

Use MIT Kerberos server
Setup Kerberos server
|
NOTE
|
An example below describes how to install Kerberos KDC to the dev-adcm-test.ru-central1.internal host with the CentOS operating system and ADCM.
-
Install Kerberos packages to the host:
$ sudo -iyum install krb5-libs krb5-server krb5-workstation -
Make changes to the configuration files.
-
In the /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kdc.conf file, set realm to
RU-CENTRAL1.INTERNAL:[kdcdefaults] kdc_ports = 88 kdc_tcp_ports = 88 [realms] RU-CENTRAL1.INTERNAL = { #master_key_type = aes256-cts acl_file = /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kadm5.acl dict_file = /usr/share/dict/words admin_keytab = /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kadm5.keytab supported_enctypes = aes256-cts:normal aes128-cts:normal des3-hmac-sha1:normal arcfour-hmac:normal camellia256-cts:normal camellia128-cts:normal des-hmac-sha1:normal des-cbc-md5:normal des-cbc-crc:normal } -
In the /etc/krb5.conf file, set
RU-CENTRAL1.INTERNALas thedefault_realmparameter value, and also fill in the[realms]and[domain_realm]sections:# Configuration snippets may be placed in this directory as well includedir /etc/krb5.conf.d/ [logging] default = FILE:/var/log/krb5libs.log kdc = FILE:/var/log/krb5kdc.log admin_server = FILE:/var/log/kadmind.log [libdefaults] dns_lookup_realm = false ticket_lifetime = 24h renew_lifetime = 7d forwardable = true rdns = false pkinit_anchors = FILE:/etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt default_realm = RU-CENTRAL1.INTERNAL default_ccache_name = KEYRING:persistent:%{uid} [realms] RU-CENTRAL1.INTERNAL = { kdc = dev-adcm-test.ru-central1.internal admin_server = dev-adcm-test.ru-central1.internal } [domain_realm] .ru-central1.internal = RU-CENTRAL1.INTERNAL ru-central1.internal = RU-CENTRAL1.INTERNAL -
Modify the /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kadm5.acl file as shown below so that any
/adminprincipal in theRU-CENTRAL1.INTERNALrealm has all administrative privileges except key extraction:*/admin@RU-CENTRAL1.INTERNAL *
-
-
Create the Kerberos database using the
kdb5_utilutility:kdb5_util create -s -P P@ssw0rd -
Run the following commands in turn to start the Kerberos and KDC services:
systemctl start kadmin systemctl start krb5kdcYou can check the status of running services with the commands:
systemctl status kadmin systemctl status krb5kdc -
Create user principals. To do this, use the Kerberos administrator console —
kadmin.local.A user principal name in a Kerberos database usually follows the
primary/instance@REALMpattern, where:-
primaryis a username (for successful authentication to ADQM, it is required that this part of a principal matches the name of an ADQM user configured to authenticate via Kerberos); -
instanceis an optional component that qualifiesprimary. Ifprimaryis a username, theninstanceis usually not specified or can be used to define an additional principal for the user (for example,john@RU-CENTRAL1.INTERNALandjohn/admin@RU-CENTRAL1.INTERNALare separate principals with different passwords and permissions).
kadmin.local -q "add_principal -pw P@ssw0rd admin/admin"kadmin.local -q "add_principal -pw P@ssw0rd adqm_kerb"For a complete description of the
kadmin.localcommand line interface and its options, see the kadmin article of the MIT Kerberos documentation. -
Start MIT Kerberos KDC on ADQM cluster
-
On the Clusters page of the ADCM interface, select the installed and prepared ADQM cluster.
-
Enable Kerberos for the cluster — click the Actions
icon and select the Manage Kerberos action.
