

Configuration parameters
This article describes the parameters that can be configured for ADPG services via ADCM. To read about the configuring process, refer to the relevant article Configure services.
|
NOTE
Some of the parameters become visible in the ADCM UI after the Show advanced flag being set.
|
ADPG
| Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
Data directory |
Directory that is used to store data on the ADPG hosts. The parameter’s value can be changed only before installation of the ADPG service |
/pg_data1 |
Sysctl parameters
This section describes Linux kernel parameters. To add a new parameter, click the child node Add property of the Sysctl parameters [key:value] option.
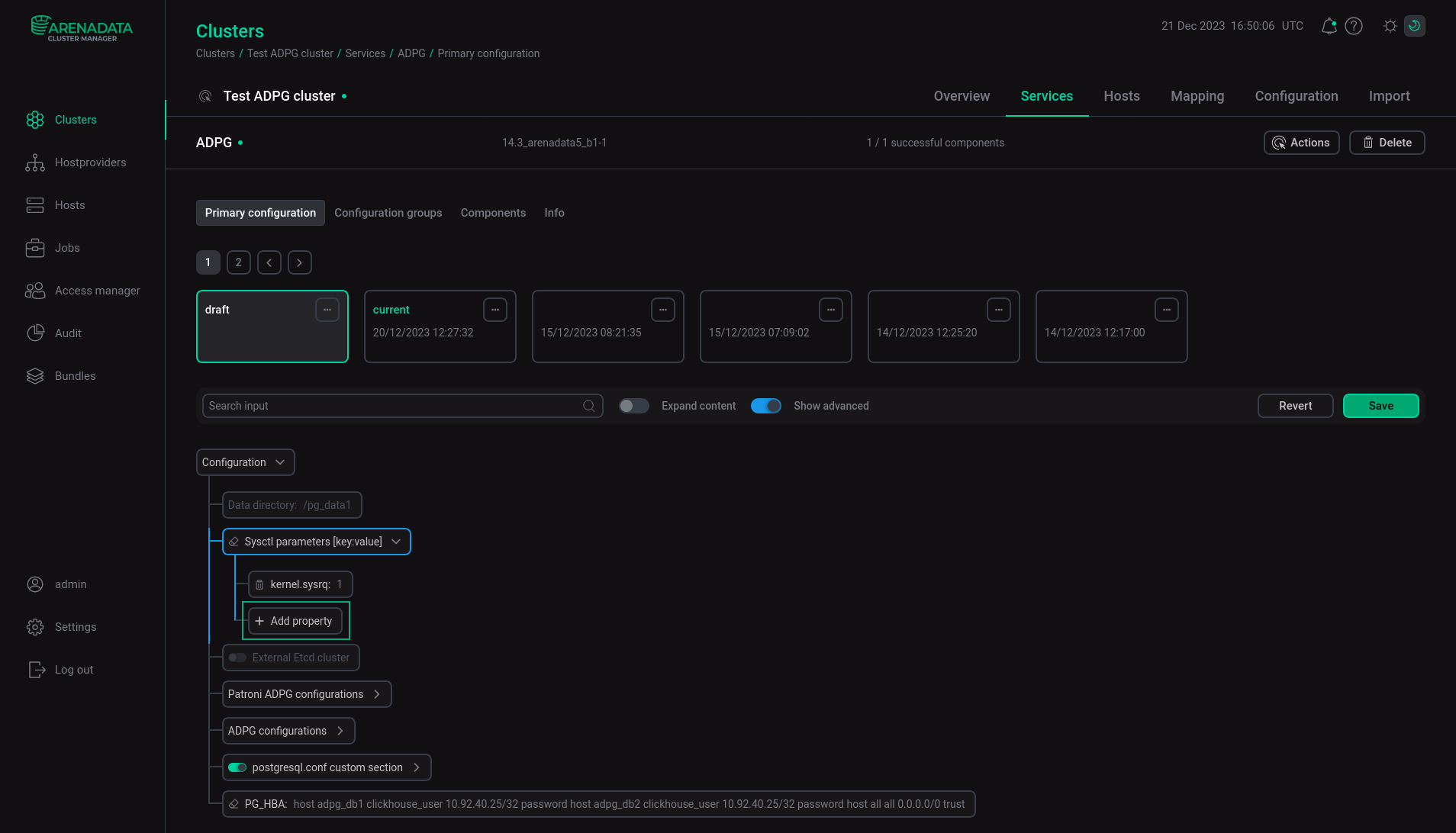
In the window that appears, specify the parameter name and value and click Apply.
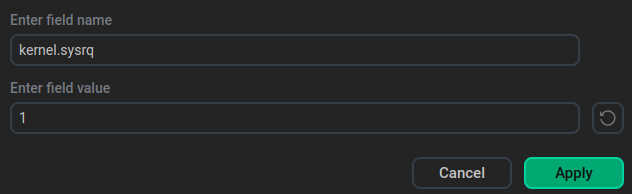
You can add multiple parameters.
