

Monitoring of transactions
The Monitoring → Transactions page in the ADB Control web interface displays the transactions that are performed in the ADB clusters connected to the monitoring system. This page includes two tabs Online and History, each of which is described in detail below.
List of transactions
Online
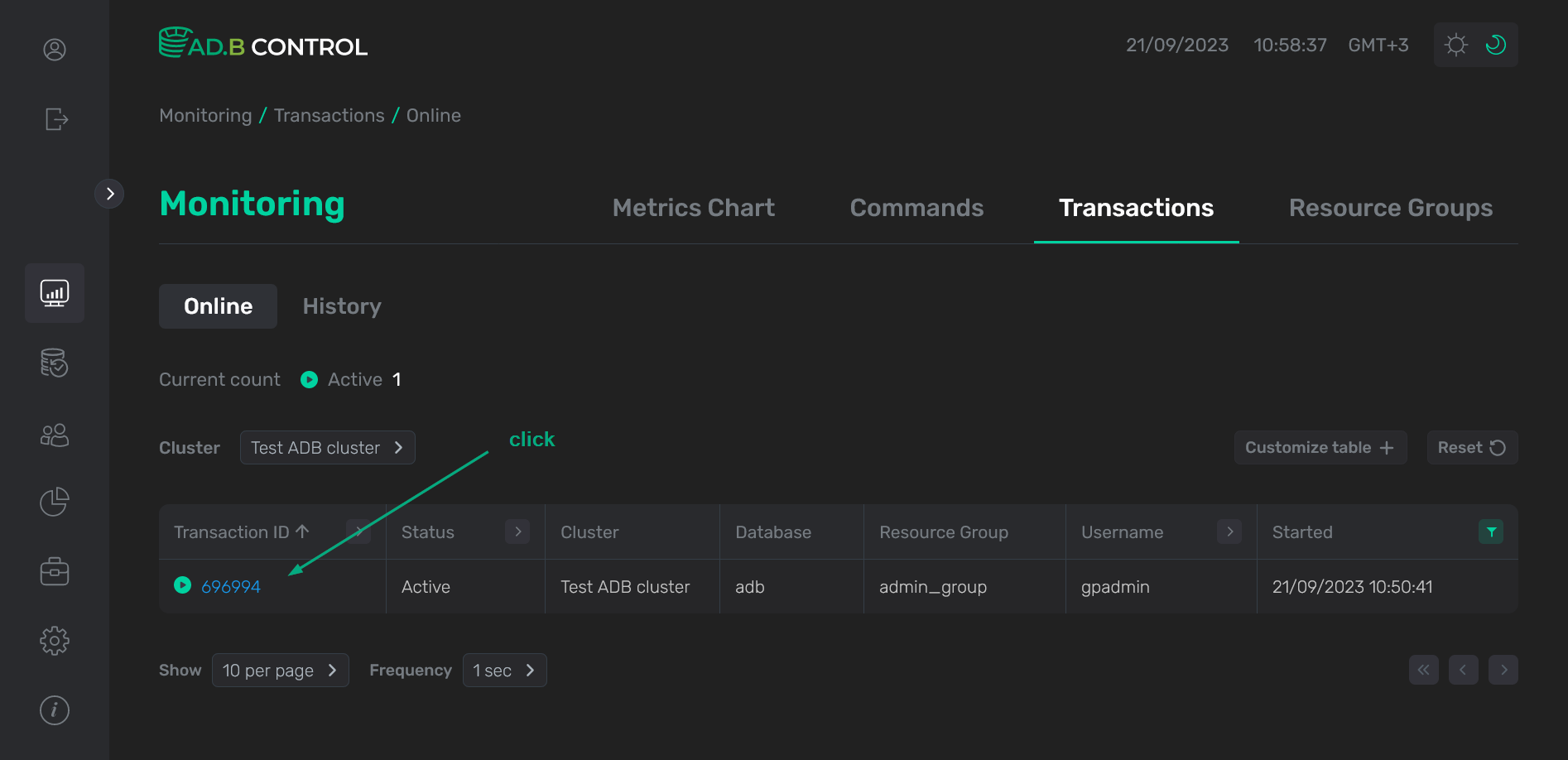
The Monitoring → Transactions → Online tab displays the currently running transactions (in the Active status).
At the top of the tab, the Current count field is located. It displays a total count of active transactions in ADB clusters connected to the monitoring system.
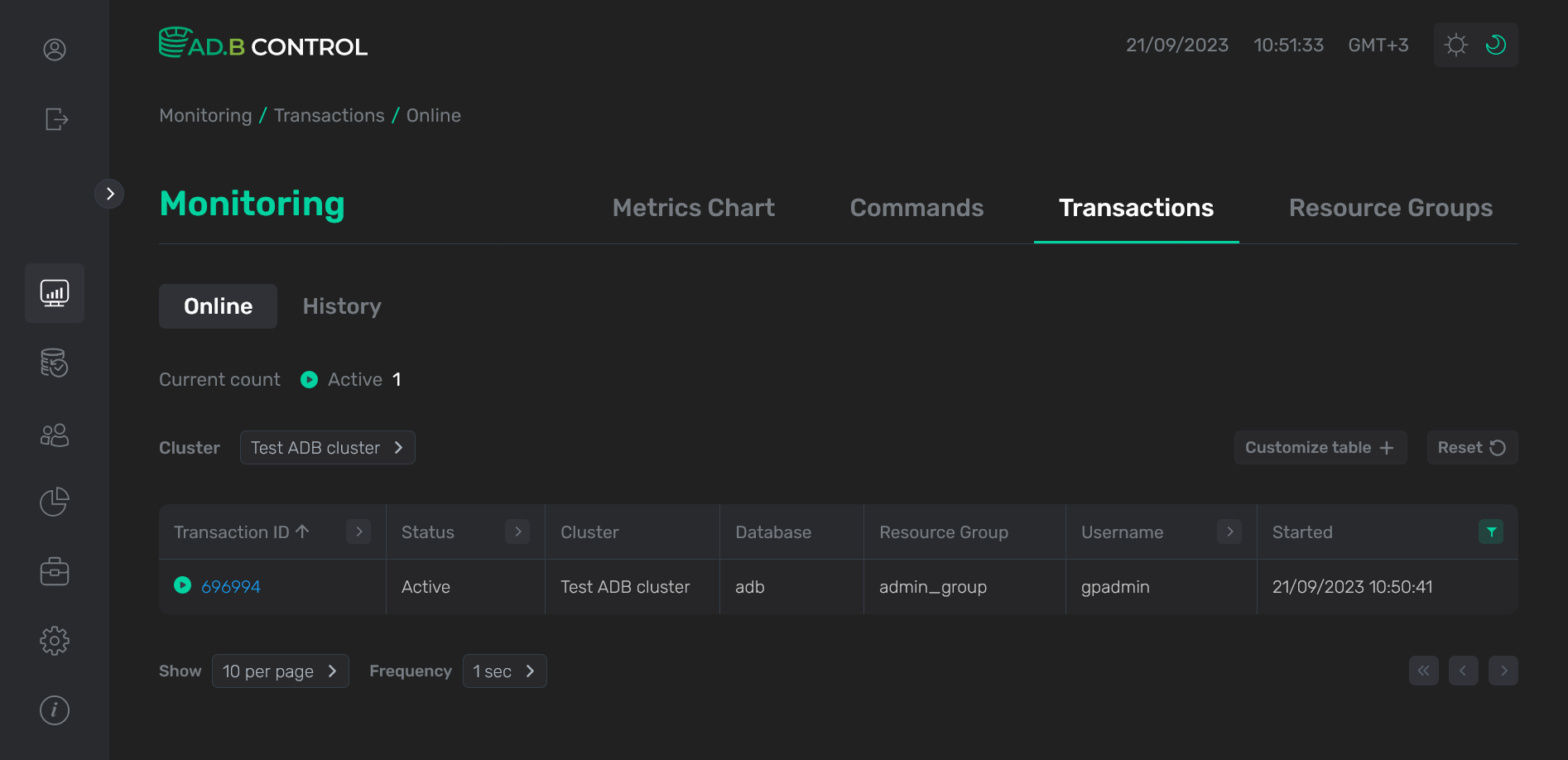
On the Monitoring → Transactions → Online tab, there is a table with the following information on transactions.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Transaction ID |