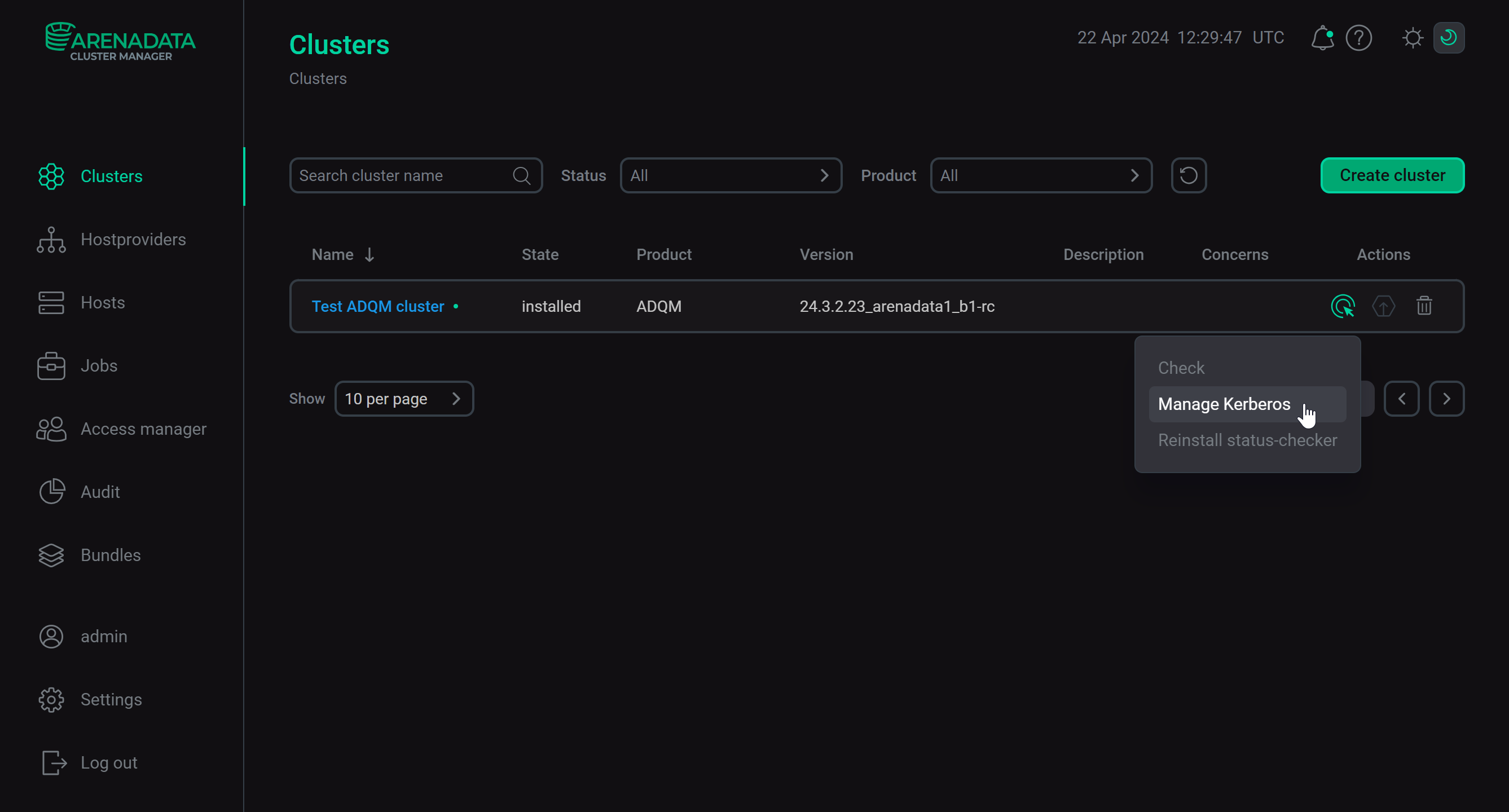 Manage Kerberos action
Manage Kerberos action -
Turn on the Existing MIT KDC option and fill in the configuration parameters in accordance with the previously specified Kerberos server settings.