External Etcd cluster
ADPG uses etcd as the Patroni Distributed Configuration Store (DCS). If you use an external etcd cluster, switch on the corresponding toggle button, expand the External Etcd [ip_address:port] node, and click Add property.
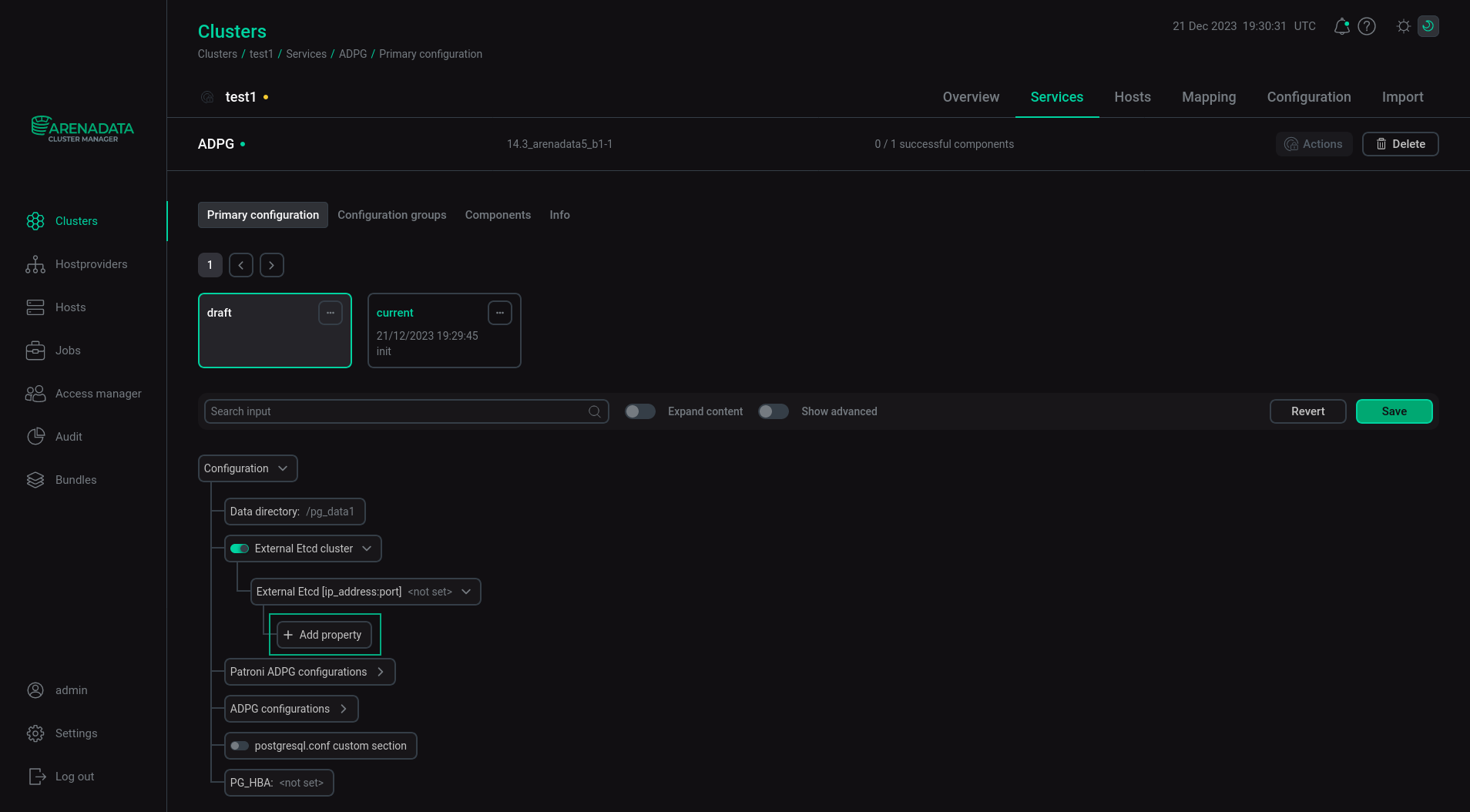
In the window that appears, specify the IP address of the etcd server in the first row and the port in the second row.
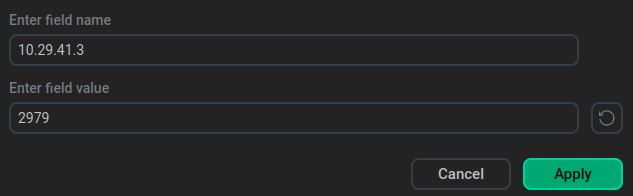
You can add multiple external etcd servers.
