Manage backup settings
To manage backup settings, open the Backup manager page and switch to Settings.
The Settings tab contains the following sub-tabs:
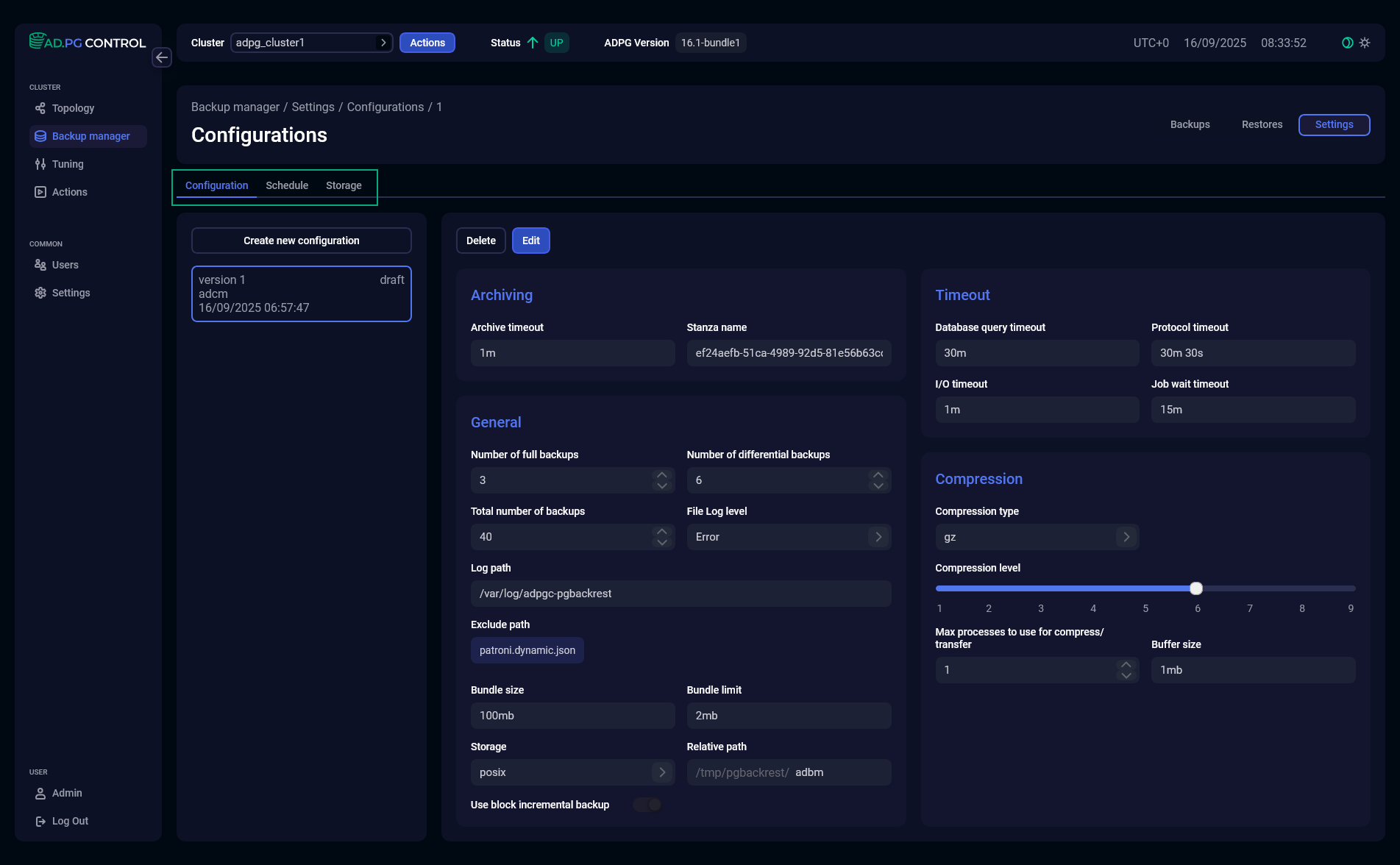
Configuration
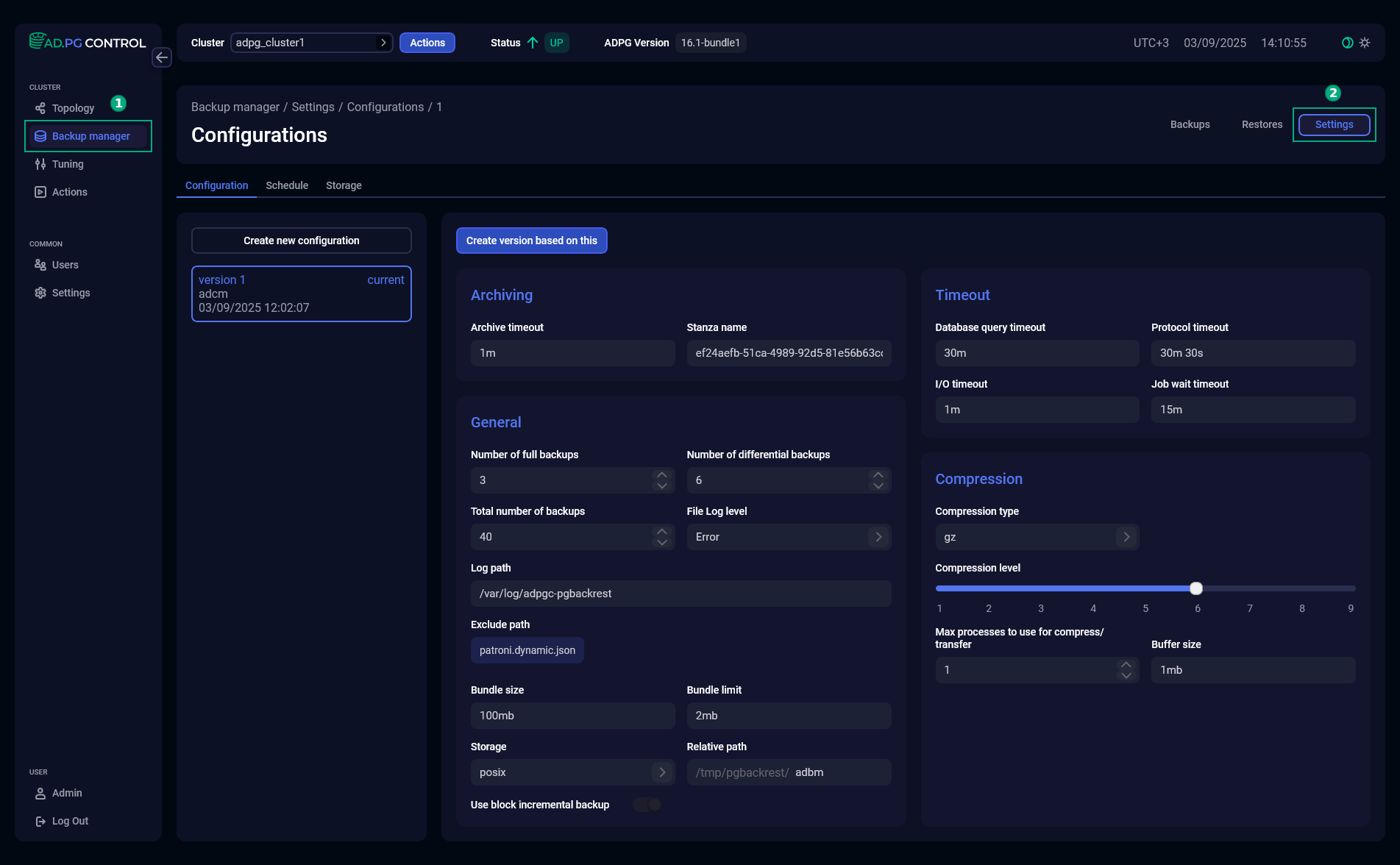
The Configuration tab displays a set of options that are used to manage database backups. You can create several configuration versions, but only one configuration can be active. It is marked as current in UI.