A unique transaction identifier |
Status |
A transaction status. Possible values are listed above |
Cluster |
A name of the ADB cluster where the transaction is launched |
Database |
A name of the database where the transaction is launched |
Resource group |
A name of the resource group that is used for the transaction |
Username |
A name of the user who started the transaction |
Started |
A transaction start timestamp in the |
Tags |
The transaction tags |
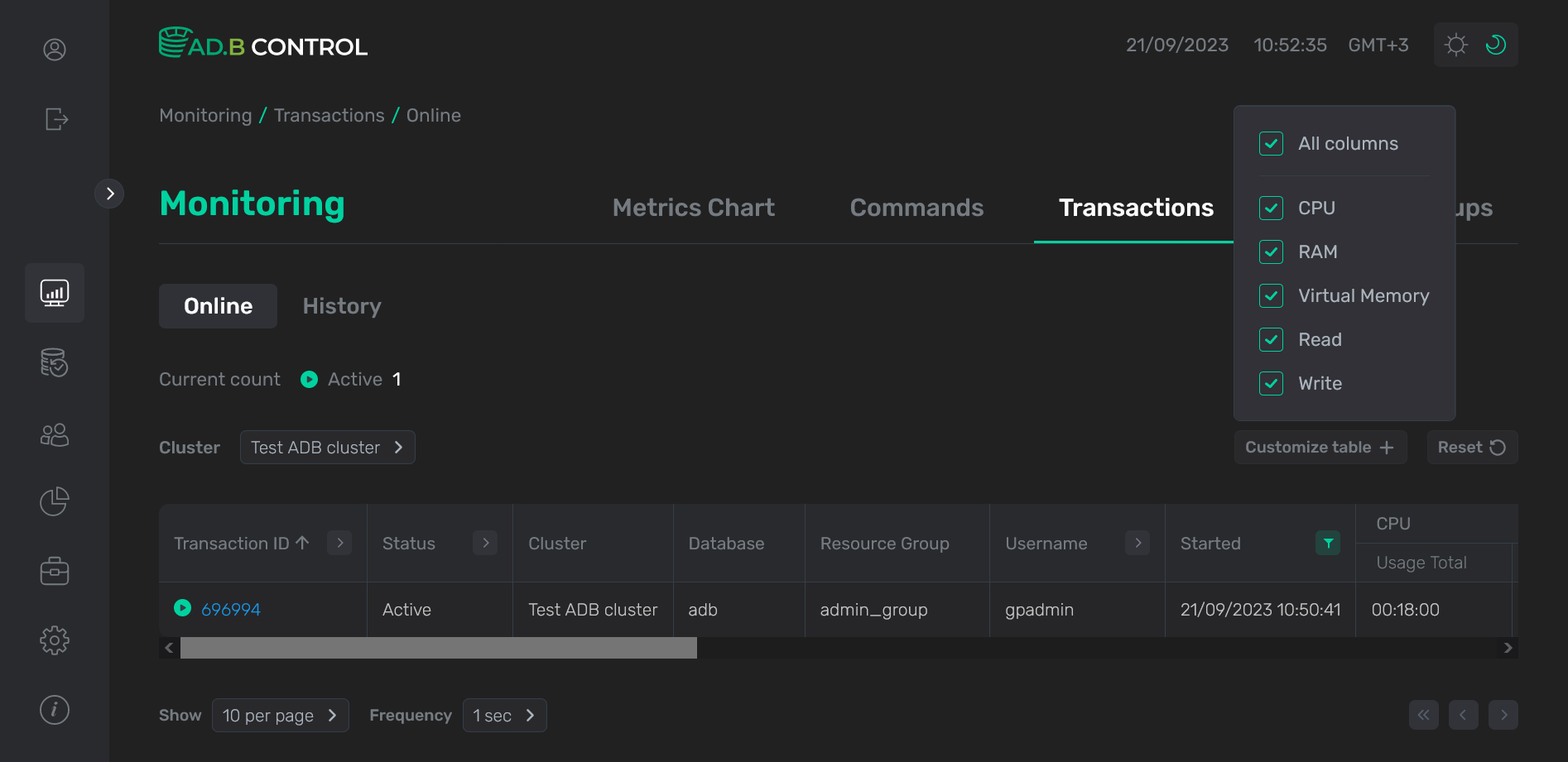
If necessary, you can add columns to the table. To do this, click Customize table and select column names in the section that opens. Currently you can add system metrics that are described below.