Enable PgBouncer
To use PgBouncer, switch on the Enable PgBouncer toggle button. When this toggle button is enabled, you can expand the corresponding node and specify settings listed in the table below.
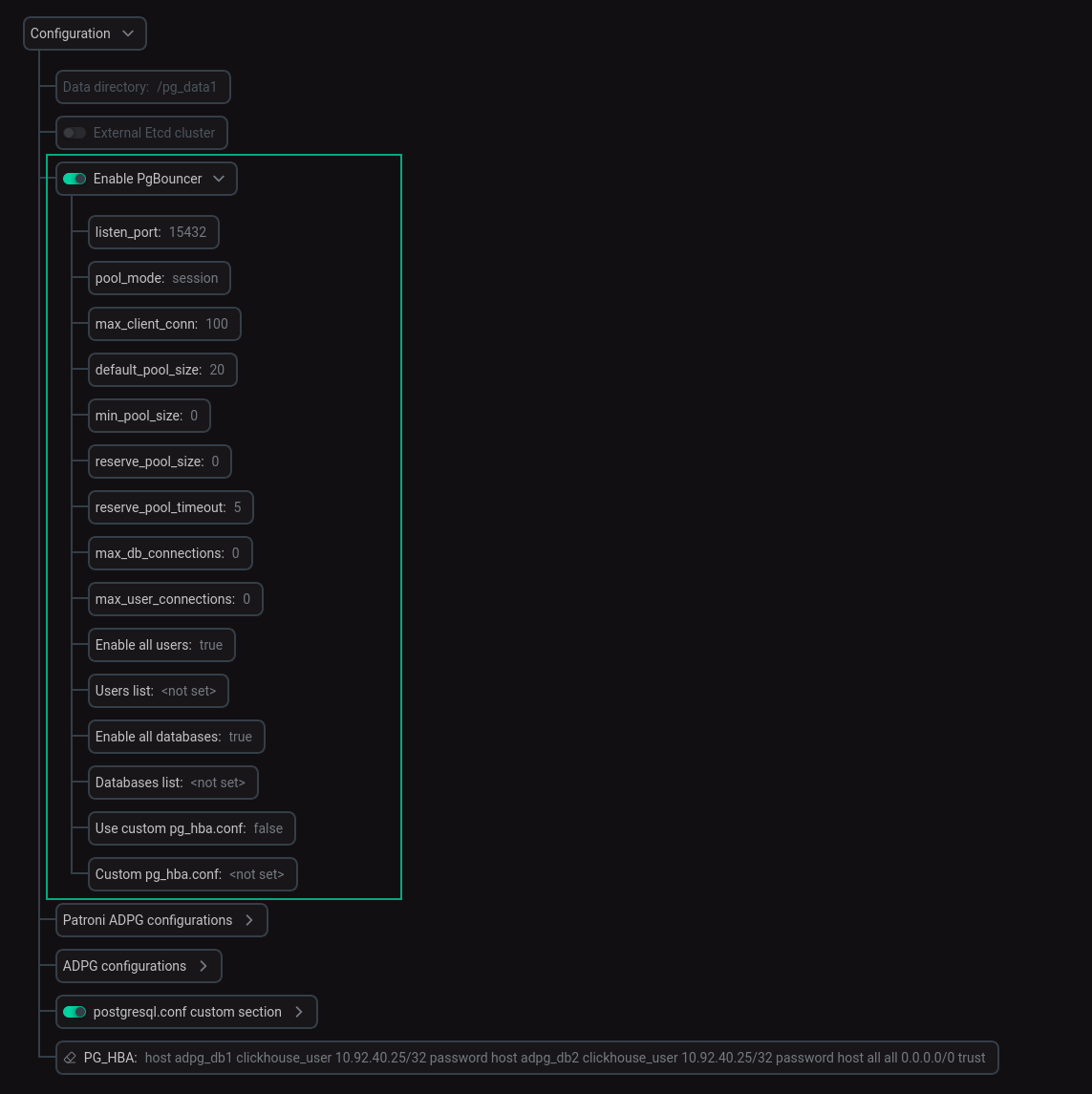
| Parameter name | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
listen_port |
The port that PgBouncer listens on. This port cannot be changed for a running cluster |
15432 |
pool_mode |
Specifies when a server connection can be reused by other clients. It can contain the following values:
|
session |
max_client_conn |
The maximum number of client connections allowed |
100 |
default_pool_size |
The number of connections to the server that are allowed for each user/database pair |
20 |
min_pool_size |
The minimum number of connections to the server to keep in the pool |
0 |
reserve_pool_size |
The number of additional connections allowed to the pool if a client connection exceeds the time specified in the |
0 |
reserve_pool_timeout |
If a client needs to wait longer than the specified time in seconds, additional connections from |
5 |
max_db_connections |
The maximum number of connections to a server for a database |
0 |
max_user_connections |
The maximum number of connections to a server for a user |
0 |
Enable all users |
When enabled, this option allows access to all users with password authentication. If the option is disabled, utilize |
Enabled |
Users list |
List of users who are allowed to access ADPG using PgBouncer, when the |
Empty |
Enable all databases |
When enabled, this option allows access to all existing databases with PgBouncer. If the option is disabled, utilize |
|
Databases list |
List of databases that are allowed to access using PgBouncer when the |
Empty |
Use custom pg_hba.conf |
When disabled, the general PG_HBA section of the ADPG service will be used for PgBouncer. If the option is enabled, it is necessary to add required settings to Custom pg_hba.conf. In this case, PgBouncer will use settings from Custom pg_hba.conf |
Disabled |
Custom pg_hba.conf |
Custom pg_hba.conf section for PgBouncer |
Empty |
After you specify required settings, click Save and execute the Reconfigure & Restart action to apply changes.