The configuration settings are grouped according to the functionality they affect.
| Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
Archive timeout |
The maximum time to wait for each WAL segment (required for backup consistency) to reach the archive repository. The following units can be used:
The minimum value is |
1m |
Stanza name |
A name of a stanza. Each PostgreSQL/ADPG cluster to back up has its configuration called stanza |
Cluster UUID |
| Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
Number of full backups |
A maximum number of full backups to retain. After this limit is reached, the oldest additional full backups will expire |
3 |
Number of differential backups |
A maximum number of differential backups to retain. After this limit is reached, the oldest additional differential backups will expire |
6 |
Total number of backups |
A total number of backups allowed for the current cluster, including backups in the |
40 |
File Log level |
A level for file logging. The possible values are:
|
Error |
Log path |
A path to the directory with |
/var/log/adpgc-pgbackrest |
Exclude path |
A path to directories and files that should be excluded from a backup |
patroni.dynamic.json |
Bundle size |
The total size of files that will be added to a single bundle. A bundle means grouping individual files into a single file before the backup launch. Most bundles will be smaller than this size, but some may be slightly larger. So, do not set this option to the maximum size that your file system allows. You can set the value in the following units:
|
100mb |
Bundle limit |
Size limit for files that will be included in bundles. Files larger than this size will be stored separately. Bundled files cannot be reused when a backup is resumed, so this option, in fact, controls the files that can be reused — higher values result in fewer resumable files. You can set the value in the following units:
|
2mb |
Storage |
A storage where backups will be saved. You can select a value from the list of storages previously added on the Storage tab |
— |
Relative path |
A path to a repository for backups relative to Repository path of the selected storage. You can use the same storage for multiple configurations and assign each of them its own separate repository within that storage. The path to the repository is displayed in the first part of the field and cannot be edited. Specify the relative path in the second part of the field |
— |
Use block incremental backup |
A toggle button that indicates whether to split files into blocks that can be backed up independently. This saves space in the repository and can improve delta restore performance, because individual blocks can be fetched without reading the entire file from the repository |
Disabled |
| Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
Database query timeout |
Sets the timeout for queries against the database, including the backup start/stop functions, which can take a significant amount of time. The timeout should be kept high unless you know that these functions will return quickly. The Database query timeout value should be less than the Protocol timeout value. The following units can be used:
The minimum value is |
30m |
Protocol timeout |
Sets the timeout that the local or the remote process can wait for a new message to be received on the protocol level. The timeout prevents processes from the indefinite waiting. The Protocol timeout value should be greater than the Database query timeout value. The following units can be used:
The minimum value is |
30m 30s |
I/O timeout |
A timeout that is used for connections and read/write operations. The entire read/write operation does not need to complete within this timeout, but some progress should be made, even if it is only a single byte. The following units can be used:
The minimum value is |
1m |
Job wait timeout |
A timeout for a lock capture at the cluster level before the job starts. It can be set in minutes — |
15m |

| Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
Compression type |
A compress type of backup files. The following compression types are supported:
|
gz |
Compression level |
A file compression level (from |
The following default compression levels are used based on Compression type:
|
Max processes to use for compress/transfer |
The maximum number of concurrent worker processes used for compression and file transfer during backups |
1 |
Buffer size |
Specifies a buffer size for I/O operations. You can set the value in the following units:
|
1mb |
You can create a new configuration in two ways:
-
Click Create new configuration — the configuration fields will be filled with the default values.
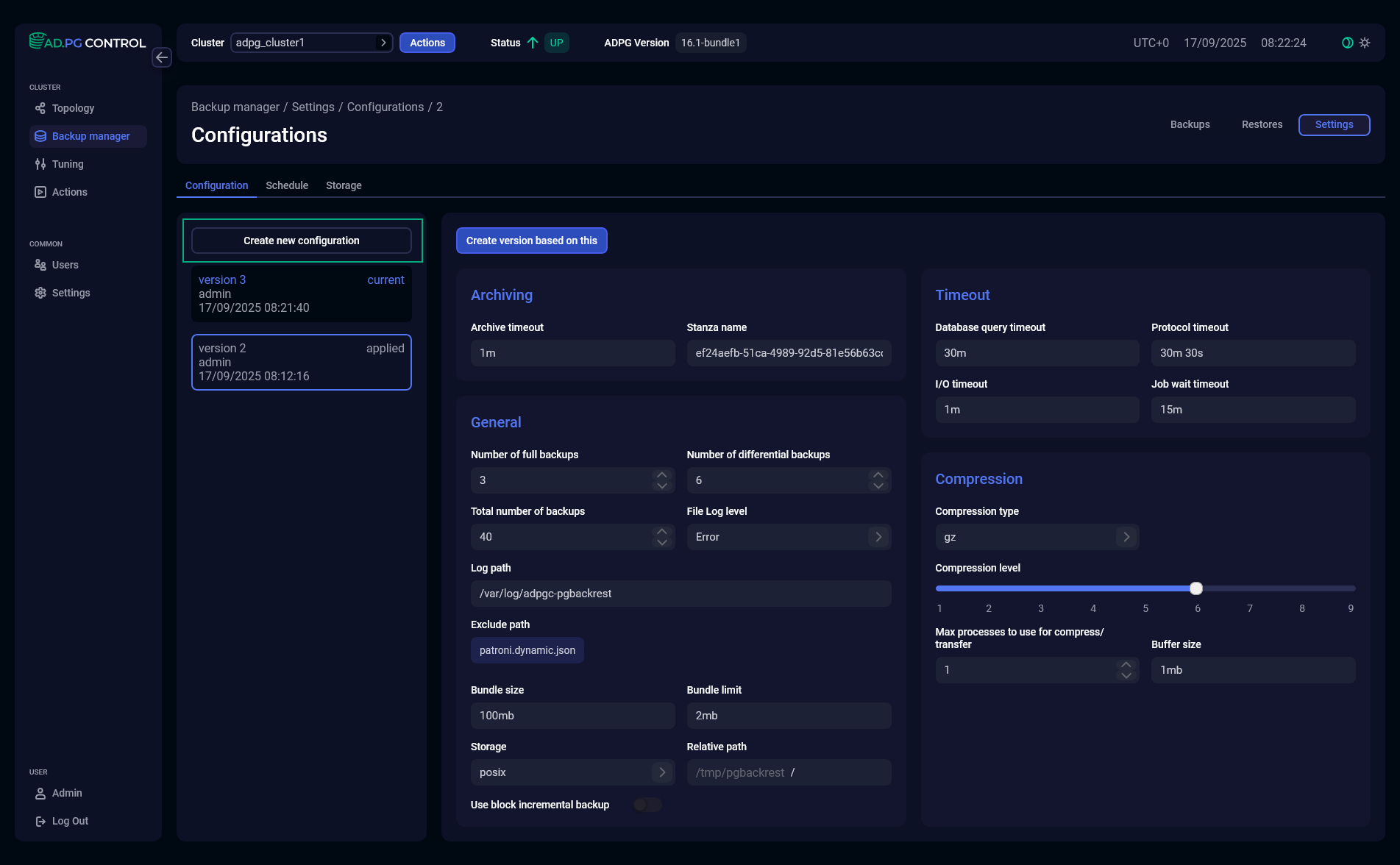 Create a new configuration with default settings
Create a new configuration with default settings -
Select a configuration version in the left part of the tab and click Create version based on this — configuration fields will be filled with the values of the selected configuration.