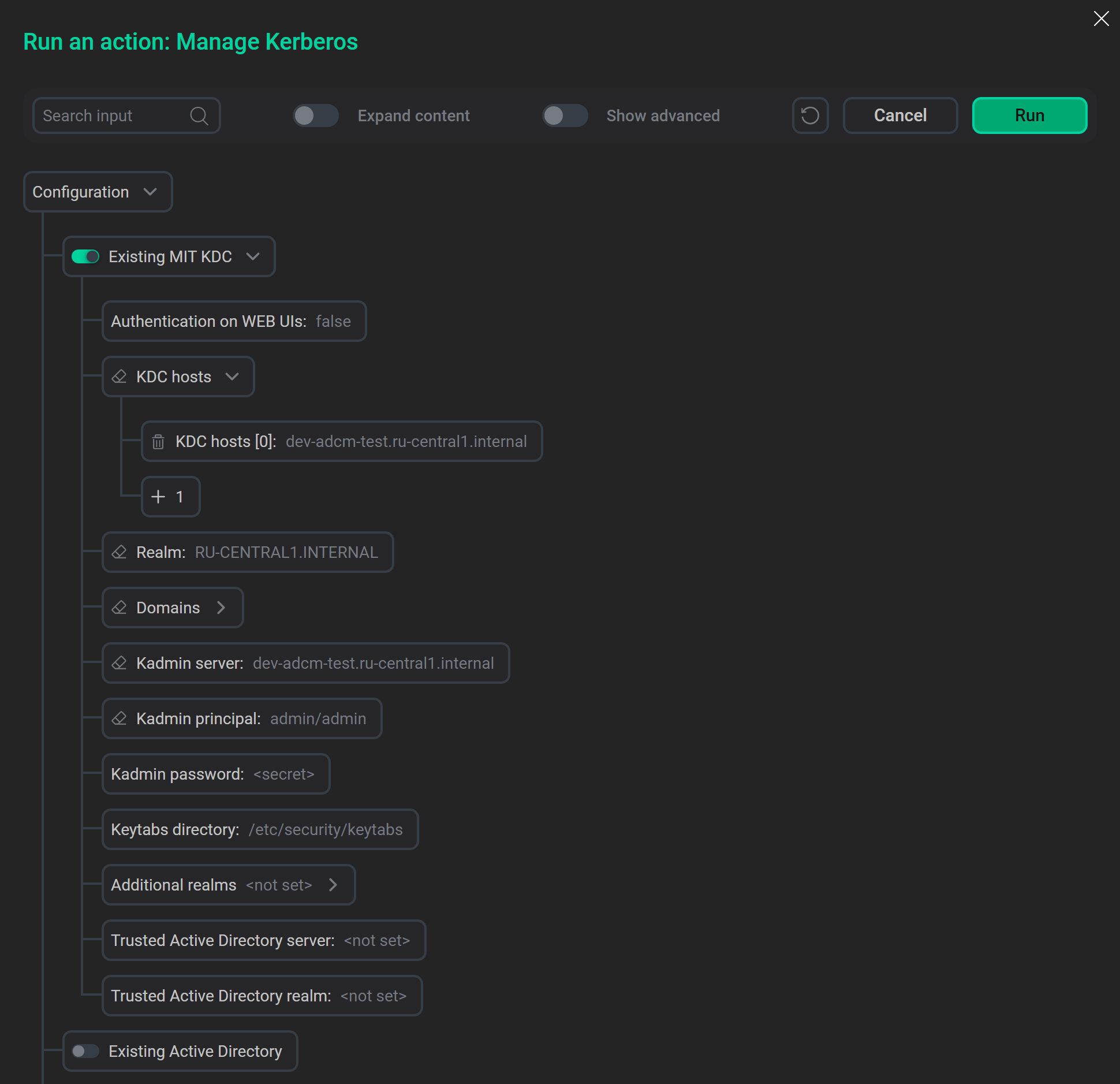 MIT KDC parameters
MIT KDC parameters -
Click Run and wait for the cluster kerberization to complete. On the Jobs page, you can monitor the progress and result of the Manage Kerberos task execution.