Above the table with a list of transactions, the Cluster filter is located. You can use this filter to select the ADB cluster and its databases for which you want to display data in the table. Initially all databases of the default cluster are selected.
In the column headers of the table with a list of transactions,
there are filters that you can use to select specific data. To open a filter, click the
icon. For those columns where the set of possible values is limited (e.g. Status), you can select a value from the drop-down list.
For some columns (e.g. Username), the search value should be entered.
For columns that show date and time (e.g. Started), the time range can be selected from the calendar.
The
icon means that a filter is defined for the column. To reset all filters, click Reset.
History
The Monitoring → Transactions → History tab displays transactions in the following statuses:
-
Committed— successfully completed transactions. -
Aborted— cancelled/terminated transactions. -
Unknown— the transactions, the final status of which is undefined. It is set on a timeout for transactions in theActivestatus, for which there are no corresponding rows in thepg_stat_activityview.
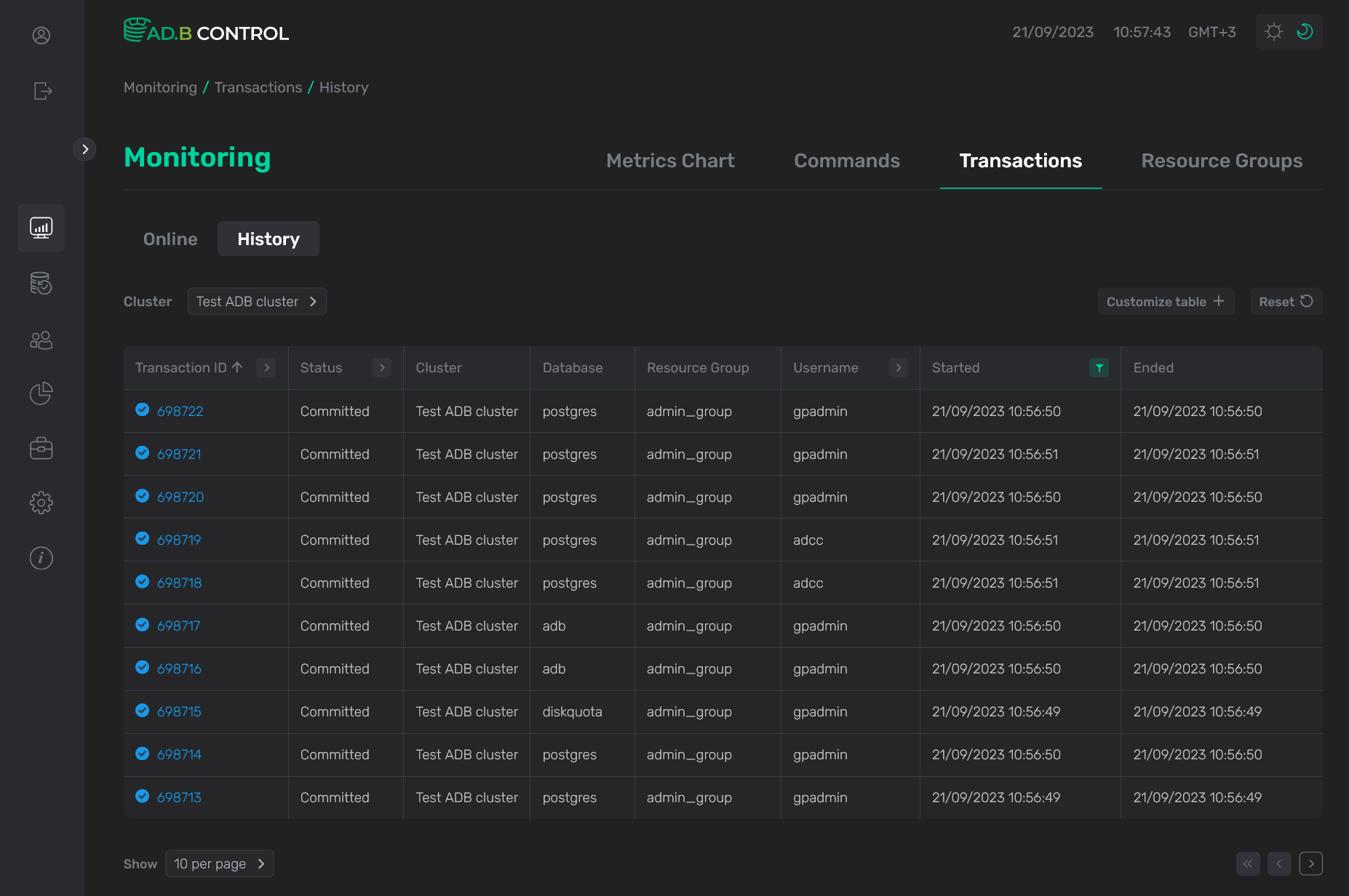
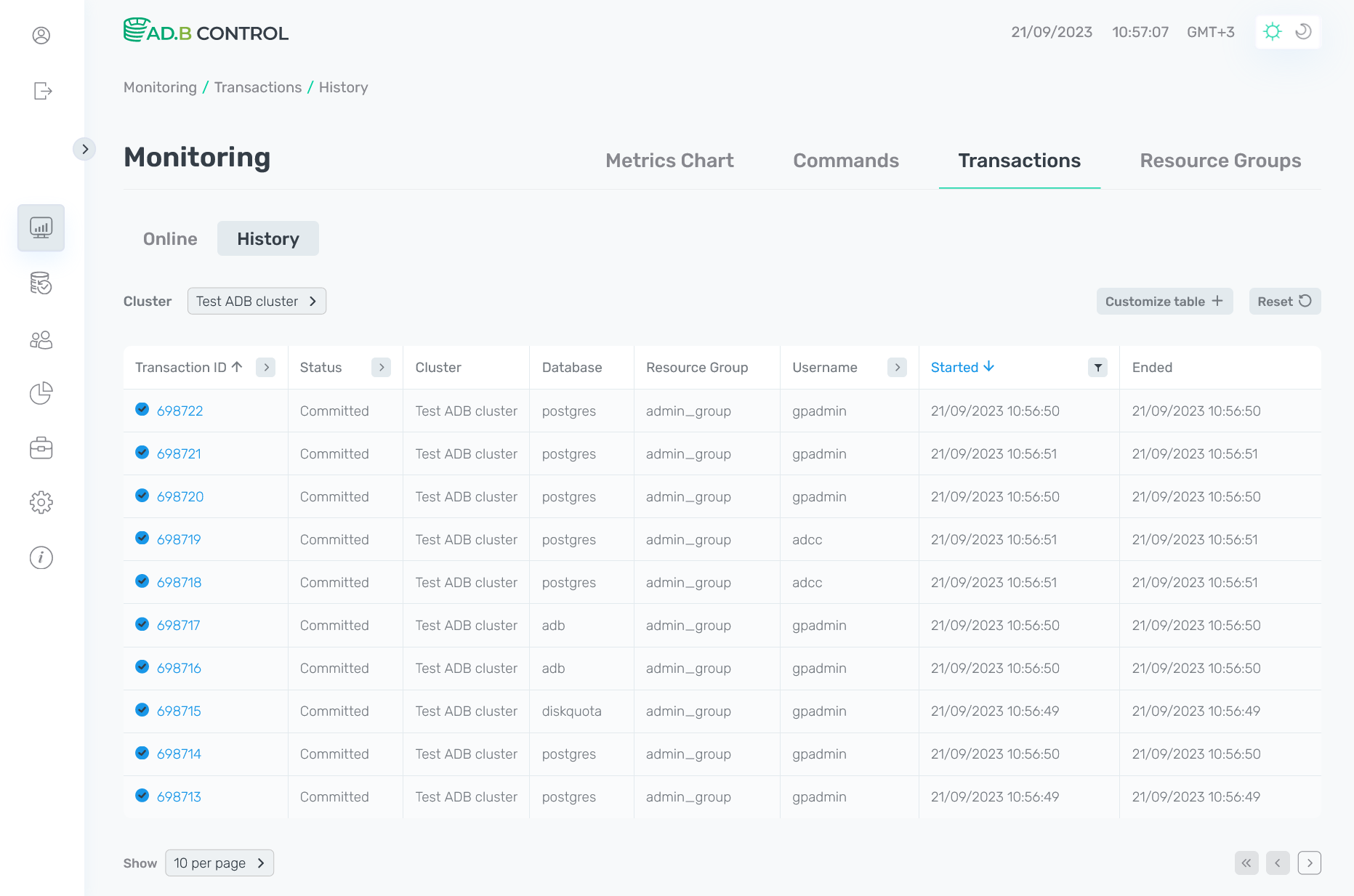
Most of the fields in the table with the list of transactions on the History tab match the fields that are described above for the Online tab. Only one new field is enabled — Ended, which displays a transaction end timestamp in the DD/MM/YYYY HH:mm:ss format. The field is filled in both as a result of successful execution and in case of error or cancellation.
Like on the Online tab, you have the ability to add additional columns to the table by clicking Customize table.