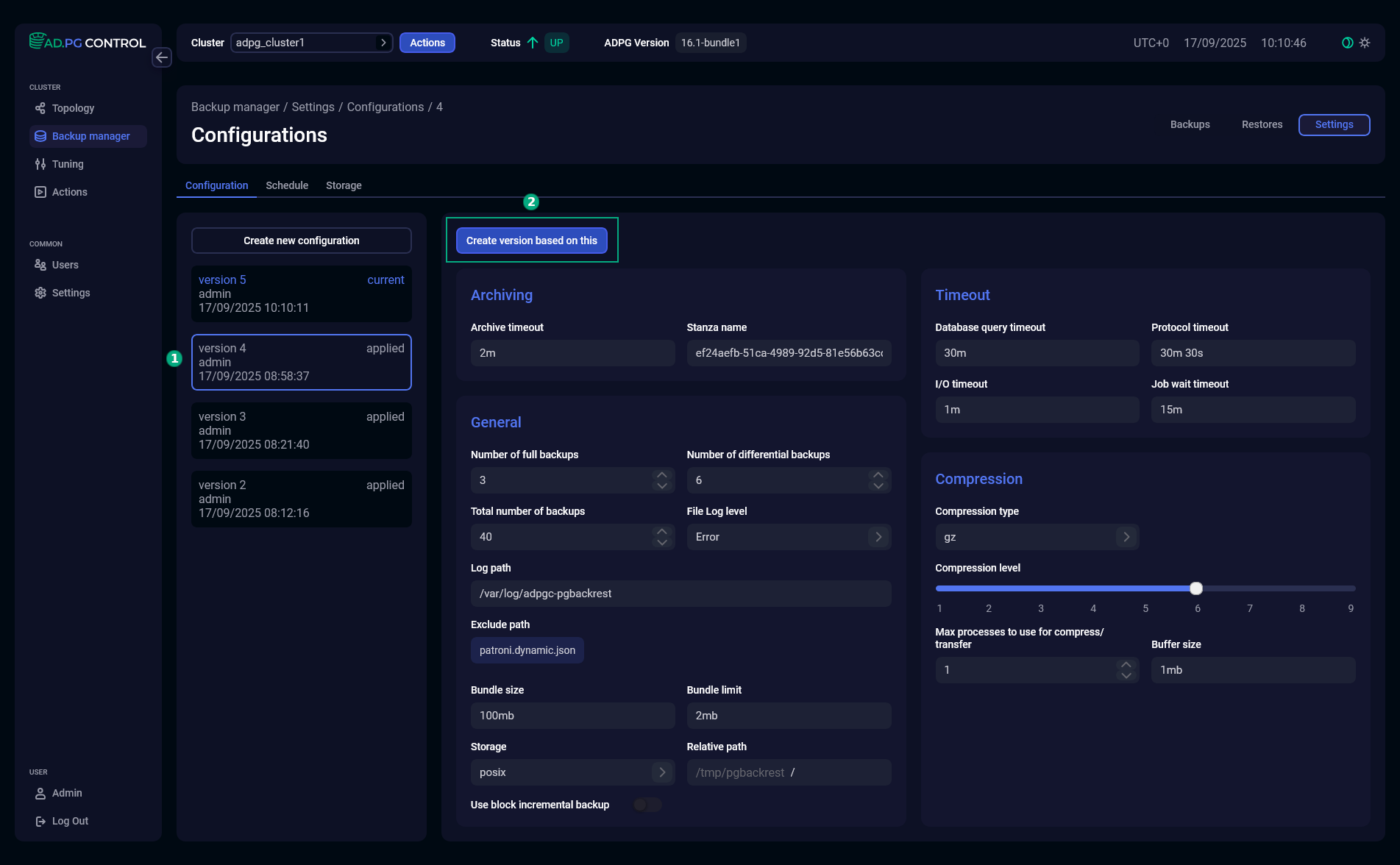 Create a new configuration based on the selected one
Create a new configuration based on the selected one
After a new configuration form is opened, edit field values according to your requirements and click Save.
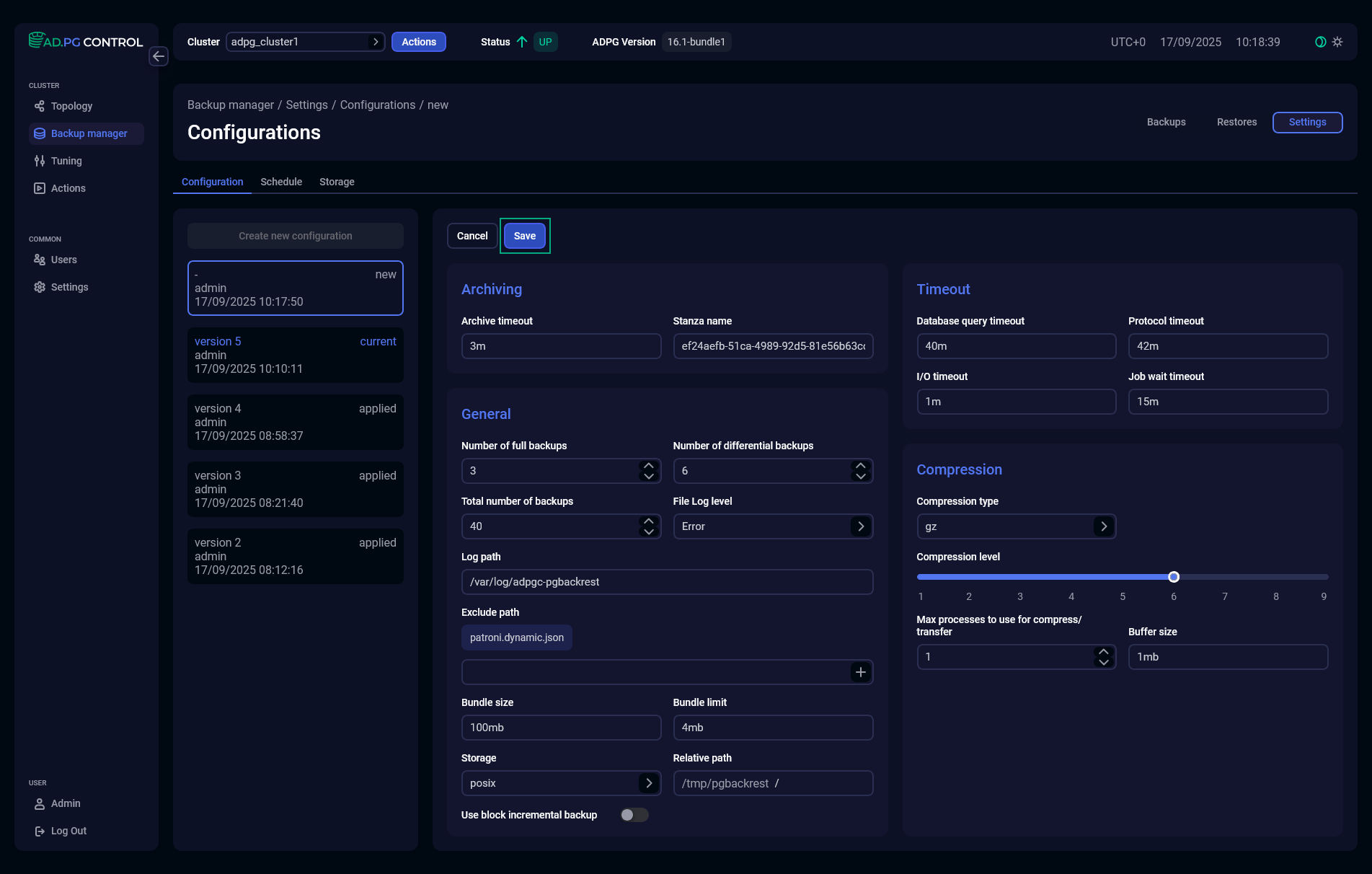
To abort creating a new configuration, click Cancel.
