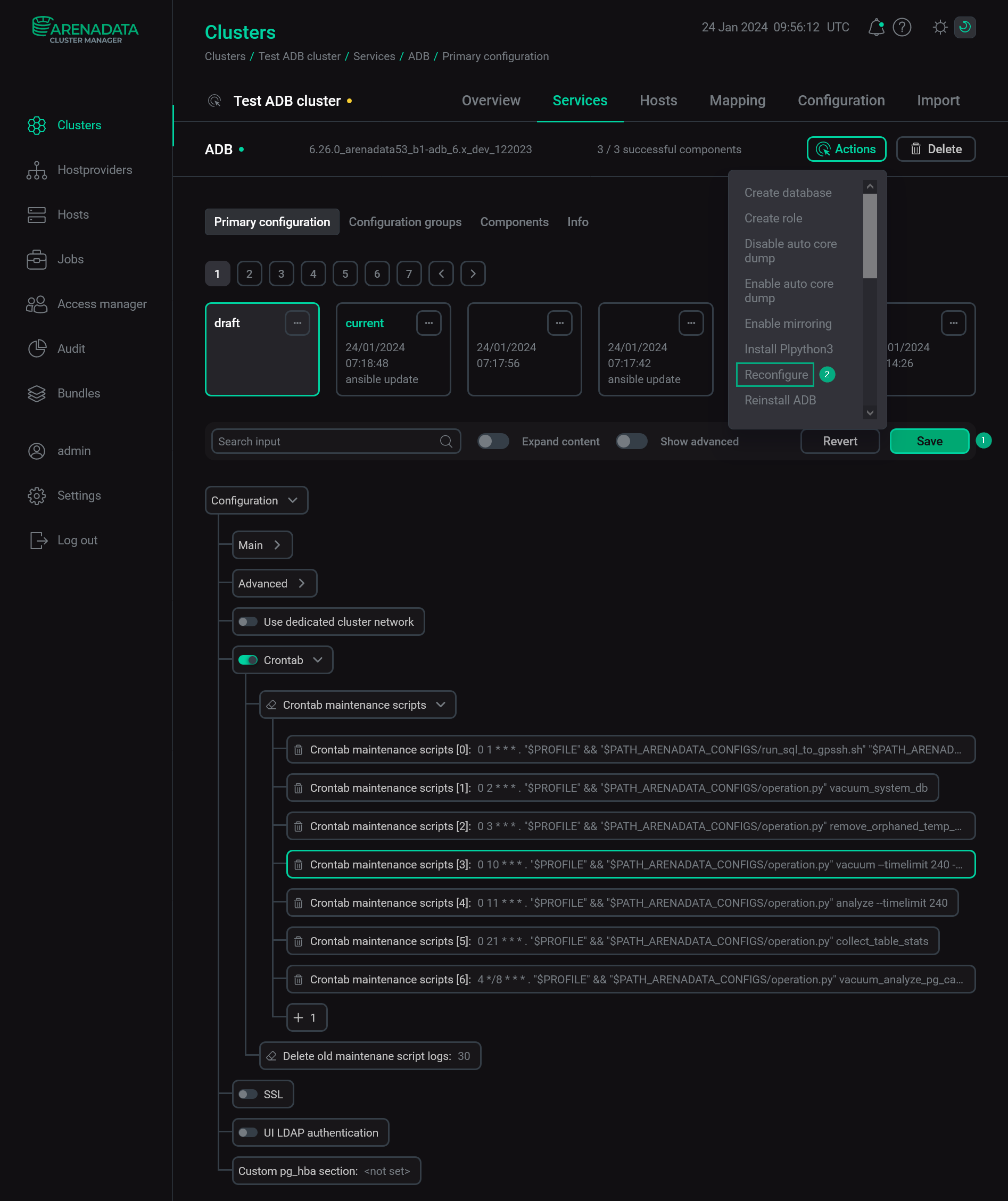 Save changes in the ADB configuration
Save changes in the ADB configuration -
After the operation.py script is run according to the schedule, view the contents of the log created in the /home/gpadmin/<Arenadata_configs_directory_name>/operation_log/ directory (by default, /home/gpadmin/arenadata_configs/operation_log/). Each log name contains date and time of the script launch — for example, 2025-11-10_10:05:01.172592.log.