Enable backups
|
IMPORTANT
|
To enable creating backups, switch on the Enable backups toggle button. When this toggle button is enabled, you can expand the corresponding node and specify settings listed in the table below. Note that the S3 options only have an effect if Repo type is set to s3.
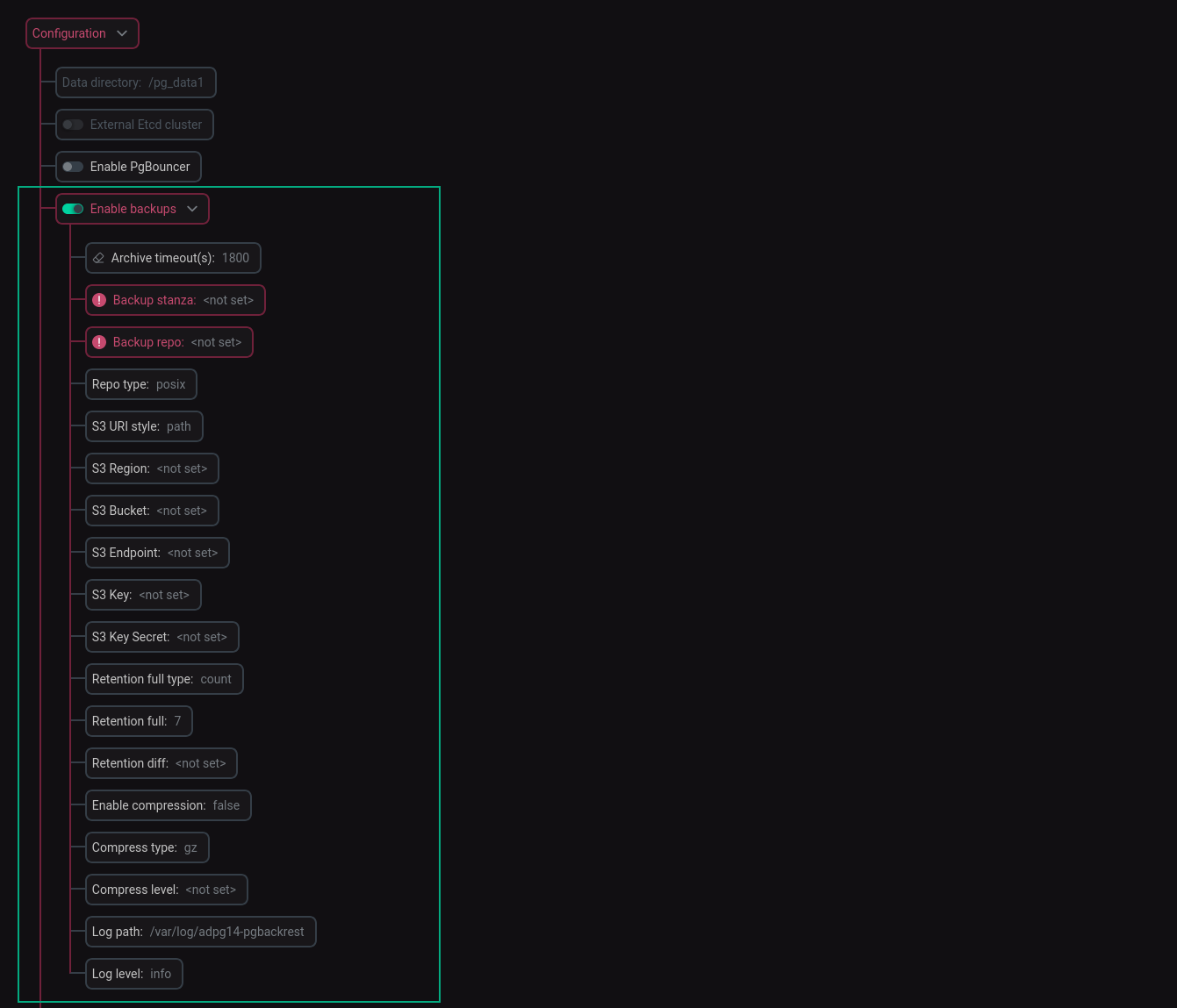
| Parameter name | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
Archive timeout(s) |
The amount of time (in seconds) to wait before forcing a switch to the next WAL file |
1800 |
Backup stanza |
The name of the current stanza. The stanza is created with the specified name and the added prefix: |
— |
Backup repo |
The path to the repository where |
— |
Repo type |
A storage type. You can use the following values:
|
posix |
S3 URI style |
An S3 URI style. The following URI styles are supported:
|
path |
S3 Region |
An S3 repository region where the bucket was created |
— |
S3 Bucket |
An S3 bucket used to store the repository with backups |
— |
S3 Endpoint |
An S3 repository endpoint. The endpoint should be valid for the specified region |
— |
S3 Key |
An S3 repository access key used to access the bucket |
— |
S3 Key Secret |
An S3 repository secret access key used to access this bucket |
— |
Retention full type |
It is possible to choose whether a time (days) or a number will be used to determine which backups are expired.
