

Use Active Directory for Kerberos
Basic concepts used in Kerberos LDAP:
-
Active Directory — database and set of services that connect users to the necessary network resources.
-
LDAP server — hierarchical database, a directory service based on Active Directory, used for centralized storage of accounts. The credentials include principals used to validate users in Kerberos.
-
LDAP — application protocol for accessing the Active Directory directory service, used in cluster kerberization to establish user principals.
-
LDAPS — LDAP activation using the SSL/TLS protocol to create secure traffic. Creating passwords for ADQM users with accounts in Active Directory during cluster kerberization is only possible using LDAPS.
-
Key distribution center (KDC) — access control system component that provides access tickets and session keys to service user requests for access to resources. It uses Active Directory as the account database.
-
DN (distinguished name) — account in Active Directory. A DN must be unique within the tree. It describes the content of attributes in the tree (navigation path) for accessing a particular entry.
A DN consists of a series of RDN (Relative Distinguished Names) determined by moving up the tree in the direction of its root entry. RDNs are written from left to right.
Prepare Active Directory to run on an ADQM cluster
-
Set up an Active Directory server (LDAP server).
-
Create a user account to connect a cluster to the LDAP server using the LDAP protocol.
-
Generate a certificate for the user by enabling LDAP over SSL using a third-party CA.
-
Set a password for the account.
-
Assign a user principal name to the account (for example,
ad_admin@EXAMPLE.COM) and generate a keytab file with these principal and keys.
Start Active Directory on ADQM cluster
To kerberize a cluster using Active Directory, follow the steps below:
-
On the Clusters page of the ADCM interface, select the installed and prepared ADQM cluster.
-
Enable Kerberos for the cluster — click the Actions
icon and select the Manage Kerberos action.
 Manage Kerberos action
Manage Kerberos action -
Turn on the Existing Active Directory option and set Active Directory parameters according to settings specified when configuring the LDAP server.
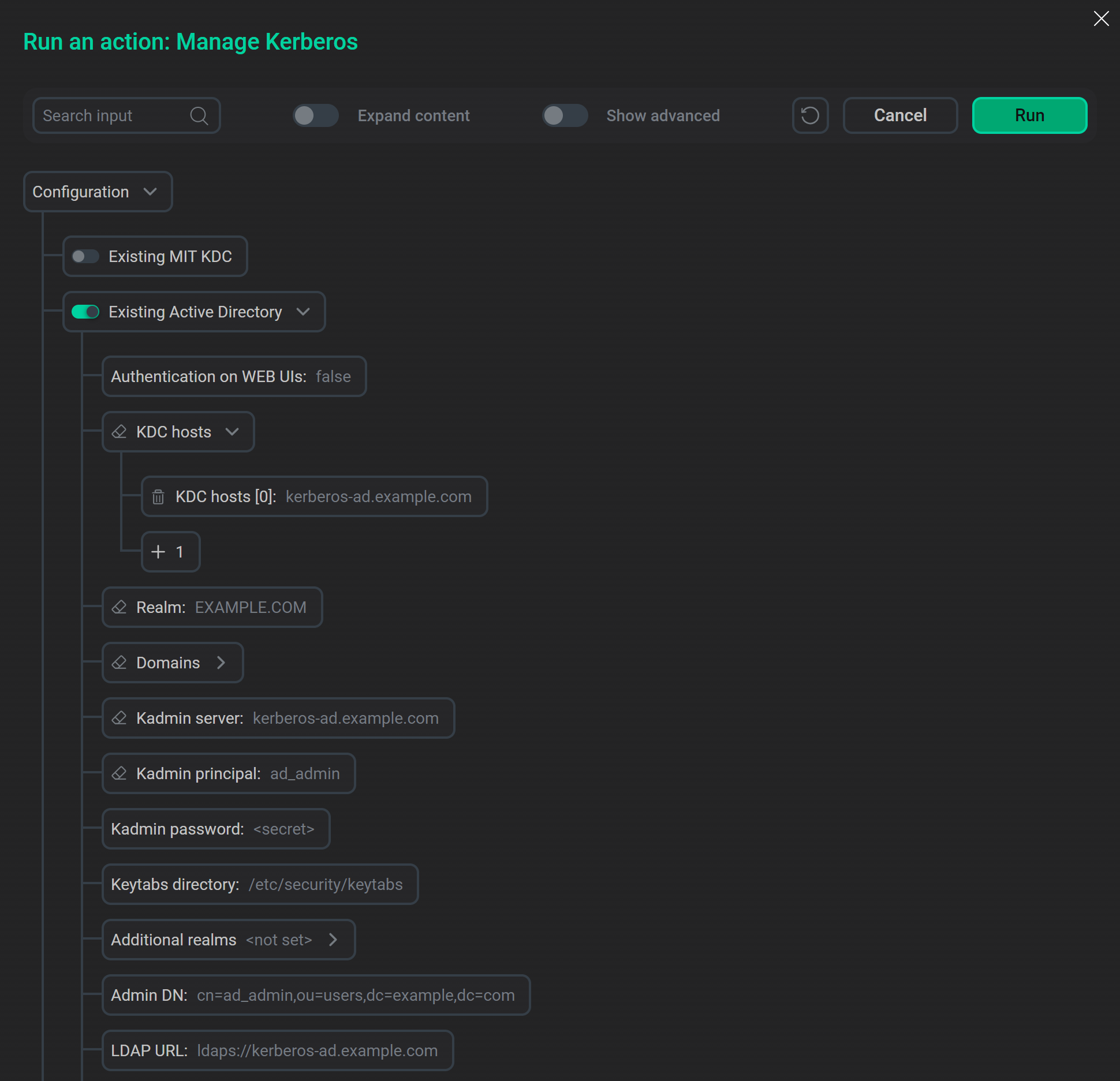 Active Directory parameters
Active Directory parameters -
Click Run and wait for the cluster kerberization to complete. On the Jobs page, you can monitor the progress and result of the Manage Kerberos task execution.
After Kerberos is successfully installed on the ADQM cluster, the corresponding settings appear on the cluster configuration page (in the Kerberos section) and on the ADQMDB service configuration page (in the Kerberos configuration section).