Transaction details
To view the transaction details, click the transaction identifier (Transaction ID) in the table on the Monitoring → Transactions → Online or Monitoring → Transactions → History tab.
The following page contains multiple sections that are described below.
Header
At the top of the page, the following information is displayed:
-
The transaction unique identifier (see Transaction ID above). In the example below —
696994. -
The transaction status (see Status above). In the example below —
Active. -
The complex transaction identifier (in the example below —
1695219736-11866-12-7156—209077013), which includes:-
cluster start timestamp;
-
session number;
-
transaction number within the current session;
-
the
lxidtransaction identifier on coordinator; -
hash code based on the cluster name (can be negative).
-
-
Run time — the transaction duration in hours, minutes, seconds.
-
The Cancel and Terminate buttons, which you can use to cancel/terminate transactions. For more information, see Cancel or terminate a transaction.


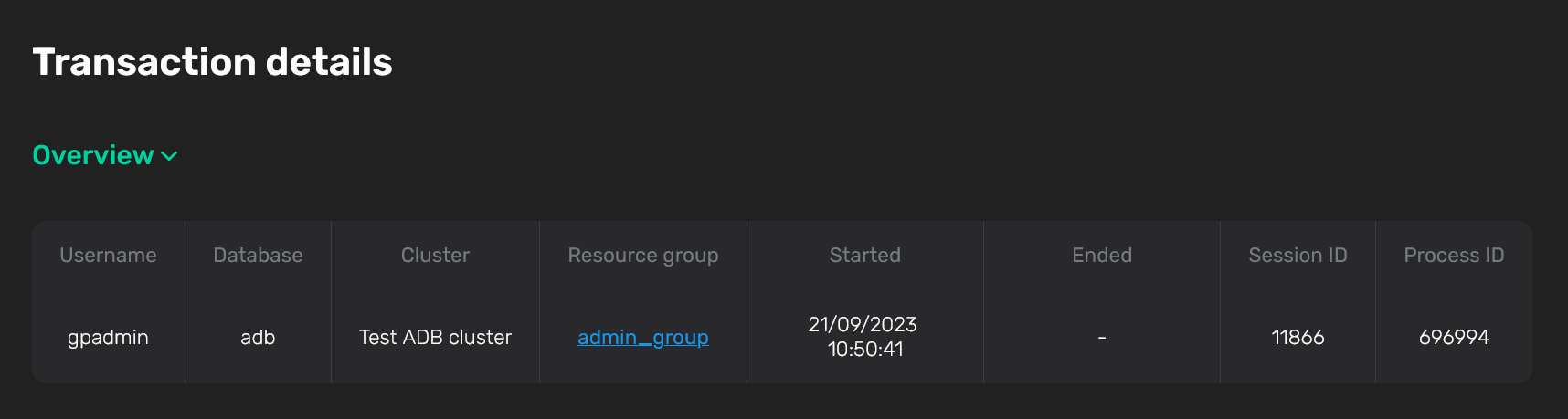
Overview
The Overview section displays the general transaction information. In addition to the fields mentioned above, the following information is available:
-
Ended — the transaction end timestamp in the
DD/MM/YYYY HH:mm:ssformat. For active transactions, the field contains-. -
Session ID — an identifier of the session, within which the transaction was started.
-
Process ID — an identifier of the process, within which the transaction was started.
Performance
The Performance section displays the statistics of system resource consumption by the selected transaction. The metrics available for monitoring are listed in System metrics collected for transactions.