|
count |
Retention full |
A number of full backups to retain or the number of days to keep each full backup depending on |
7 |
Retention diff |
A number of differential backups to retain |
— |
Enable compression |
Enables the backup compression |
false |
Compress type |
A backup compress type. You can use one of the following values: |
gz |
Compress level |
A file compression level (from |
The following default compression levels are used based on
|
Log path |
A path to the directory with log files |
/var/log/adpg16-pgbackrest |
Log level |
A logging level of messages written to log files. Possible values are: |
info |
Use custom config |
If checked, all the |
false |
Global options |
Settings to add to the |
— |
Custom options |
Settings to add to the |
— |
|
NOTE
If you check Use custom config and specify custom pgBackRest settings, ADPG writes these settings to the pgBackRest configuration file without checking. In case of incorrect settings, an error message will not be displayed in the ADCM UI. You need to verify the settings and check if the directory for storing backups exists and is accessible by yourself.
|
For more information, see Backup and restore using pgBackRest.
Enable Patroni basic auth
To enable Patroni basic auth for Patroni REST API, switch on the Enable Patroni basic auth toggle button. When this toggle button is enabled, you can expand the corresponding node and specify settings listed in the table below.
| Parameter name | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
username |
Basic-auth username ( |
— |
password |
Basic-auth password ( |
— |
If you enable Patroni basic auth for an existing cluster, run the Reconfigure & Restart action of the ADPG service.
After enabling Patroni basic auth, unsafe (POST) calls to Patroni are authenticated, but safe (GET) calls will be processed without authentication.
Patroni ADPG configurations
This section describes Patroni configuration settings that can be changed in ADCM UI. For more information on these settings, refer to ADPG High Availability overview. After you specify parameter values, execute the Reconfigure & Restart action of the ADPG service to apply changes.
| Parameter name | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
synchronous_mode |
Enables Patroni synchronous mode |
false |
synchronous_node_count |
Specifies the number of synchronous standby nodes. The parameter value should not be more than the count of hosts with the ADPG component of the ADPG service installed on. This parameter is ignored if |
1 |
synchronous_mode_strict |
Prevents Patroni from switching off the synchronous replication on the primary when no synchronous standby candidates are available. Enables |
false |
maximum_lag_on_failover |
Specifies the amount of transactions in bytes that can be lost |
1048576 |
ttl |
The TTL to acquire the leader lock (in seconds). It defines the length of time before initiation of the automatic failover process |
30 |
loop_wait |
The time that Patroni waits (sleeps) before starting a new loop iteration (in seconds) |
10 |
retry_timeout |
The timeout for DCS and PostgreSQL operation retries (in seconds). DCS or network issues shorter than this value do not cause Patroni to demote the leader |
10 |
patroni_listen_port |
The port that Patroni listens to for the REST API. Can only be changed before the ADPG service installation |
8008 |
use_custom_patroni_log_dir |
When enabled, you can specify custom logging settings for Patroni |
false |
patroni_log_dir |
An existing folder to store Patroni logs. The parameter only has an effect if |
/var/log/adpg16-patroni |
patroni_log_file_size |
The size limit of a single Patroni log file, in bytes. The parameter only has an effect if |
25000000 |
patroni_log_file_num |
The number of log files to retain. The parameter only has an effect if |
4 |
patroni_log_level |
The level of logging. It can contain the following values: |
info |
Patroni ADPG tags
The Patroni ADPG tags section allows you to utilize Patroni tags. It becomes visible in the ADCM UI after the Show advanced toggle button is activated. Use ADCM configuration groups to assign Patroni tags to individual hosts.