Ensure that the table processing order corresponds to the one defined in the custom function. To do this, pay attention to the log entries marked as
DO, which mean that theVACUUMcommand is started for the corresponding tables.Note that the order of events with the same timestamp in the log may differ from the actual one. In this case, compare identifiers of worker processes
ForkPoolWorker. The smaller the identifier, the earlier the start of processing.Log fragment for the VACUUM operation2025-11-10 08:25:02,665: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-3: pid=3437270: DO: 'vacuum "arenadata_toolkit"."daily_operation_1_prt_p202511";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:02,665: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-7: pid=3437279: DO: 'vacuum "arenadata_toolkit"."db_files_history_1_prt_p202511";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:02,665: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-2: pid=3437269: DO: 'vacuum "arenadata_toolkit"."daily_operation_1_prt_p202510";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:02,665: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-1: pid=3437268: DO: 'vacuum "arenadata_toolkit"."daily_operation_1_prt_other";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:02,665: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-4: pid=3437272: DO: 'vacuum "arenadata_toolkit"."db_files_current";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:02,665: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-5: pid=3437275: DO: 'vacuum "arenadata_toolkit"."db_files_history_1_prt_other";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:02,667: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-8: pid=3437281: DO: 'vacuum "arenadata_toolkit"."operation_exclude";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:02,669: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-9: pid=3437283: DO: 'vacuum "kadb"."offsets";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:02,665: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-6: pid=3437277: DO: 'vacuum "arenadata_toolkit"."db_files_history_1_prt_p202510";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:02,988: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-4: pid=3437272: DONE: 'vacuum "arenadata_toolkit"."db_files_current";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:02,990: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-9: pid=3437283: DONE: 'vacuum "kadb"."offsets";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:03,090: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-5: pid=3437275: DONE: 'vacuum "arenadata_toolkit"."db_files_history_1_prt_other";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:03,092: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-8: pid=3437281: DONE: 'vacuum "arenadata_toolkit"."operation_exclude";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:03,186: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-6: pid=3437277: DONE: 'vacuum "arenadata_toolkit"."db_files_history_1_prt_p202510";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:03,186: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-2: pid=3437269: DONE: 'vacuum "arenadata_toolkit"."daily_operation_1_prt_p202510";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:03,196: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-1: pid=3437268: DONE: 'vacuum "arenadata_toolkit"."daily_operation_1_prt_other";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:03,398: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-3: pid=3437270: DONE: 'vacuum "arenadata_toolkit"."daily_operation_1_prt_p202511";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:03,431: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-7: pid=3437279: DONE: 'vacuum "arenadata_toolkit"."db_files_history_1_prt_p202511";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:04,020: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-4: pid=3437272: DO: 'vacuum "public"."spatial_ref_sys";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:04,123: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-10: pid=3437285: DO: 'vacuum "public"."etl_staging_main";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:04,123: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-8: pid=3437281: DO: 'vacuum "public"."etl_staging_orders";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:04,124: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-2: pid=3437269: DO: 'vacuum "public"."etl_staging_products";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:04,129: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-5: pid=3437275: DO: 'vacuum "public"."etl_staging_users";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:04,326: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-4: pid=3437272: DONE: 'vacuum "public"."spatial_ref_sys";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:04,424: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-9: pid=3437283: DONE: 'vacuum "public"."etl_temp_processing";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:04,526: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-2: pid=3437269: DONE: 'vacuum "public"."etl_staging_products";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:04,526: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-5: pid=3437275: DONE: 'vacuum "public"."etl_staging_users";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:04,641: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-8: pid=3437281: DONE: 'vacuum "public"."etl_staging_orders";' for 'adb' 2025-11-10 08:25:04,727: INFO: ForkPoolWorker-10: pid=3437285: DONE: 'vacuum "public"."etl_staging_main";' for 'adb'
IMPORTANT-
If there is no selected function in some databases, the following message is written to the log:
This function <schema_name>.<function_name> does not exist in the database. -
If the
--vacuum-orderargument has an invalid value (other thannewest-first/newest-lastand not containing a point), the following message is written to the log:--vacuum-order parameter is only valid for vacuum action or invalid function name.
In both cases, the
VACUUMoperation is not applied to the databases for which errors have been detected. -