At the top of the Performance section, the current and average metric values with skews for all cluster segments are displayed.
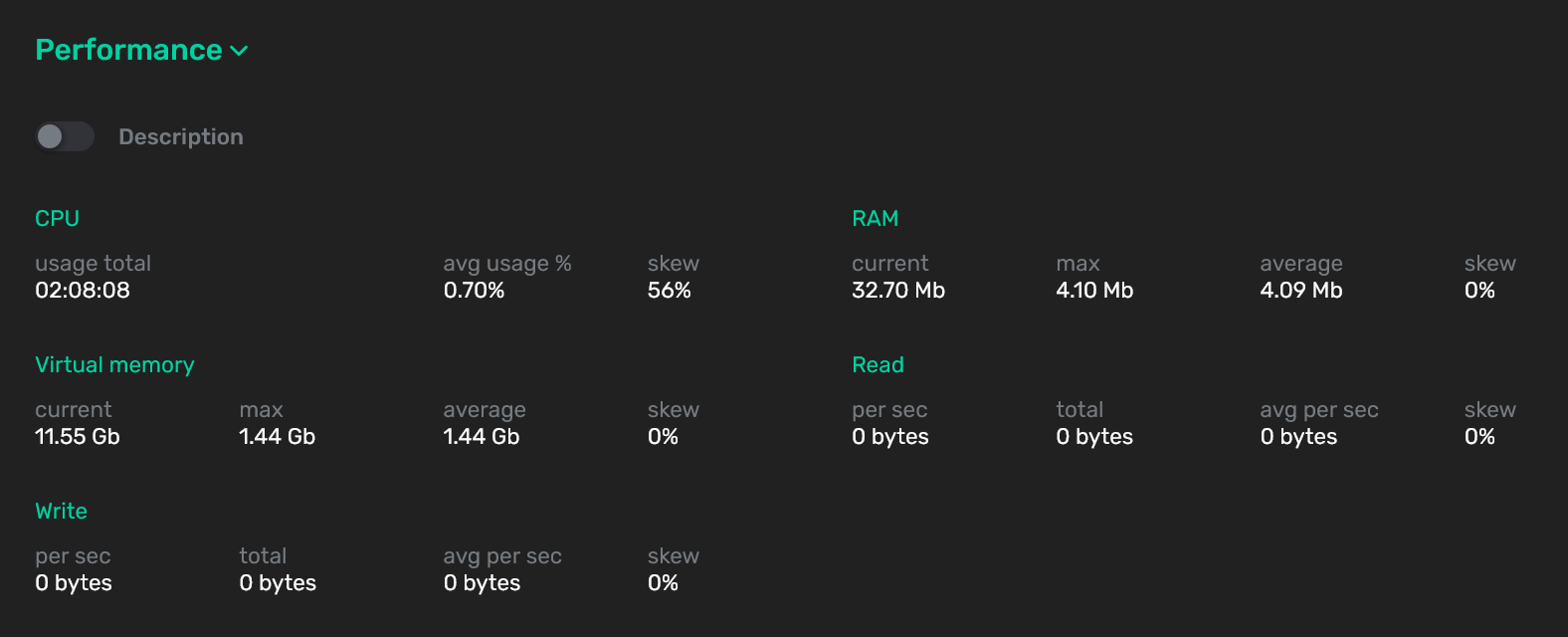

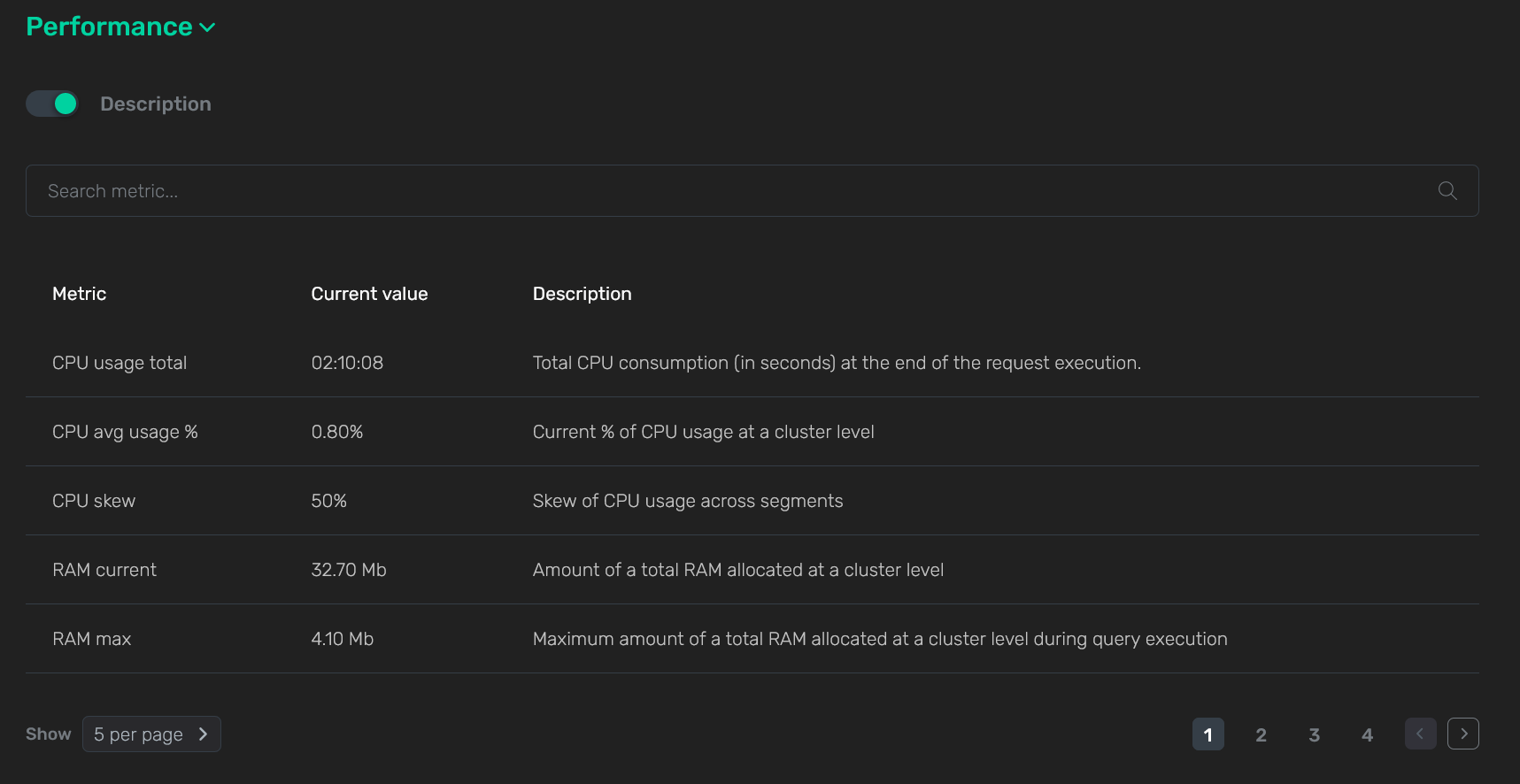
You can select an alternative display of metrics by activating the switcher that is located under the Performance section. The result is a table where not only the current value but also a detailed description is displayed for each metric.