| Tag name | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
clonefrom |
If set to |
false |
noloadbalance |
If set to |
false |
replicatefrom |
The name of another replica to replicate from. Used to support cascading replication |
empty (the string type) |
nosync |
If set to |
false |
nofailover |
Controls whether this node is allowed to participate in the leader elections and become a leader. The default |
false |
failover_priority |
Controls the priority that a node has during failover. Nodes with higher priority will be preferred over lower-priority nodes if they received/replayed the same amount of WAL. However, nodes with higher values of receive/replay LSN are preferred regardless of their priority. If |
empty (the integer type) |
nostream |
If set to |
false |
ADPG configurations
The ADPG configurations section contains the postgresql.conf and Custom postgresql.conf nodes. Settings from the Custom postgresql.conf field have higher priority than settings from postgresql.conf and can be applied to certain hosts with the ADPG service using ADCM configuration groups.
postgresql.conf
The postgresql.conf text field allows you to specify the content of the postgresql.conf file (the default path is /pg_data1/adpg16/postgresql.conf). The configuration parameters set in this field will be applied to all ADPG nodes. To switch to editing mode, click postgresql.conf in the Configuration tree.
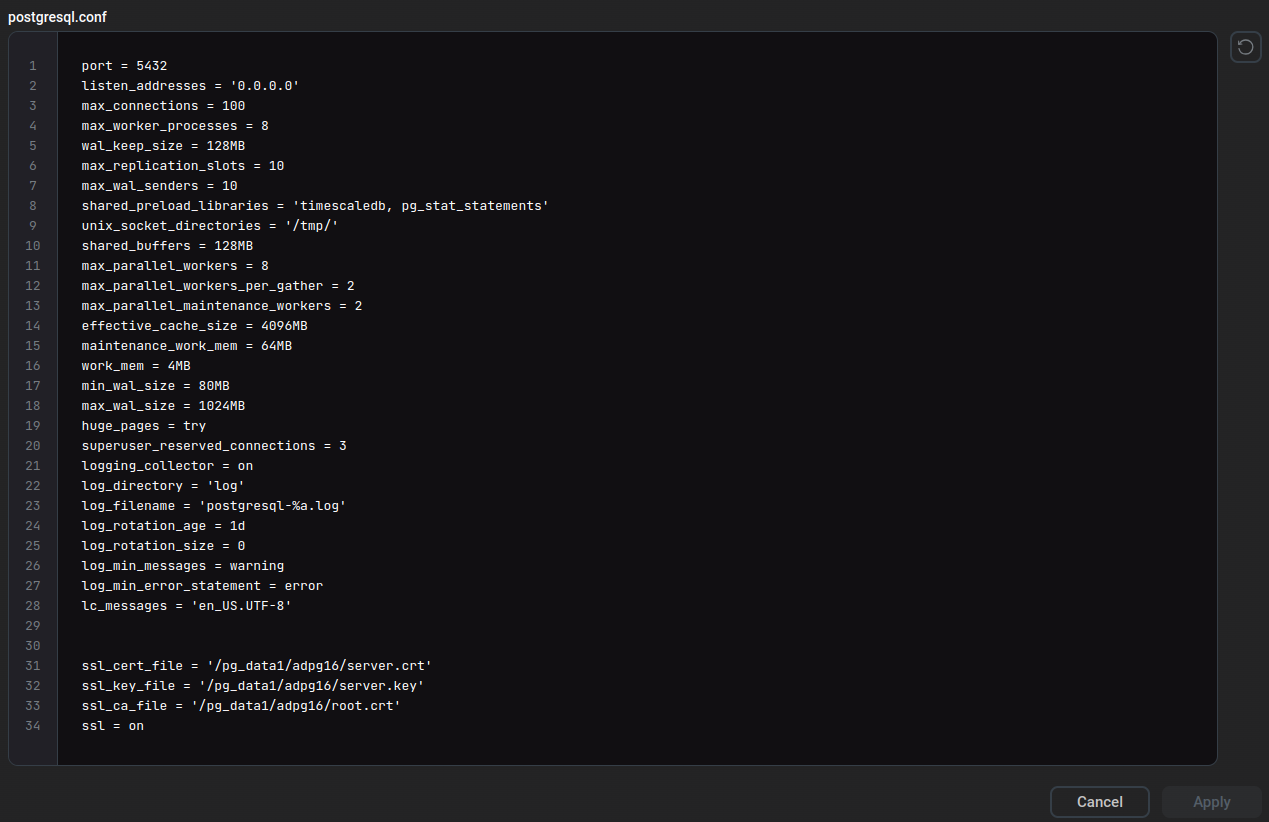
In the window that appears, specify the required parameters and click Apply.