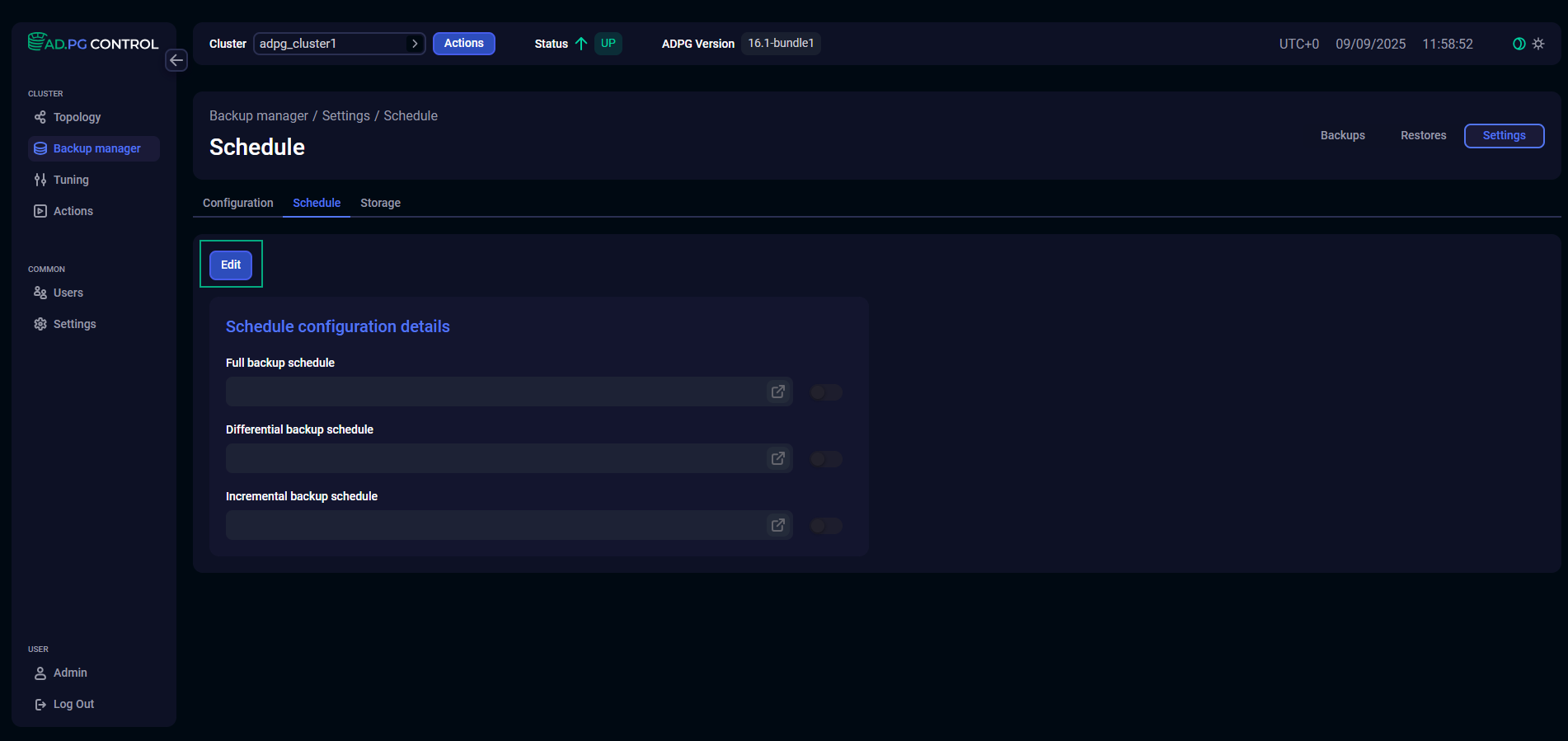
Schedule
The Schedule tab allows you to specify an automatic backup schedule. To change it, click Edit.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Full backup schedule |
A schedule for automatic creation of full backups. If you are going to create full backups only manually, do not activate the toggle button that is located next to the field |
Differential backup schedule |
A schedule for automatic creation of differential backups. If you are going to create differential backups only manually, do not activate the toggle button that is located next to the field |
Incremental backup schedule |
A schedule for automatic creation of incremental backups. If you are going to create incremental backups only manually, do not activate the toggle button that is located next to the field |
In edit mode, you can set a schedule for full, differential, and incremental backups separately. To do this, switch on a corresponding toggle button and specify a cron expression for the current schedule.
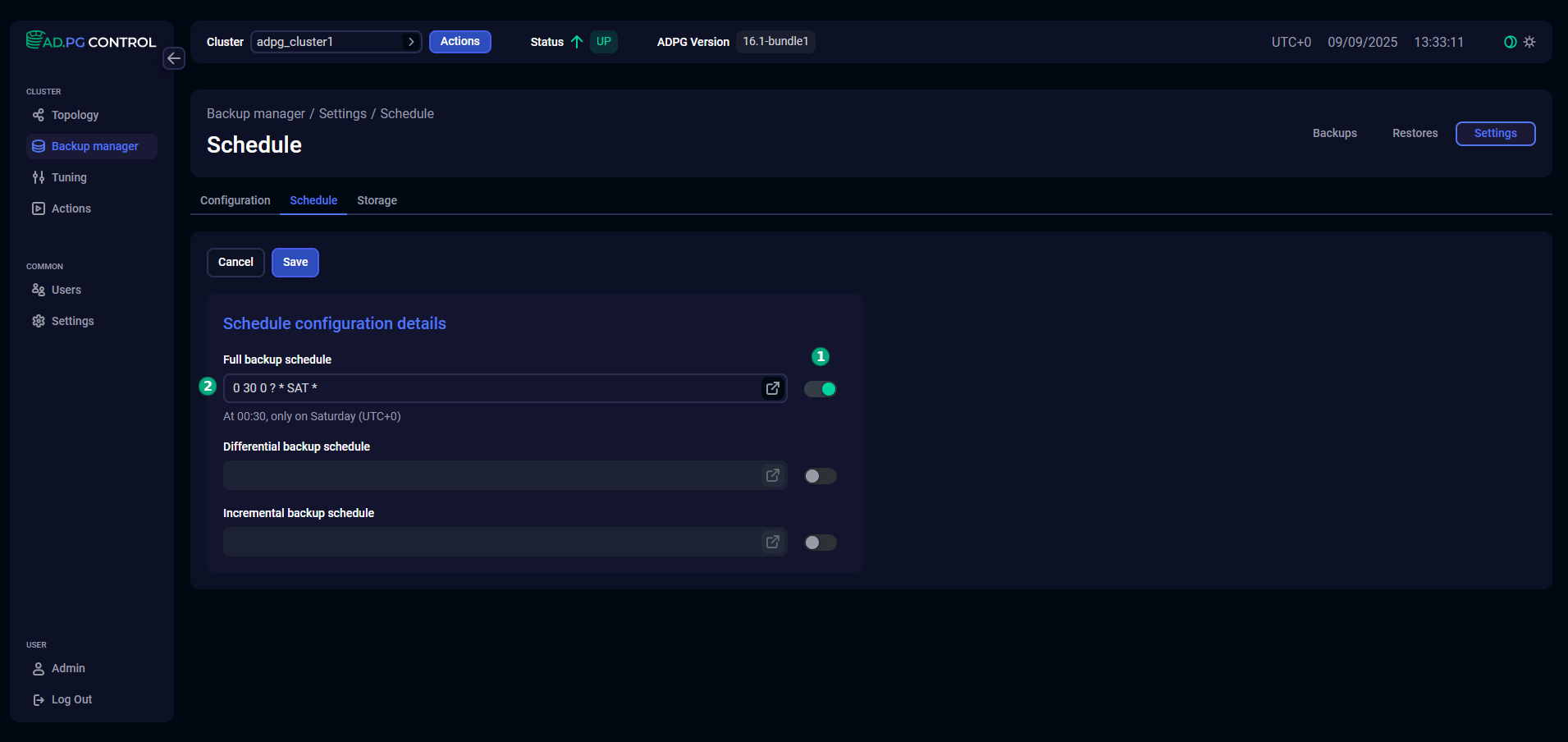
You can utilize Cron expression generator to create a cron expression. To do this, click the
icon. In the opened Cron expression generator window, you can set a schedule by selecting seconds, minutes, hours, days, months, and years. The selected values are converted to the
cron expression that will be used as the field value. You can see the generated cron expression in the top part of the window along with its description. To save the current expression and return to the Schedule tab, click Generate.