Active Directory parameters
The following parameters are required to kerberize an ADQM cluster with Active Directory.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
KDC hosts |
Address of the host where KDC is installed (for kerberization with LDAP, this address is the same as the address of the LDAP server) |
Realm |
Realm for authentication in Kerberos |
Kadmin server |
Address of the server on which the Kerberos administration system is installed (this address is often the same as the address of the KDC server) |
Kadmin principal |
Principal name of the user created to connect a cluster to Active Directory with rights to create users and groups in the Container DN container |
Kadmin password |
Password for the Kadmin principal user principal |
Admin DN |
DN of the user used to connect a cluster to Active Directory |
LDAP URL |
LDAP server address ( |
Container DN |
DN of a container where service principals are located |
TLS CA certificate Path (optional) |
Local path where the CA certificate for the Admin DN user is stored on all cluster hosts (if the certificate is up-to-date, the TLS CA certificate parameter does not need to be specified) |
TLS CA certificate (optional) |
Contents of the CA certificate for the Admin DN user that will be written to a host in the path specified in TLS CA certificate Path |
Test user authentication via Kerberos
After a successful kerberization, ADQM commands can only run on cluster nodes after getting a Kerberos ticket. Below is an example that demonstrates how to access the cluster kerberized with Active Directory:
-
Create an ADQM user that has an entry in the Active Directory database and a principal for the specified realm. To do this, use the
IDENTIFIED WITH kerberosclause in theCREATE USERquery:CREATE USER adqm_kerb_ad IDENTIFIED WITH kerberos; -
Create a Kerberos ticket for the user principal:
$ kinit -V adqm_kerb_ad@EXAMPLE.COMEnter a password:
Password for adqm_kerb_ad@EXAMPLE.COM:The kinit article of the MIT Kerberos documentation describes all available options of the
kinitcommand. -
Check the ticket:
$ klistTicket cache: FILE:/tmp/krb5cc_1000 Default principal: adqm_kerb_ad@EXAMPLE.COM Valid starting Expires Service principal 05/05/2023 09:05:36 05/06/2023 09:05:36 krbtgt/EXAMPLE.COM@EXAMPLE.COM
-
To test authentication via Kerberos, send some command to ADQM using the
curlutility version that supports the SPNEGO mechanism:$ echo "select currentUser()" | curl --negotiate -u : http://<host_name>:8123/ --data-binary @-In case of successful authentication, the command should return the kerberized user name:
adqm_kerb_ad