It is necessary to use ADCM to edit the postgresql.conf file. When the ADPG service executes the Reconfigure & Restart action, postgresql.conf is rewritten with settings specified in the postgresql.conf field. If you make changes directly to postgresql.conf, these changes will be lost.
After modifying postgresql.conf, execute the Reconfigure & Restart action to apply changes.
The table below contains a description of some parameters that can be specified in postgresql.conf.
| Parameter name | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
port |
The TCP port the server listens on |
5432 |
max_connections |
Determines the maximum number of concurrent connections to the server. For a replica host, the value of this parameter should be greater than or equal to the value on the leader host. If this requirement is not met, the replica host will reject all requests |
100 |
shared_buffers |
Sets the amount of memory the server used for the shared memory buffer. The higher the value of this parameter, the less the load on the host hard drives will be |
128 MB |
max_worker_processes |
Sets the maximum number of background processes that the system can support |
8 |
max_parallel_workers |
Sets the maximum number of workers that the system can support for parallel operations |
8 |
max_parallel_workers_per_gather |
Sets the maximum number of workers that can be started by a single Gather or Gather Merge node |
2 |
max_parallel_maintenance_workers |
Sets the maximum number of parallel workers that can be started by a single utility command |
2 |
effective_cache_size |
Sets the planner’s assumption about the effective size of the disk cache that is available to a single query. This is taken into account when estimating the cost of using the index. A higher value makes it more likely index scans will be used, a lower value makes it more likely sequential scans will be applied. When setting this parameter, you should consider both PostgreSQL shared buffers and the portion of the kernel’s disk cache that will be used for PostgreSQL data files, though some data might exist in both places. Also, take into account the expected number of concurrent queries on different tables, since they will have to share the available space. This parameter does not affect the size of shared memory allocated by PostgreSQL, and it does not reserve kernel disk cache. It is used only for estimation purposes. The system also does not assume data remains in the disk cache between queries. If this value is specified without units, it is taken as blocks, that is |
4096 MB |
maintenance_work_mem |
Specifies the maximum amount of memory to be used by maintenance operations, such as |
64 MB |
work_mem |
Sets the base maximum amount of memory to be used by a query operation (such as a sort or hash table) before writing to temporary disk files. Note that for a complex query, several sort or hash operations might be running in parallel. Each operation will be allowed to use as much memory as this value specifies before it starts to write data into temporary files. Several running sessions can also do such operations concurrently. Therefore, the total memory used can be many times greater than the value of |
4 MB |
min_wal_size |
Until WAL disk usage stays below the |
80 MB |
max_wal_size |
Sets the memory limit to which the log size can grow between automatic checkpoints. Increasing this setting may increase the recovery time after a failure. The specified limit can be exceeded automatically with a high load on ADPG |
1024 MB |
wal_keep_size |
Sets the minimum size of segments retained in the pg_wal directory, in case a standby server needs to fetch them for streaming replication. If a standby server connected to the sending server falls behind by more than |
128 MB |
huge_pages |
Defines whether huge pages can be requested for the main shared memory area. The following values are valid:
|
try |
superuser_reserved_connections |
Determines the number of connection "slots" that are reserved for PostgreSQL superuser connections |
3 |
logging_collector |
Enables the logging collector. The logging collector is a background process that captures log messages sent to stderr and redirects them into log files |
The logging collector is enabled ( |
log_directory |
Determines the directory that contains log files. It can be specified as an absolute path, or relative to the cluster data directory |
log |
log_filename |
Specifies the log file name pattern. The value can include strftime %-escapes to define time-varying file names. If you specify a file name pattern without escapes, use a log rotation utility to save disk space |
postgresql-%a.log |
log_rotation_age |
Determines the maximum period of time to use a log file, after which a new log file is created. If this value is specified without units, it is taken as minutes. Set |
1d |
log_rotation_size |
Determines the maximum size of a log file. After a log file reaches the specified size, a new log file is created. If the value is set without units, it is taken as kilobytes. Set |
0 |
log_min_messages |
Specifies the minimum severity level of messages that are written to a log file. Valid values are |
warning |
log_min_error_statement |
Specifies which SQL statements that cause errors are logged. Valid values are |
error |
Custom postgresql.conf
You can use the Custom postgresql.conf field to set configuration parameters for specific ADPG nodes using ADCM configuration groups. The settings specified in this field have higher priority than the settings specified in postgresql.conf. To switch to editing mode, click Custom postgresql.conf in the Configuration tree.
In the window that appears, specify the required parameters and click Apply.