The backup schedule uses the UTC+0 time zone regardless of the time zone selected on the Settings page.
Storage
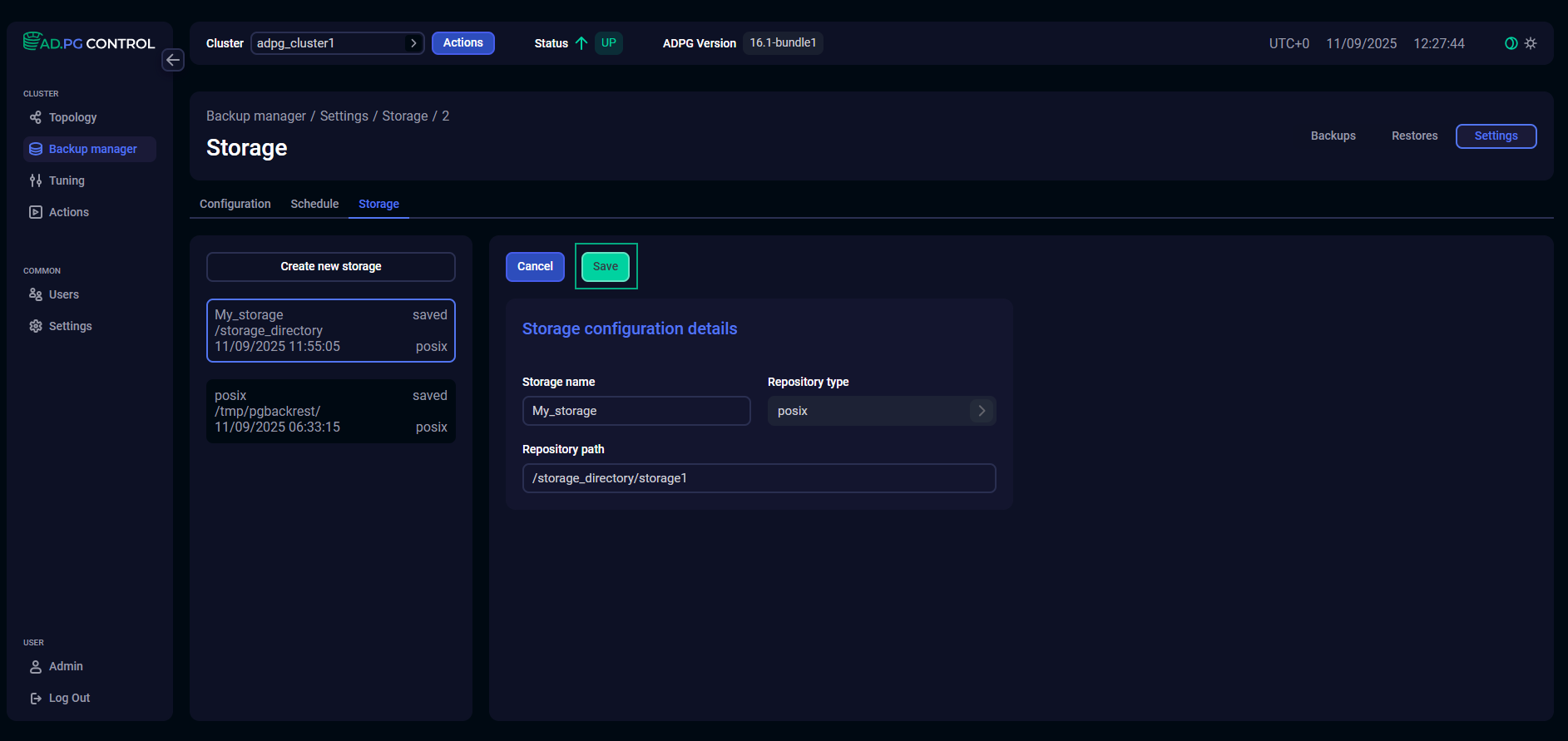
On the Storage tab, you can manage backup storages.
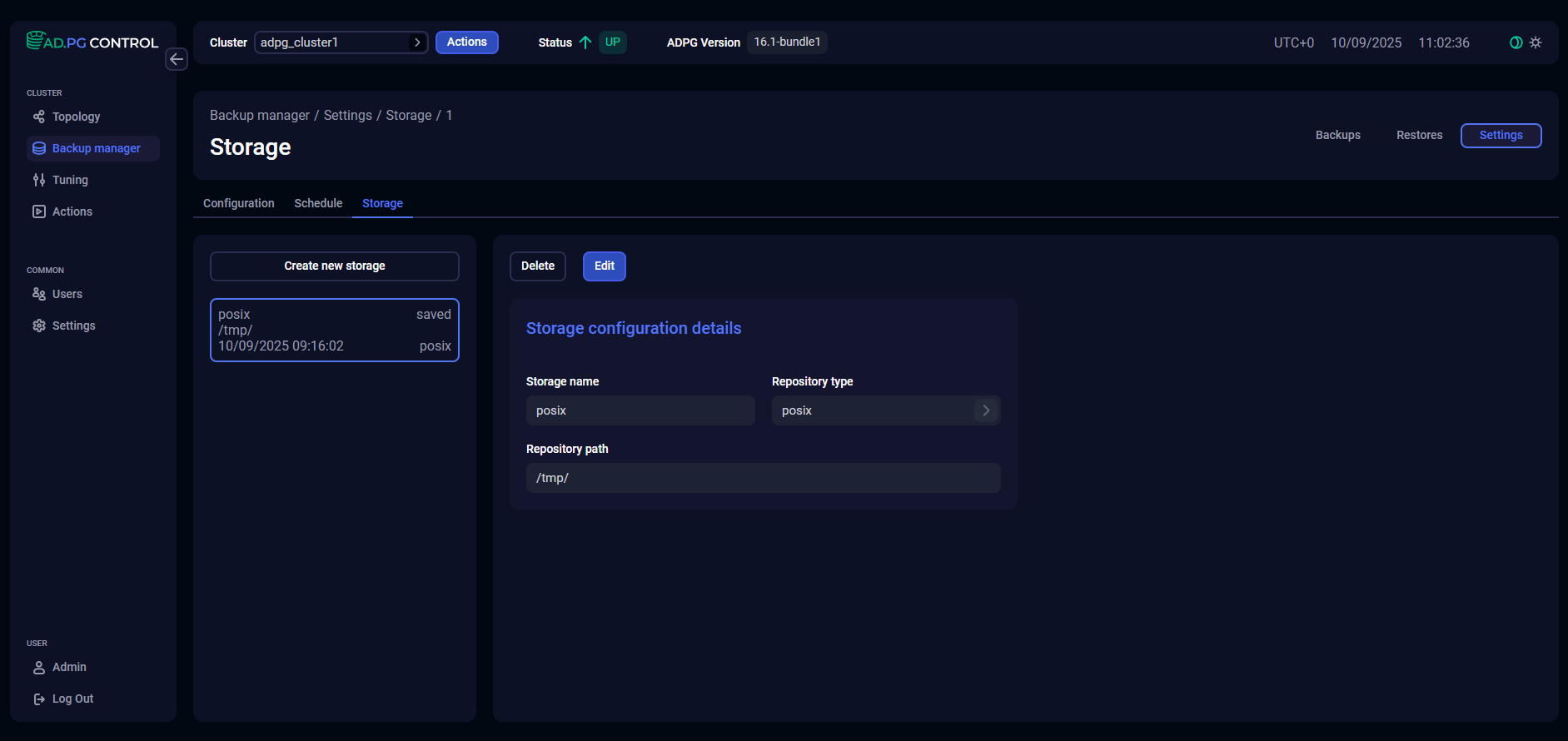
Create a storage
To add a new storage, click the Create new storage button and specify the settings listed in the table below. All fields are required.