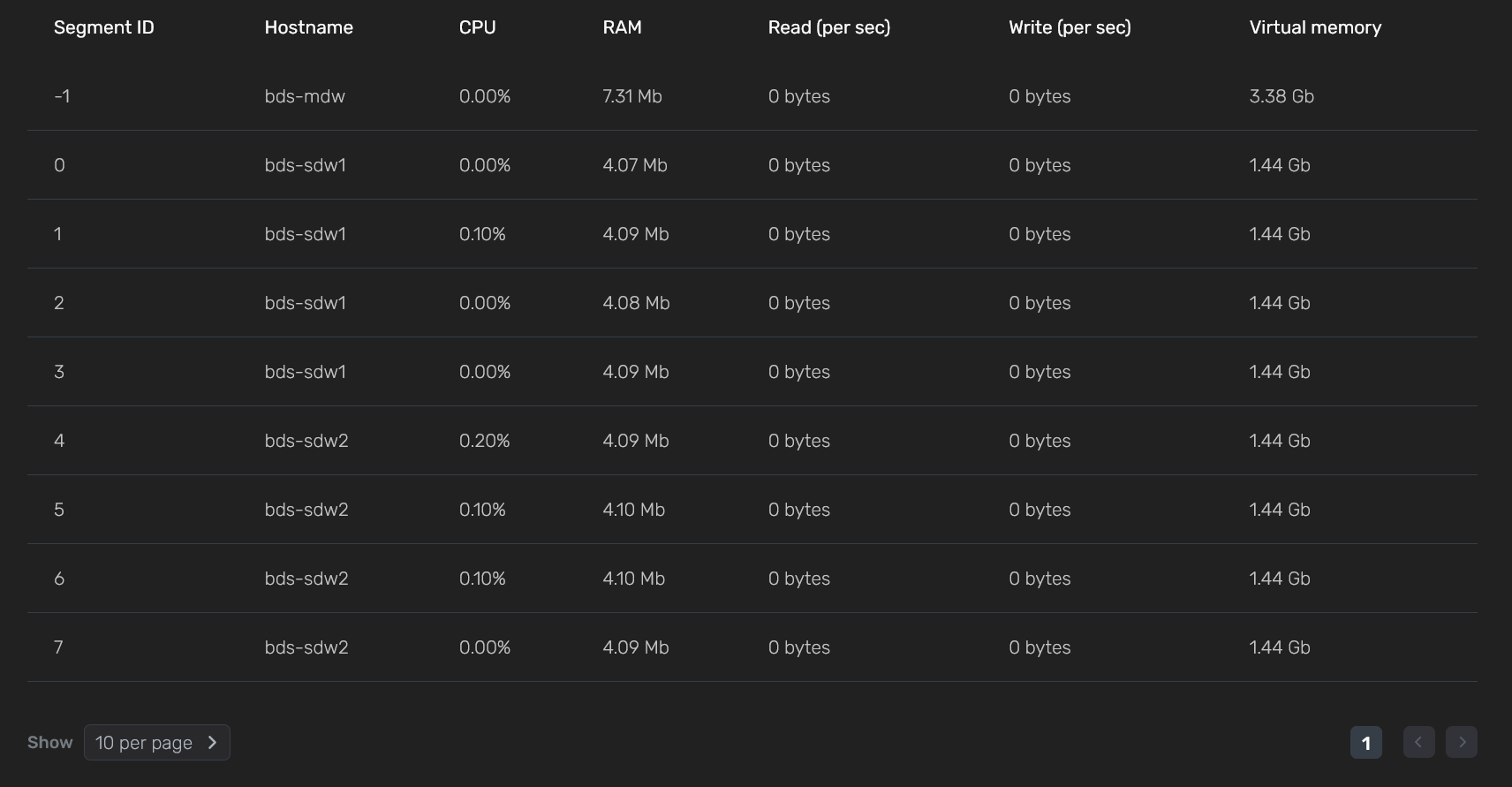
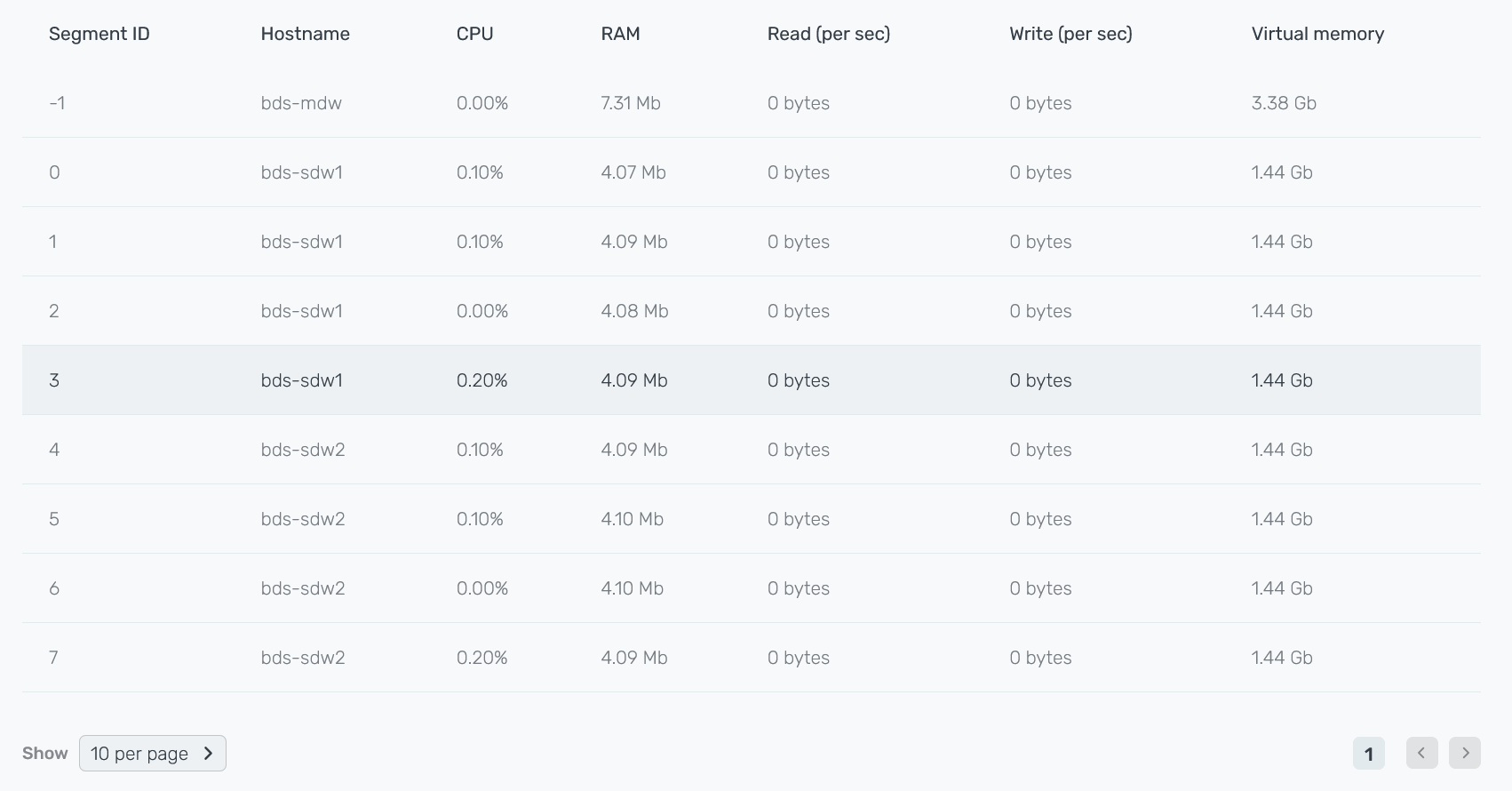
In the bottom part of the Performance section, the metric values are shown separately for each cluster segment, including the coordinator segment seg-1 (where Segment ID equals to -1).
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Segment ID |
A content identifier for a segment instance. Corresponds to |
Hostname |
A host name |
CPU |
The amount of CPU consumed by the segment (percentage). Based on the metric values for all segments, the average value CPU avg usage % is calculated |
RAM |
The amount of RAM consumed by the segment (in bytes). Based on the metric values for all segments, the average value RAM average is calculated |
Read (per sec) |
The amount of data read per second by the segment (in bytes). Based on the metric values for all segments, the average value Read avg per sec is calculated |
Write (per sec) |
The amount of data written per second by the segment (in bytes). Based on the metric values for all segments, the average value Write avg per sec is calculated |
Virtual memory |
The amount of virtual memory allocated by the segment (in bytes). Based on the metric values for all segments, the average value Virtual memory average is calculated |
|
IMPORTANT