Note that some parameters must have the same values on leader and replica nodes according to the Patroni requirements. Specifying these parameters in the Custom postgresql.conf field has no effect. You can set their values only in the postgresql.conf field for all ADPG nodes simultaneously. These parameters and their default values are listed in the table below.
| Parameter name | Default value |
|---|---|
max_connections |
100 |
max_locks_per_transaction |
64 |
max_worker_processes |
8 |
max_prepared_transactions |
0 |
wal_level |
hot_standby |
track_commit_timestamp |
off |
max_wal_senders |
10 |
max_replication_slots |
10 |
wal_keep_segments |
8 |
wal_keep_size |
128 MB |
SSL configuration
The settings of this section are applied when SSL is enabled using the Manage SSL action. Its parameters are listed in the table below. Only the PG_HBA field is available for editing. Other settings are specified during the Manage SSL action.
| Parameter name | Description |
|---|---|
Enable SSL |
Read-only boolean field that indicates whether SSL is enabled via the Manage SSL action |
postgresql.conf |
Read-only field that contains SSL settings specified during the Manage SSL action |
PG_HBA |
Field to specify rules for SSL connections |
PG_HBA
The section allows you to add lines to the pg_hba.conf file. The pg_hba.conf file configures the client authentication.
ADPG Control Agents
Balancer
| Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
leader as replica |
Specifies if the leader handles read only transactions |
False |
leader_port |
Sets a port on the host with the HAProxy component for write transactions |
6432 |
replica_port |
Specifies a port on the host with the HAProxy component for read only transactions |
6433 |
balancer_stats_port |
Defines a port on which a web page with a HAProxy statistics report is available |
7000 |
pgbouncer_leader_port |
All connections to this port are transferred to a PgBouncer instance of an ADPG leader node |
16432 |
pgbouncer_replica_port |
All connections to this port are transferred to PgBouncer instances of ADPG replica nodes |
16433 |
balancer_global_maxconn |
Sets the maximum number of concurrent connections that HAProxy can process |
100 |
Chrony
| Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
NTP servers |
Addresses of valid NTP servers. For example, |
— |
Etcd
|
IMPORTANT
The listen_peer_urls_port and listen_client_urls_port Etcd configuration settings cannot be changed after installation.
|
| Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
listen_peer_urls_port |
Specifies the port for peer communication |
2380 |
listen_client_urls_port |
Specifies the port for client requests |
2379 |
Space quota(bytes) |
The maximum number of bytes the etcd db file can consume |
2147483648 |
Enable log compaction |
Enables etcd auto-compaction |
true |
Autocompaction mode |
Etcd autocompaction mode |
periodic |
Autocompaction retention |
Etcd autocompaction retention for mvcc key/value store in hour or revision number |
10h |
Monitoring
| Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
Listen port |
Port on the host with the Balancer service to retrieve HAProxy metrics in the Prometheus format |
8405 |
Metrics endpoint |
Endpoint on the host with the Balancer service to retrieve HAProxy metrics in the Prometheus format |
/metrics |
| Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
Listen port |
Port on the host with the ADPG service to retrieve connection pooler metrics in the Prometheus format |
9188 |
| Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
Listen port |
Port on the host with the ADPG service to retrieve PgBackRest metrics in the Prometheus format |
9854 |
Metrics endpoint |
Endpoint on the host with the ADPG service to retrieve PgBackRest metrics in the Prometheus format |
/metrics |
| Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
Listen port |
Port on the host with the ADPG service to retrieve PostgreSQL metrics in the Prometheus format |
9187 |
| Group | Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
— |
scrape_interval |
Specifies how frequently to scrape targets |
1m |
— |
scrape_timeout |
Specifies how long to wait until a scrape request times out |
10s |
— |
Password for Grafana connection |
A password of a Grafana user ( |
— |
— |
Prometheus users to login/logout to Prometheus |
User credentials for logging into the Prometheus web interface |
— |
Service parameters |
config.file |
Path to the Prometheus server configuration file |
/etc/admprom/prometheus/prometheus.yml |
storage.tsdb.path |
Path to the Prometheus server database |
/var/lib/admprom/prometheus |
|
web.console.libraries |
Path to console management libraries |
/usr/share/admprom/prometheus/console_libraries |
|
web.console.templates |
Path to Prometheus server console templates |
/usr/share/admprom/prometheus/consoles |
|
web.config.file |
Specifies which web configuration file to load. The file should have the YAML format |
/etc/admprom/prometheus/prometheus-auth.yml |
|
storage.tsdb.retention.time |
Specifies how long to retain samples in the storage. Supported units: |
15d |
|
web.listen-address |
Address to access the Prometheus web interface |
0.0.0.0:11200 |
| Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
Grafana administrator’s password |
Password of the Grafana |
— |
Grafana listen port |
Port to access the Grafana web interface |
11210 |
| Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
Listen port |
Port on the cluster’s host to access host system metrics in the Prometheus format |
11203 |
Metrics endpoint |
Endpoint on the cluster’s host to retrieve system metrics in the Prometheus format |
/metrics |