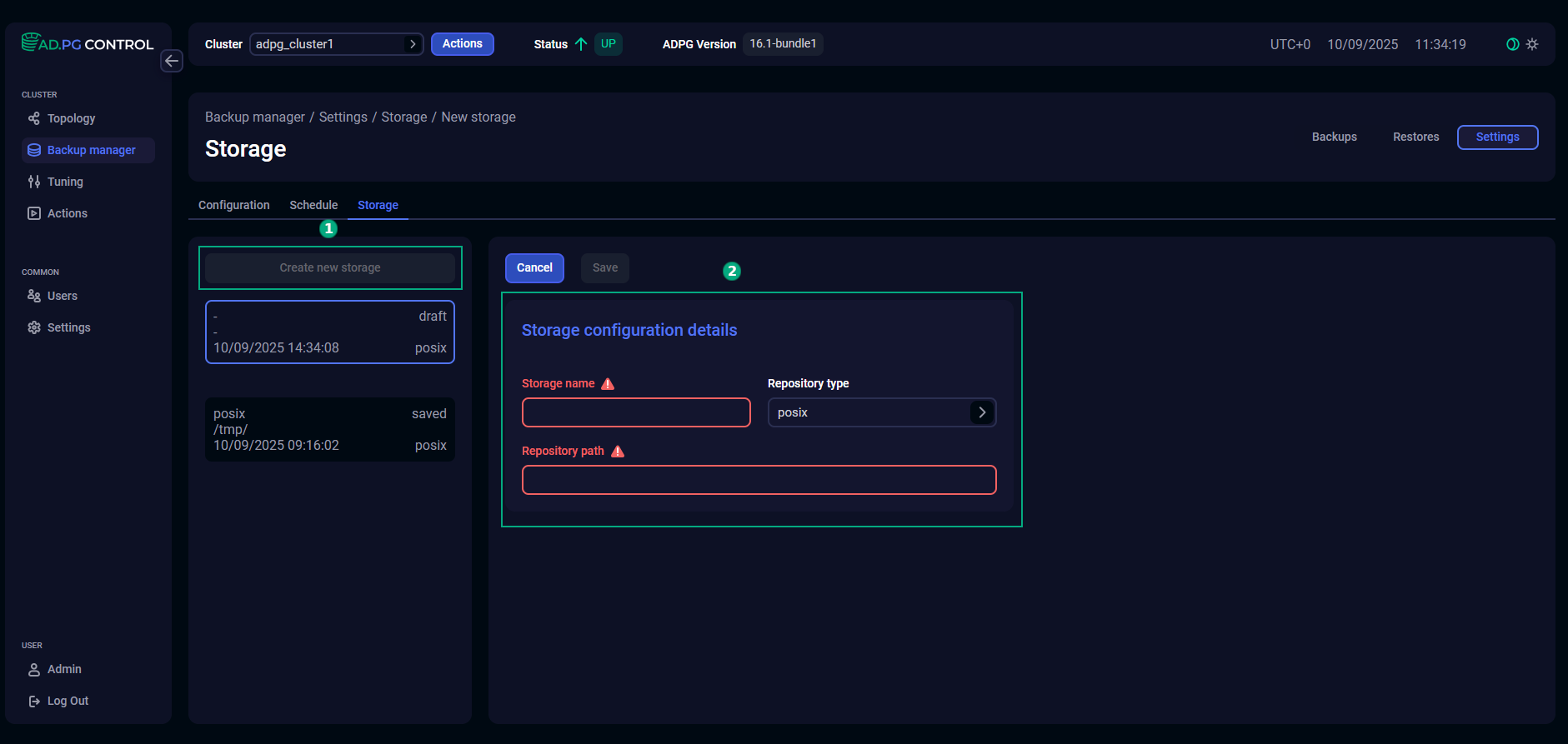
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Storage name |
A unique storage name that is used to select storage on the Configuration tab |
Repository type |
A repository type. You can use the following values:
|
Repository path |
A path to the storage repository where backups should be stored, and WAL segments should be archived. The repository directory should be created in advance. For POSIX and CIFS storages, check that directories have been created on all ADPG/PostgreSQL nodes and network connections between them are correctly configured |
If you select the s3 repository type, the s3 configuration form with additional S3-specific parameters will be displayed. Fill it according to your S3 repository settings.