System metrics are collected from ADB segments by ADB Control agents only for transactions longer than 15 seconds. Due to this fact, the section with metrics will be empty for the transactions that complete faster. |
Commands
The Commands section lists the commands that are performed within the current transaction.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Command ID |
A unique command identifier, which includes:
To open the page with command details, click the command identifier |
SQL ID |
A common identifier for SQL commands with the same structure |
Command text |
The first symbols of a command text. To view the full text (in case of long queries), hover the mouse over the field value |
CCNT |
A command number within the current session |
Status |
A command status. Possible values:
|
Planner |
A name of the query optimizer that is used to produce the query execution plan. Possible values:
|
Resource group |
A name of the resource group that is used for the command |
Run time |
A command duration in hours, minutes, seconds |
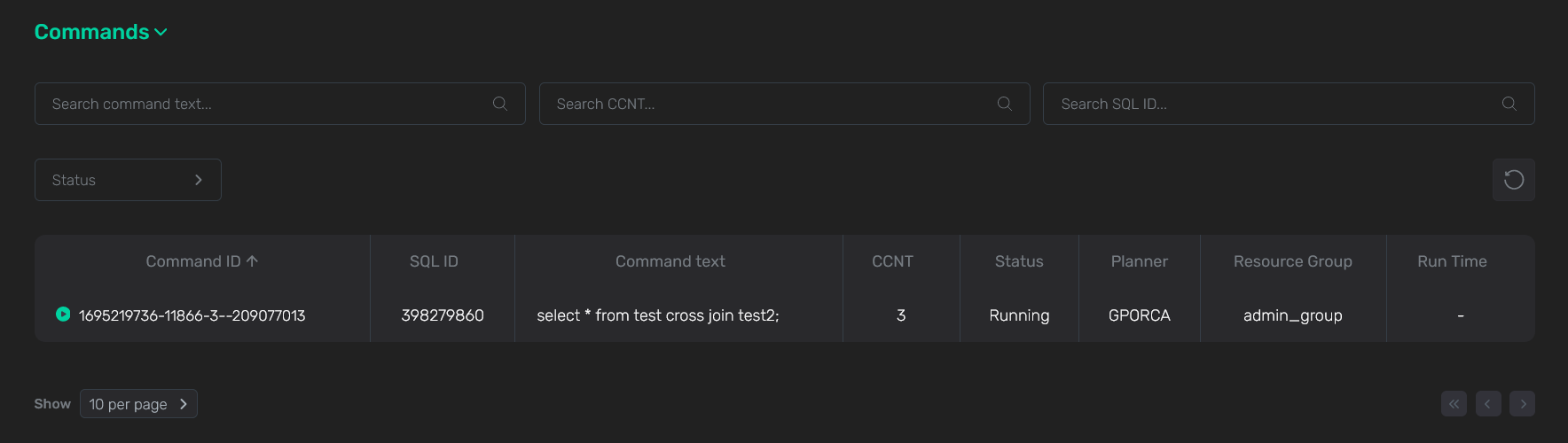
Above the table with commands, there are filters that you can use to select specific data:
-
Search command text… — filter by the command text (see Command text above). You can search by any substring of the SQL command.