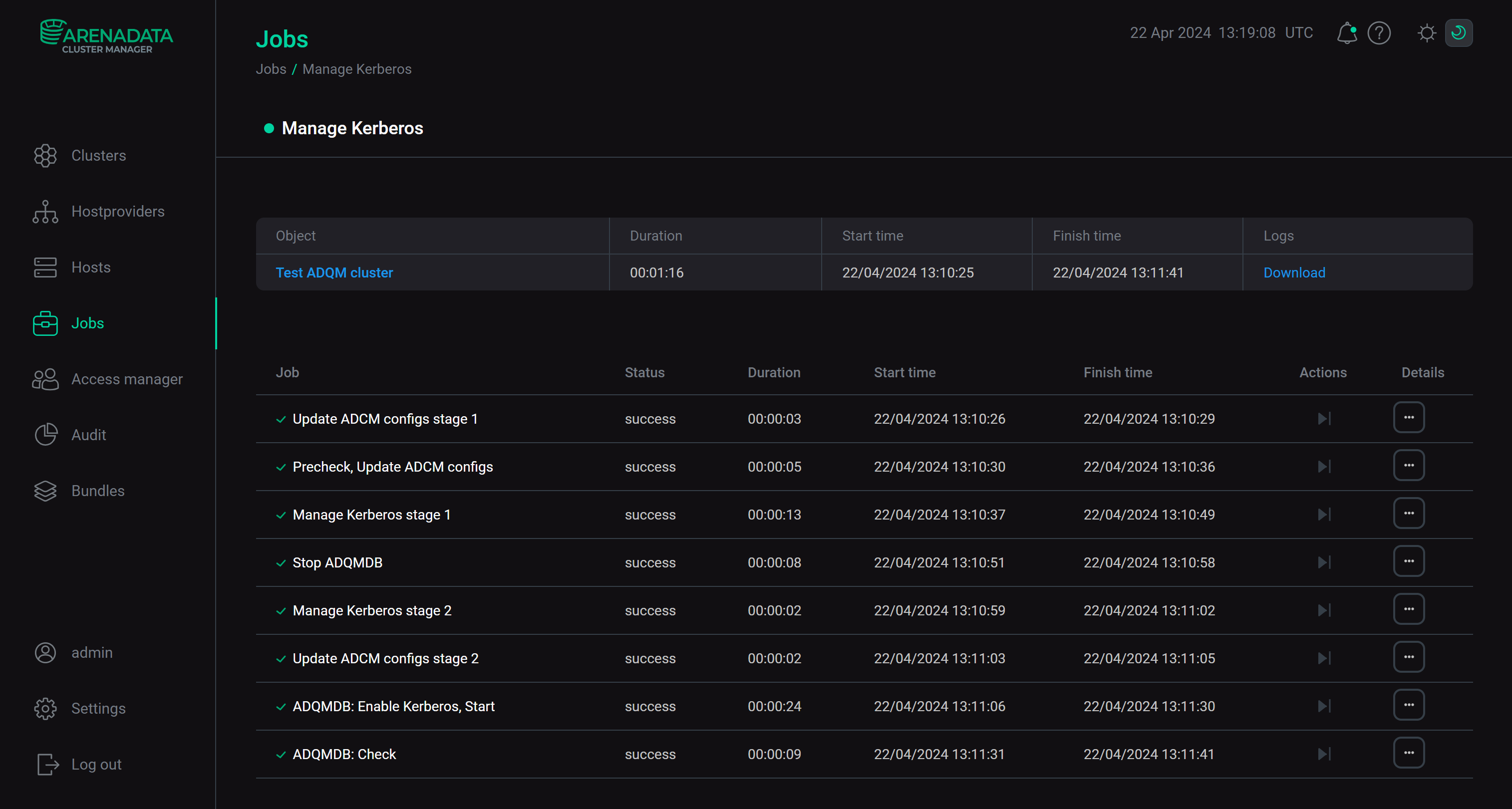 Kerberization process
Kerberization process
After Kerberos is successfully installed on the ADQM cluster, the corresponding settings appear on the cluster configuration page (in the Kerberos section) and on the ADQMDB service configuration page (in the Kerberos configuration section).