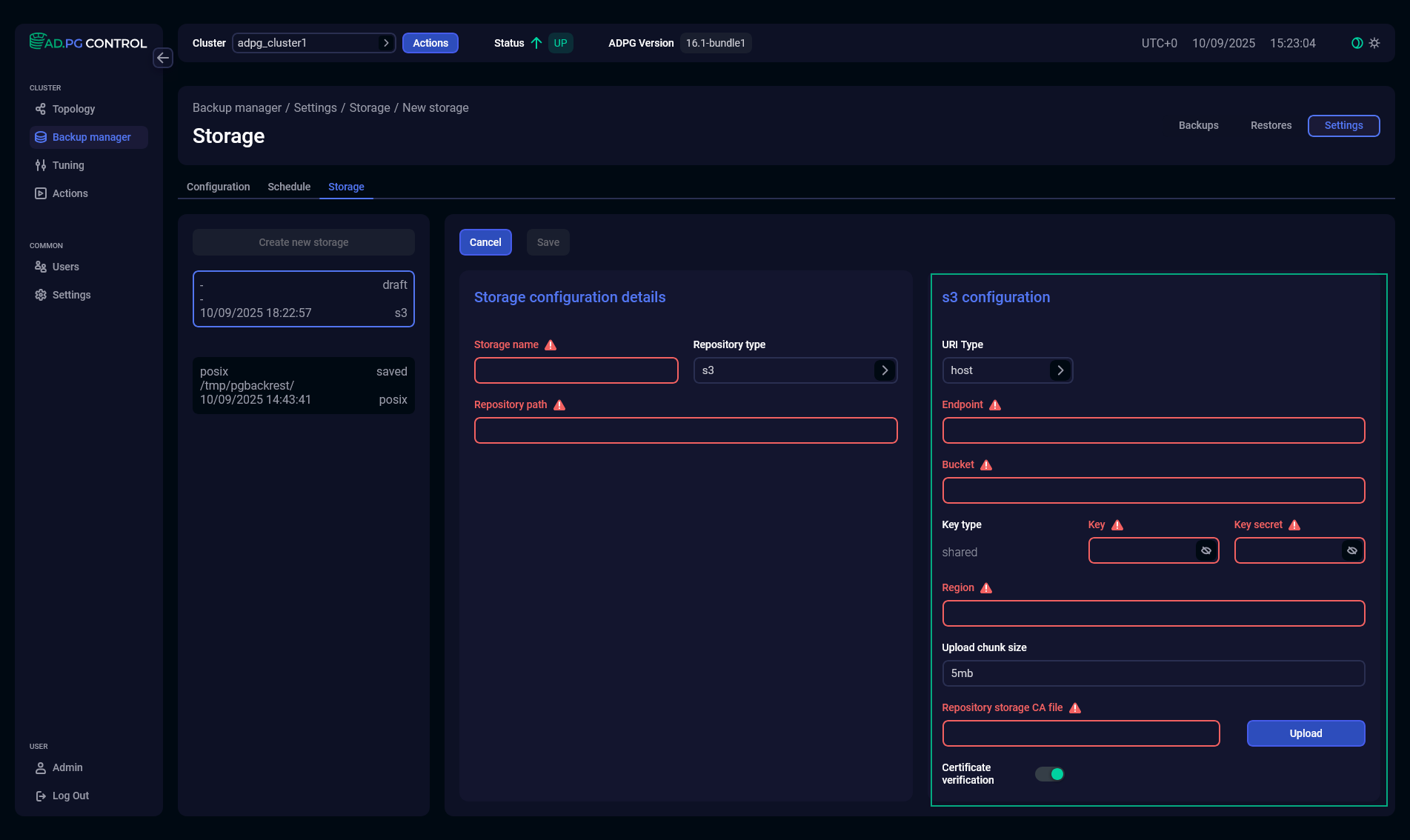
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
URI Type |
An S3 URI type that will be used to identify resources stored in S3. The following URI types are supported:
|
S3 Endpoint |
An S3 repository endpoint. The endpoint should be valid for the specified region |
S3 Bucket |
An S3 bucket used to store the repository with backups |
Key type |
An S3 repository key type. At present, only the |
S3 Key |
An S3 repository access key used to access the bucket |
S3 Key Secret |
An S3 repository secret access key used to access this bucket |
Upload chunk size |
A size of the uploaded data chunk. A chunk is a piece of a larger file that is uploaded as part of a multipart upload. You can set the value in the following units:
The minimum value is |
S3 Region |
An S3 repository region where the bucket was created |
Repository storage CA file |
A certificate authority (CA) file to access the S3 storage. To select a file, click Upload |