-
Search CCNT… — filter by the command number within a session (see CCNT above). Enter a full value.
-
Search SQL ID… — filter by the identifier that is common for SQL commands with the same structure (see SQL ID above). Enter a full value.
-
Status — filter by the command status (see Status above). Select a value from the drop-down list.
Cancel or terminate the transaction
On the page with transaction details, you can cancel a transaction by clicking one of the following buttons:
-
Cancel — calls the
pg_cancel_backendfunction, which cancels a transaction in the process. -
Terminate — calls the
pg_terminate_backendfunction, which terminates the process within which the transaction is running.
After clicking the button, confirm the operation.
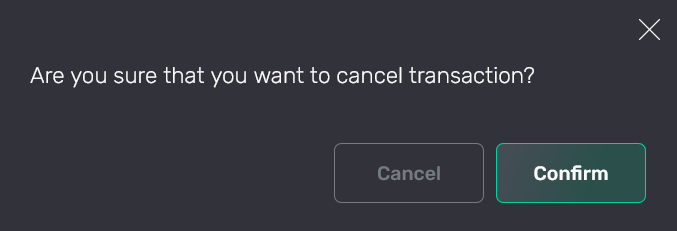
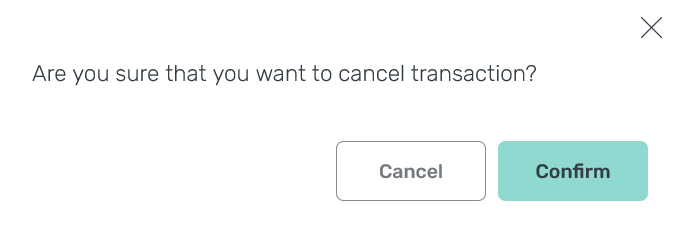
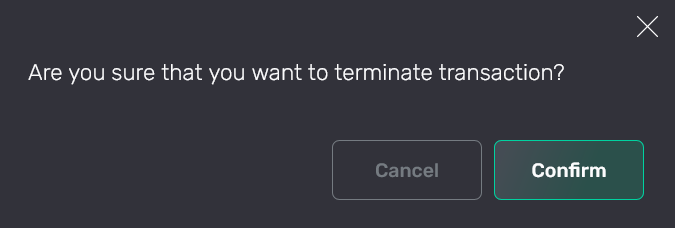
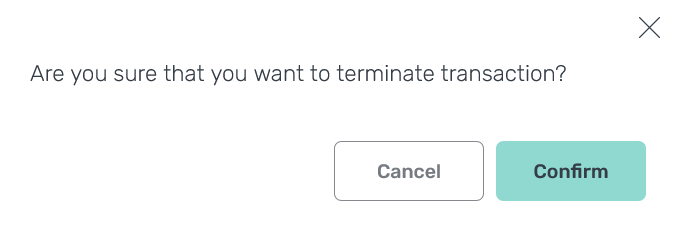
After a transaction is cancelled or terminated, it acquires the Aborted status, whereas all transaction commands get the Cancelled status.
|
IMPORTANT
|
System metrics collected for transactions
Both Online and History tabs allow you to view the statistics of the system resource consumption by transactions (on the Performance tab in the transaction details). The metrics available for transactions are listed below.
|
NOTE
The Online tab displays current metric values, whereas the History tab shows metric values at the end of the transaction execution. |
| Group | Metric | Description |
|---|---|---|
CPU |
CPU usage total |
The total CPU consumption across cluster segments (in seconds) |
CPU avg usage % |
The CPU percent average for all segment processes executing the query. Calculated as the result of dividing the total CPU consumption on all cluster segments (excluding the coordinator and standby) by the total number of processes processing the query on segment hosts (excluding the coordinator and standby) |
|
CPU skew |
The indicator that displays the CPU consumption skew across cluster segments (percentage). A value other than zero indicates that one of the segments uses more CPU than others |
|
RAM |
RAM current |
The current amount of RAM consumed at the cluster level (in bytes) |
RAM max |
The maximum amount of RAM consumed at the cluster level during the transaction execution (in bytes) |
|
RAM average |
The average amount of RAM consumed across cluster segments (in bytes). The RAM consumption at any given moment is calculated based on the operating system metric rss (Resident Set Size) |
|
RAM skew |
The indicator that displays the RAM consumption skew across cluster segments (percentage). A value other than zero indicates that one of the segments uses more RAM than others |
|
Virtual memory |
Virtual memory current |
The current amount of virtual memory allocated at the cluster level (in bytes) |
Virtual memory max |
The maximum amount of virtual memory allocated at the cluster level during the transaction execution (in bytes) |
|
Virtual memory average |
The average amount of virtual memory allocated across cluster segments (in bytes). The virtual memory consumption at any given moment is calculated based on the operating system metric vsize (Virtual Memory Size) |
|
Virtual memory skew |
The indicator that displays the virtual memory skew across cluster segments (percentage). A value other than zero indicates that one of the segments uses more virtual memory than others |
|
Read |
Read per sec |
The current amount of data read per second at the cluster level (in bytes) |
Read total |
The total amount of data read across cluster segments (in bytes). The following formula is used for calculation: |
|
Read avg per sec |
The average amount of data read across cluster segments per second (in bytes). The data read rate at any given moment is calculated based on the I/O Read information from /proc/[pid]/stat as a delta between the current and previous values |
|
Read skew |
The indicator that displays the data reading skew across cluster segments (percentage). A value other than zero indicates that one of the segments reads more data from a disk than others |
|
Write |
Write per sec |
The current amount of data written per second at the cluster level (in bytes) |
Write total |
The total amount of data written across cluster segments (in bytes). The following formula is used for calculation: |
|
Write avg per sec |
The average amount of data written across cluster segments per second (in bytes). The data write rate at any given moment is calculated based on the I/O Write information from /proc/[pid]/stat as a delta between the current and previous values |
|
Write skew |
The indicator that displays the data writing skew across cluster segments (percentage). A value other than zero indicates that one of the segments writes more data to a disk than others |