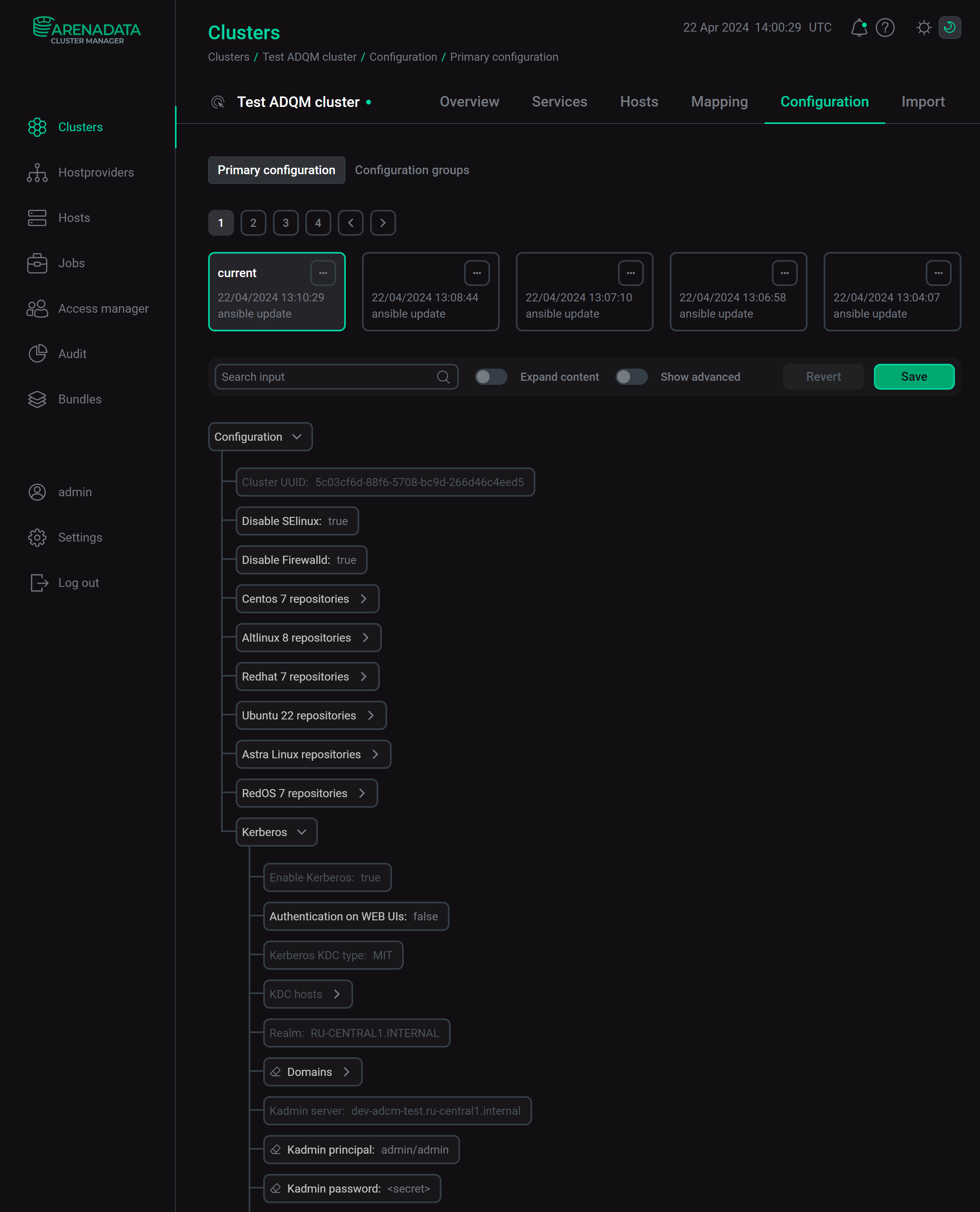
Test user authentication via Kerberos
After a successful kerberization, ADQM commands can only run on cluster nodes after getting a Kerberos ticket. Below is an example that demonstrates how to access the kerberized cluster:
-
Create an ADQM user that has a principal in the Kerberos database. To do this, use the
IDENTIFIED WITH kerberosclause in theCREATE USERquery:CREATE USER adqm_kerb IDENTIFIED WITH kerberos; -
Create a Kerberos ticket for the user principal:
$ kinit -V adqm_kerb@RU-CENTRAL1.INTERNALEnter a password:
Password for adqm_kerb@RU-CENTRAL1.INTERNAL:The kinit article of the MIT Kerberos documentation describes all available options of the
kinitcommand. -
Check the ticket:
$ klistTicket cache: FILE:/tmp/krb5cc_1000 Default principal: adqm_kerb@RU-CENTRAL1.INTERNAL Valid starting Expires Service principal 05/04/2023 07:13:58 05/05/2023 07:13:58 krbtgt/RU-CENTRAL1.INTERNAL@RU-CENTRAL1.INTERNAL
-
To test authentication via Kerberos, send some command to ADQM using the
curlutility version that supports the SPNEGO mechanism:$ echo "select currentUser()" | curl --negotiate -u : http://<host_name>:8123/ --data-binary @-In case of successful authentication, the command should return the kerberized user name:
adqm_kerb