Certificate verification |
Defines whether to verify an S3 storage certificate. On the S3 configuration form, it is displayed as a toggle button activated by default. If the toggle button is activated, the Repository storage CA file field is enabled |
After you specify all storage parameters, click Save.
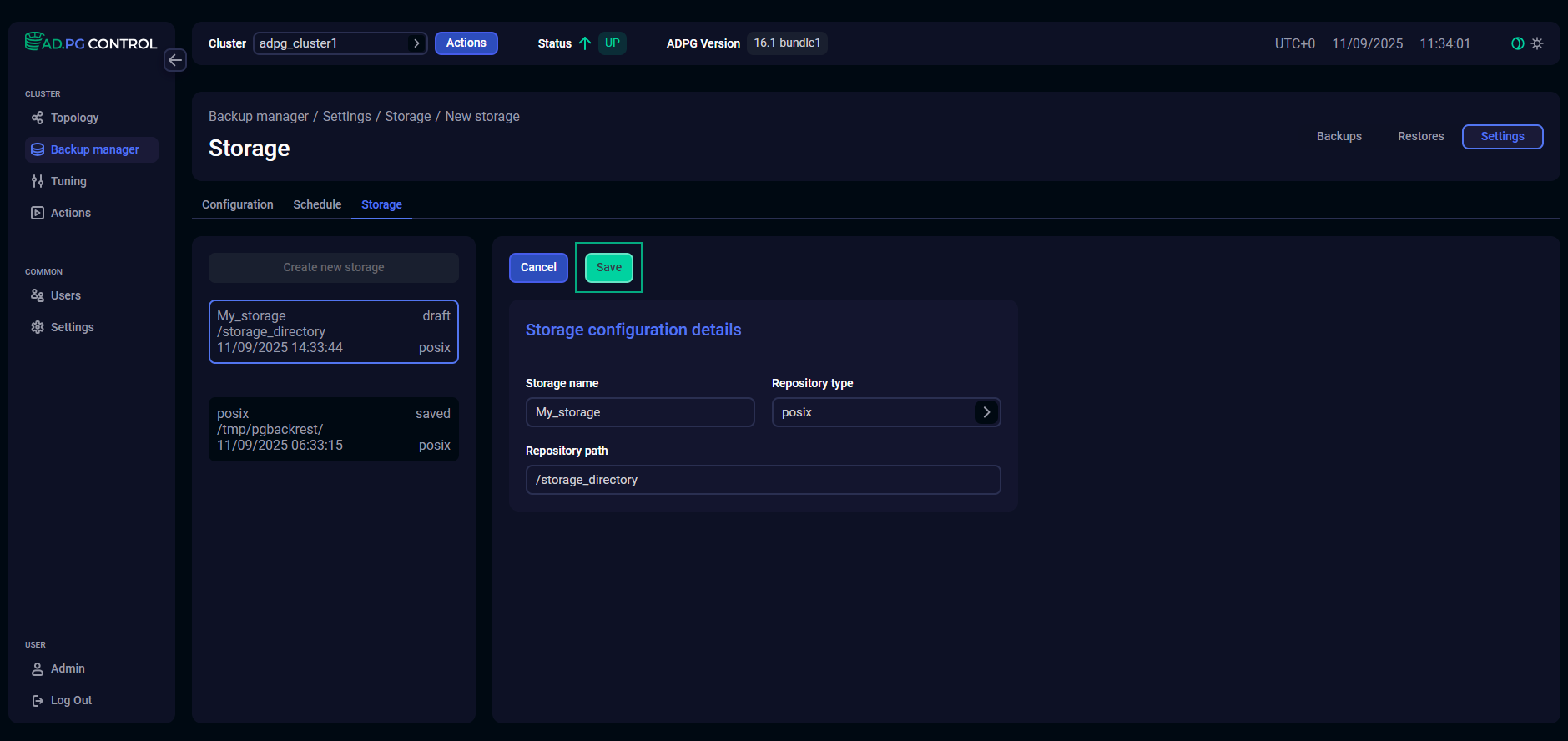
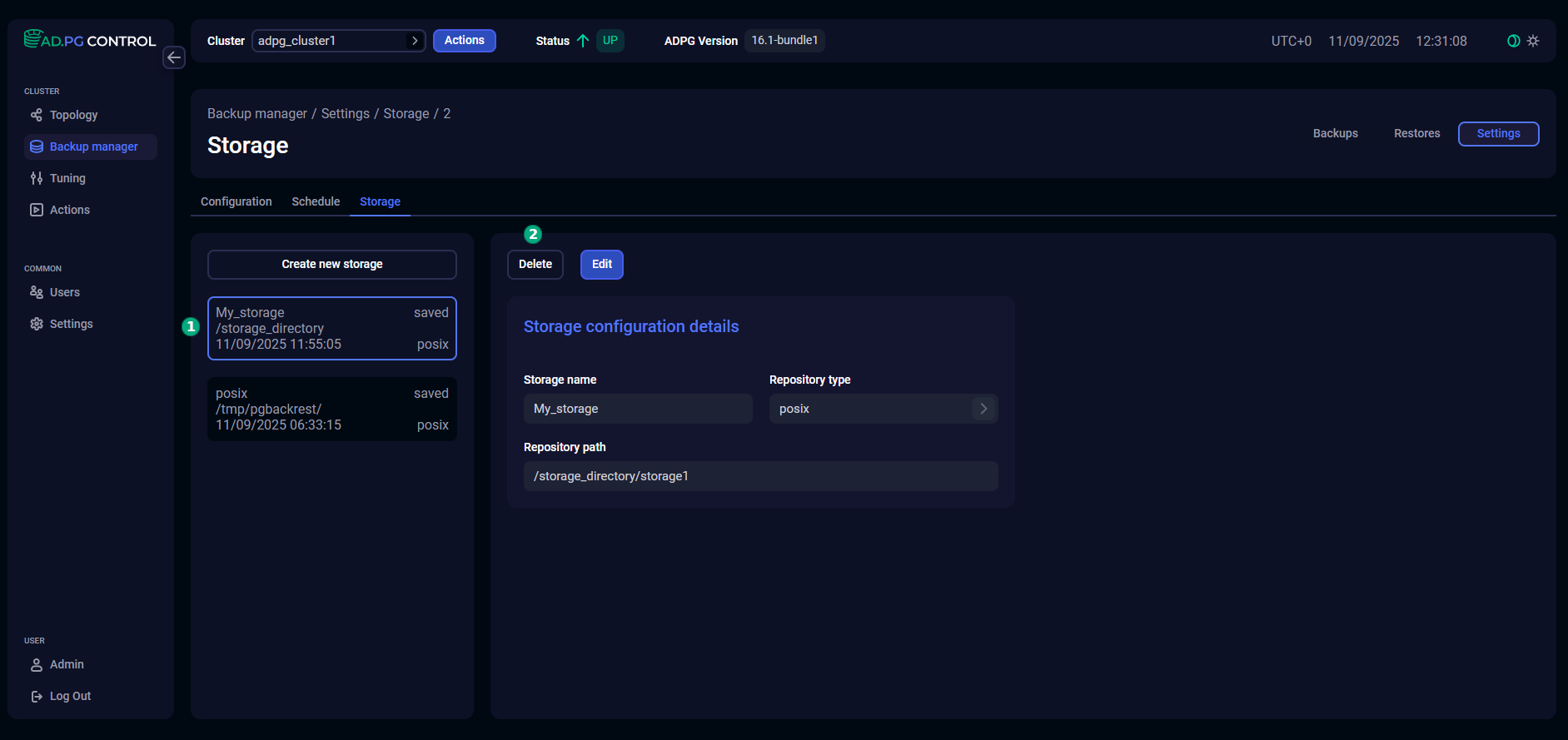
Edit storage settings
The possibility of editing storage settings is provided for cases when access to the storage needs to be restored. For example, if the access has been denied for some external reason, such as an expired certificate or a changed server name. When editing settings, note that if previously created backups are unavailable in the directory specified in the Repository path parameter, the Restore action will fail.
To change storage settings, select the desired storage in the left part of the tab and click Edit.
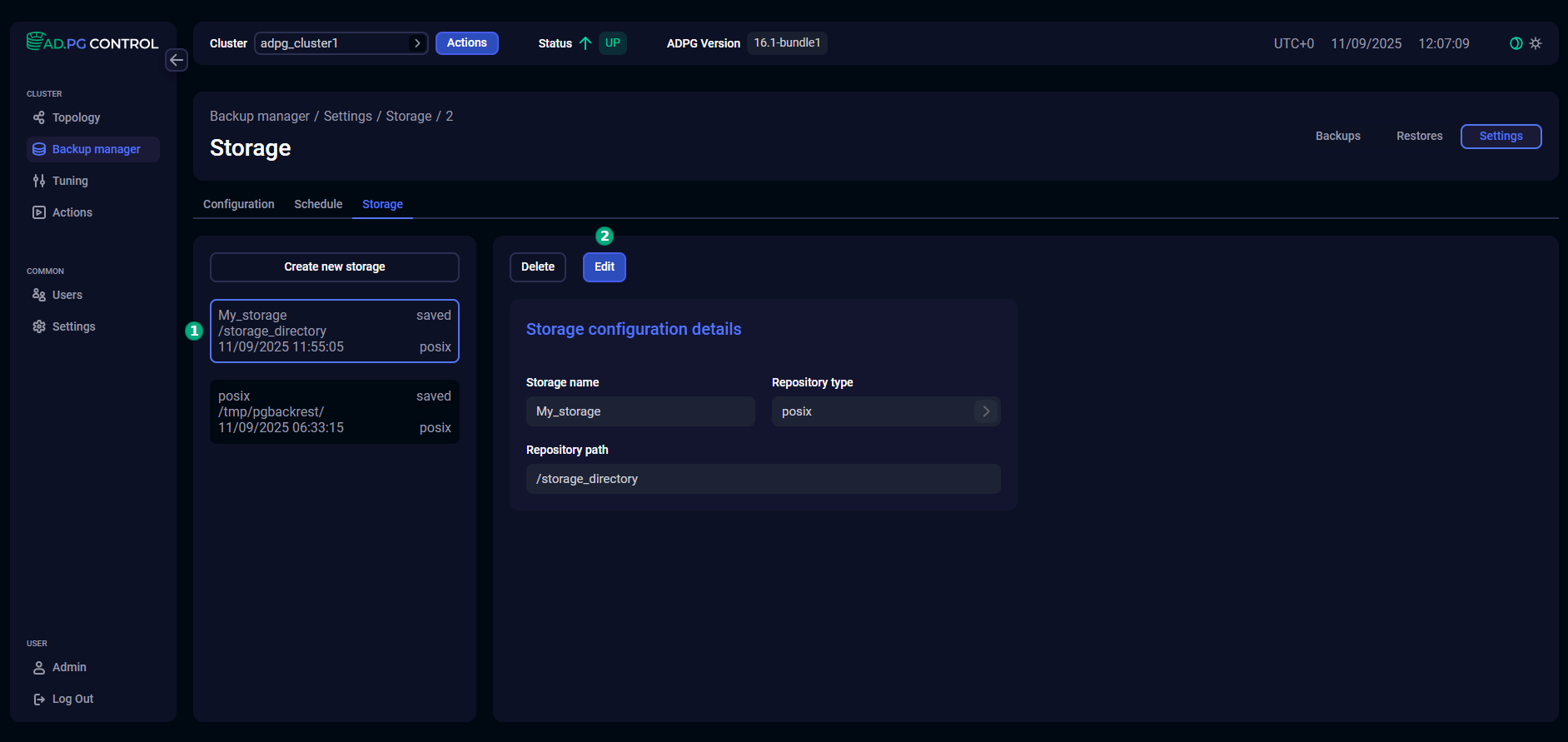
Update the required settings and click Save.